
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
80
Contributing to the maintenance of stability and development of the financial sector;
Promoting balanced and efficient functioning of financial markets;
Contributing to poverty reduction.
In November 2015, Mozambique revised its public debt management strategy with technical
assistance from the World Bank and the IMF. Key issue was the development of the domestic
capital market (IMF 2015b). In order to provide a more efficient and transparent debt portfolio
and minimize its costs, Mozambique developed a MTDS for the years 20152018, including the
following objectives (MoEF 2015, p. 4):
Identification of the type and size of contracted debt;
Define priorities which should be considered when deciding on new financing;
Identification and analysis of borrowing limits and indicators of debt sustainability;
Minimizing the costs and risks of the debt portfolio;
Establishing clear rules for new borrowings;
Establishing institutional coordination mechanisms for the management of public debt.
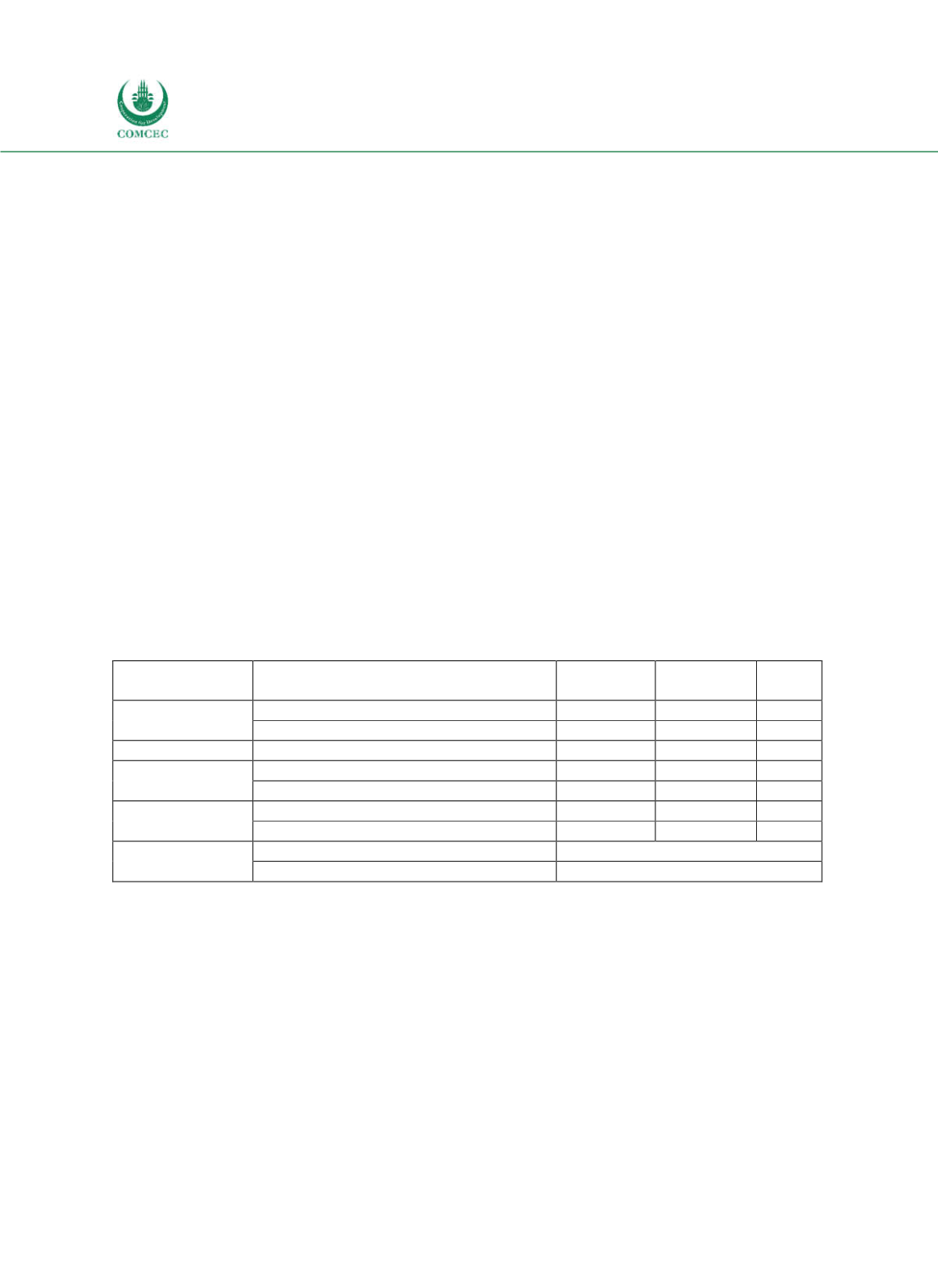
Public debt management faces several challenges (see Table 42):
Cost of debt: the weighted average interest rate was high at 9.5%, caused mainly by the high
interest rates on domestic debt;
Refinancing risk: more than 40% of domestic debt matures within one year;
Interest rate risk: more than 70% of domestic debt has to be refixed within one year;
Exchange rate risk: about 95% of Mozambique’s debt is external.
Table 4-2: Mozambique - Cost and Risk Indicators for the Govt.'s Debt Portfolio (2014)
Type of risk
Risk indicator
Domestic
debt
External
debt
Total
debt
Solvency
Nominal stock of public debt (Mio. $)
1102
7067 8173
Nominal stock of public debt (% of GDP)
7
42
49
Cost of debt
Weighted average interest rate (in %)
9.5
1.8 2.9
Refinancing
risk
ATM (years)
1.6
13.1 13.5
Debt maturing in 1 year (% of total)
43.3
2.7 8.3
Interest rate
risk
ATR (years)
1.1
13 12.6
Debt refixing in 1 Year (% of total)
70.7
4.7 13.8
Exchange rate
risk
FX debt (% of total debt)
94.5
ST FX debt (% of reserves)
6.7
Note: ATM = Average Time to Maturity; ATR = Average Time to Refixing; FX = Foreign exchange; ST = Short-term.
Source: MoEF (2015).
In order to ensure the mediumterm debt sustainability, the strategy highlights the alignment
of the available fiscal space with the project prioritization according to the Integrated
Investment Plan (IIP), the State Budget and the Economic and Social Plan (PES). In particular,
infrastructure projects under Public Private Partnerships (PPP) should be prioritized. Apart
from that, foreign direct investment and the sale of public assets would strengthen private
investment. Connected to debt management, the strategy considers the revenue side to be very
important. By broadening the tax base, intensifying audit and inspection measures and by
pushing forward the computerization of tax collection, greater efficiency in revenue collection
could translate into revenue growth and smaller budget deficits (MoEF 2015). The strategy
identifies various challenges regarding the implementation of the objectives, including
















