
Risk Management in
Islamic Financial Instruments
103
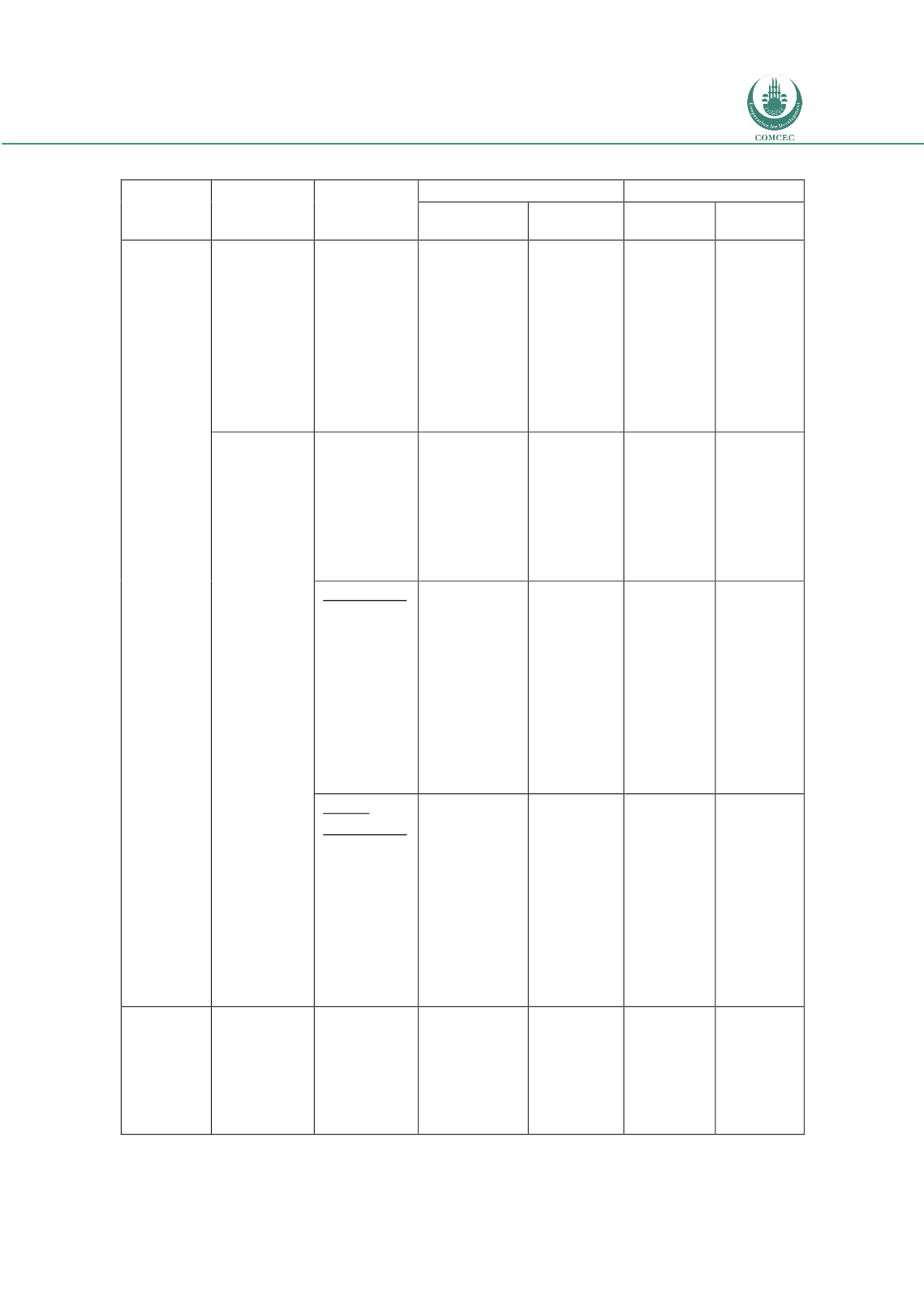
Table 5.1 Types of Risks – Description and Influence
Type of risk
Definition
Institution
Depositors
Bank
Shareholders
Demand
Investment
Transaction
Risks
Credit risk
Credit risk is
failure of
counter - party
to meet his or
her obligations
timely and on
the agreed
terms of the
contract
The bank faces
counter - party
risks in the
various forms of
contracts: such
as,
Bay mua’jal,
mudaraba,
musharaka
murabaha,
They face
the risk that
the bank
does not
honor
requests for
withdrawals
at face value
They face the risk
that the bank does
not honor requests
for withdrawals at
market
value
Market risk
Market risk is
the risk
associated
with change in
the market
value of held
assets
Mark– up risk
is risk of
divergence
between the
murabaha
contract mark
– up and the
market
benchmark
rate
The bank may
incur losses if
the benchmark
rate changes
adversely
Foreign
Exchange risk
is the risk of
the impact of
exchange rate
movements on
assets
denominated
in foreign
currency
This exposes the
bank to risks
associated with
their deferred –
trading
transactions
Business
Risk
Business risk
Business risk
results from
competitive
pressures from
existing
counter parts

















