
Risk Management in
Islamic Financial Instruments
72
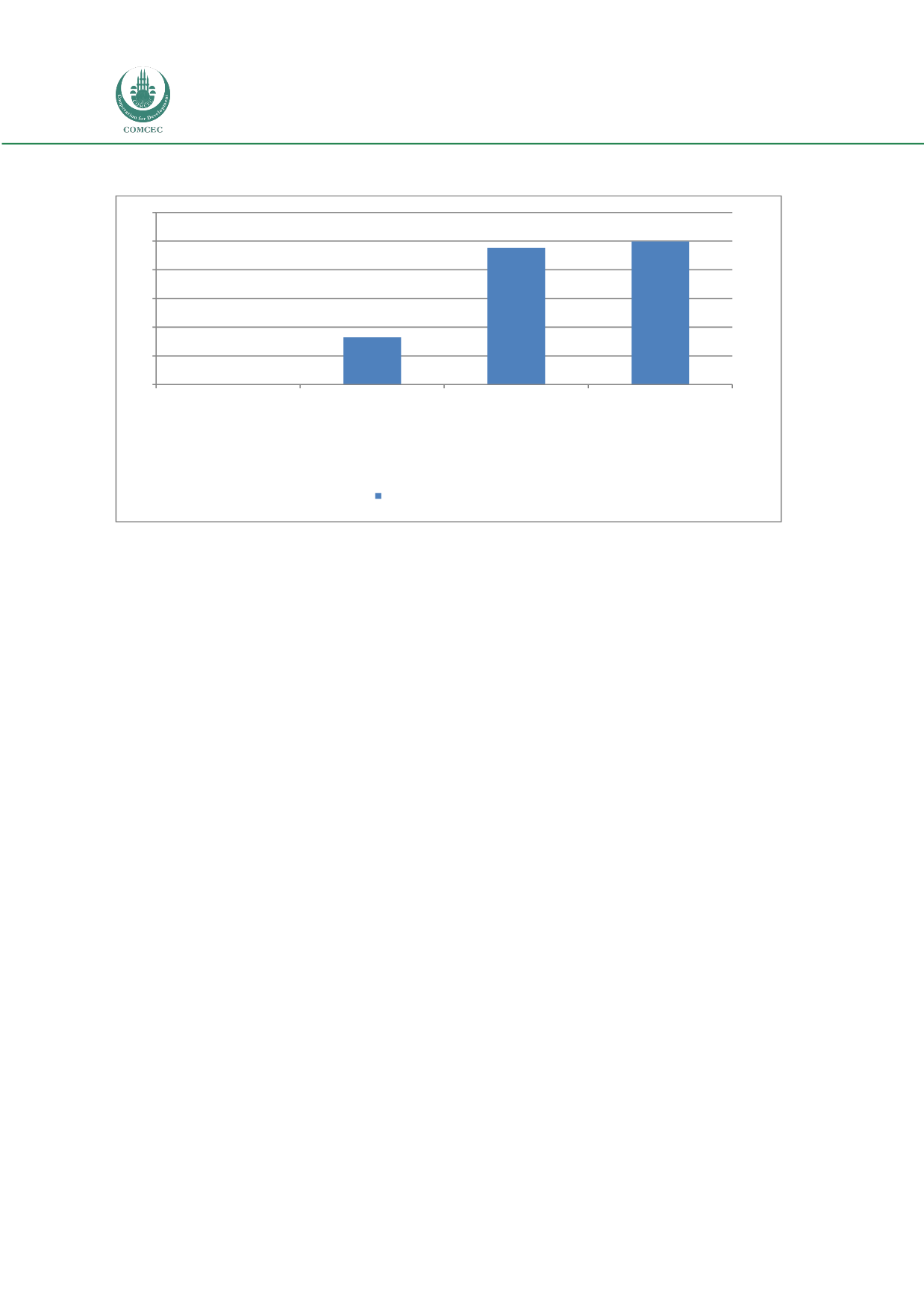
Chart 4.12: Liquidity Ratio for Sub-Saharan Africa Region
Source: BankScope Database 2013
4.4 ANALYSIS OF RISK MATRICES ACROSS FIVE MAJOR COUNTRY
JURISDICTIONS
This section presents a comparative analysis of the risk matrices for the Islamic and
conventional banks for five major Islamic financial markets: a) Malaysia, 2) Turkey, 3)
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 4) United Arab Emirates, and 5) Bangladesh.
4.4.1 Malaysia
4.4.1.1 Overview of Malaysian Islamic Finance Services Industries
Malaysia is the largest Islamic financial hub in the Asia-Pacific region, with total Islamic
financial assets worth USD272.5 billion as of the end of 2011. Malaysia is home to a wide range
of investment, wholesale, retail and structured products for a range of purposes and sectors.
Islamic financial institutions currently use a wide range of Shariah contracts and innovative
instruments, such as profit and FOREX rate swaps, which have been accepted globally. (GIFF
2012)
The country also provides an efficient regulatory environment that is conducive for the Islamic
financial services industries (IFSI). Under the existing legal framework, both conventional and
Islamic financial systems coexist and work together harmoniously in a competitive
environment.
16,46
47,72
49,88
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Interbank Ratio
%
2011
Net Loans / Tot Assets
%
2011
Net Loans / Dep & ST
Funding
%
2011
Liquid Assets / Dep & ST
Funding
%
2011
SUB SAHARAN Islamic

















