46
3.2.4.
Wakalah-Mudarabah
(Agency-Partnership) Hybrid Model
This hybrid model combines the features of two different models:
wakalah
and
mudarabah
. The
wakalah
contract is used for the underwriting in which the
wakalah
fee is an up-front fixed fee
charged by the TO while the
mudarabah
contract is adopted for investing the participants' fund
in the Islamic finance market and sharing the outcomes of investment.
The core factor in using the
wakalah
contract is to give the TOs the function as an agent or
wakil
.
Hence, the TO will be entrusted with the contributed funds. They are also responsible for the
underwriting process. This part pays attention to classify the risks according to their insurability
and attributing to each the appropriate rates to be paid. The importance of this is to reduce risks
and unnecessary loss of fund. Nevertheless, poor underwriting is considered one of the factors
that drive the
Takaful
companies into bankruptcy. Tolefat (2006) emphasised that the mixed
model is the prevailingmodel in theMiddle Easternmarket, and it is broadly accepted by
Takaful
companies around the world.
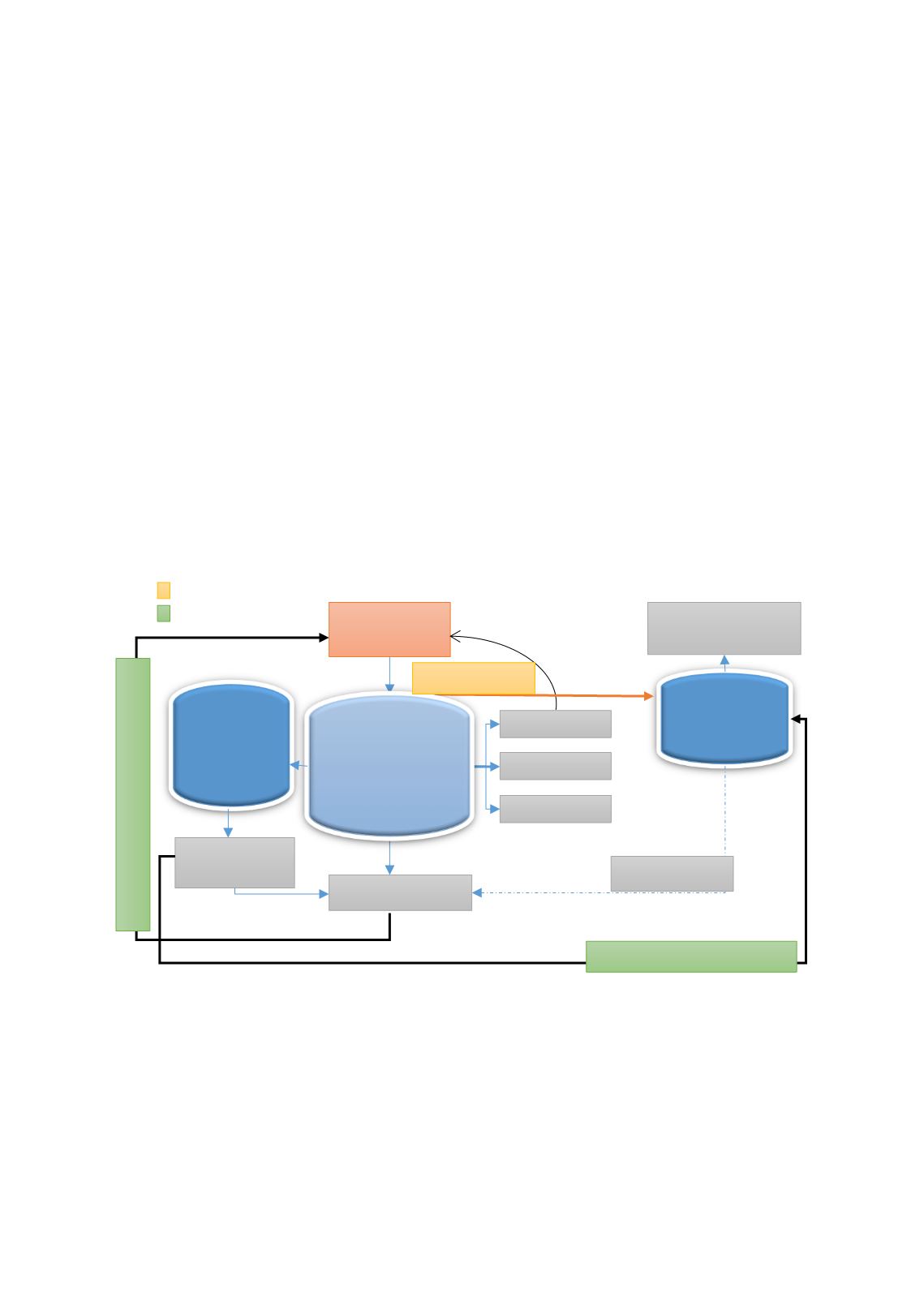
F
IGURE
8: W
AKALAH
-M
UDARABAH
H
YBRID
M
ODEL
Notes:
The figure presents two parties – Participants and TO. Takaful Fund and Shareholders’ Fund are both
managed by the TO.
Source: Source: Adapted from PwC (2008).
The structure of the
Wakalah-Mudarabah
Hybrid model is presented i
n Figure 8above:
1.
The participants contribute to the
Takaful
fund through
tabarru'
contract;
2.
The participants appoint the TO as agent and
mudarib
;
3.
The TO will deduct up-front fee which is called the
wakalah
fee to manage the fund;
Participants
Surplus/
Deficit
Re-Takaful
Reserves
Shari’ah
-
compliant
Investments
Investment
Profits
Shareholders’
Fund
Qard Hasan
Management
Expenses
Claims
Takaful
Fund
Wakalah Fee
100% - X of Investment Profits
X of Investment Profits
Contribution
Wakalah
Mudarabah