
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
111
all government debt as of November 30, 2016.
21
In the past five years their volume has more
than pentadrupled while total debt in securities has risen by factor 2.1 (Directorate General of
Budget Financing and Risk Management 2016b and personal communication).
In addition, the government provides credit and investment guarantees for projects in
infrastructure, including but not limited to water provision, electricity, toll roads and energy
projects.
The limit on cumulative guarantee liability is stipulated by the medium debt strategy plan to
be 2.57% of GDP at the end of 2017. In 2015 it stood at 0.25% of GDP (Directorate General of
Budget Financing and Risk Management 2015).
Domestic debt market
The domestic market in the narrow sense consists of the tradable domestic securities, which
makes up half of the total outstanding government debt.
22
It is held by commercial banks
(23%), the central bank (8%), institutional investors such as insurances, mutual funds or
pension funds (23%) and nonresidents including foreign governments and central banks
(38%). Nine percent are held by individuals and others (Directorate General of Budget
Financing and Risk Management 2016b, p. 56 and personal communication). While it may be
desirable to raise the share of domestic currencydenominated debt further in order to reduce
the exchange rate risk, given the development stage of Indonesia and the growth of the
domestic financial market the potential to do so without repercussions may be limited in the
short run.
Foreign borrowing
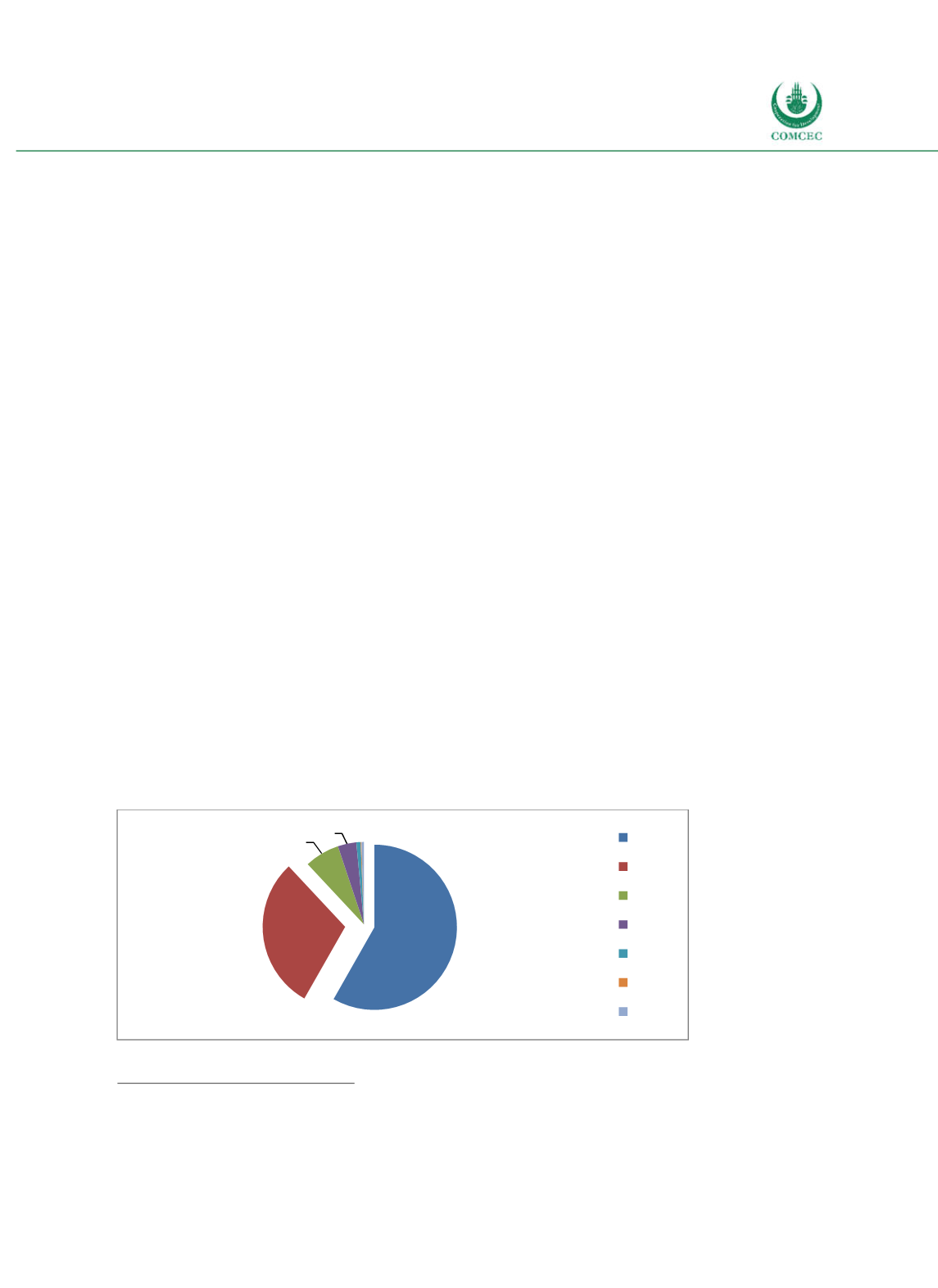
42% of the outstanding government debt at the end of 2016 was denominated in foreign
currency (see Figure 418). This ratio has largely been unaltered in the past five years, but the
dollar denominated debt instruments have gained in importance at the expense of Yen
denominated instruments. Notably, more than one third of IDR denominated tradable
securities is held by nonresidents, indicating that IDR denominated bonds are increasingly
attractive to nonresidents.
Figure 4-18: Indonesia - Currency Composition of Central Government Debt
Source: MoF (2017b)
21
See Directorate of Islamic Financing (2015) for an excellent review of Shariacompliant Government Financial
Instruments.
22
In addition there are nontradable securities (7% of total debt) and domestic loans (less than 0.1% of total debt).
58%
30%
7% 4% 1%
IDR USD JPY EUR SDR AUD Other
















