
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
72
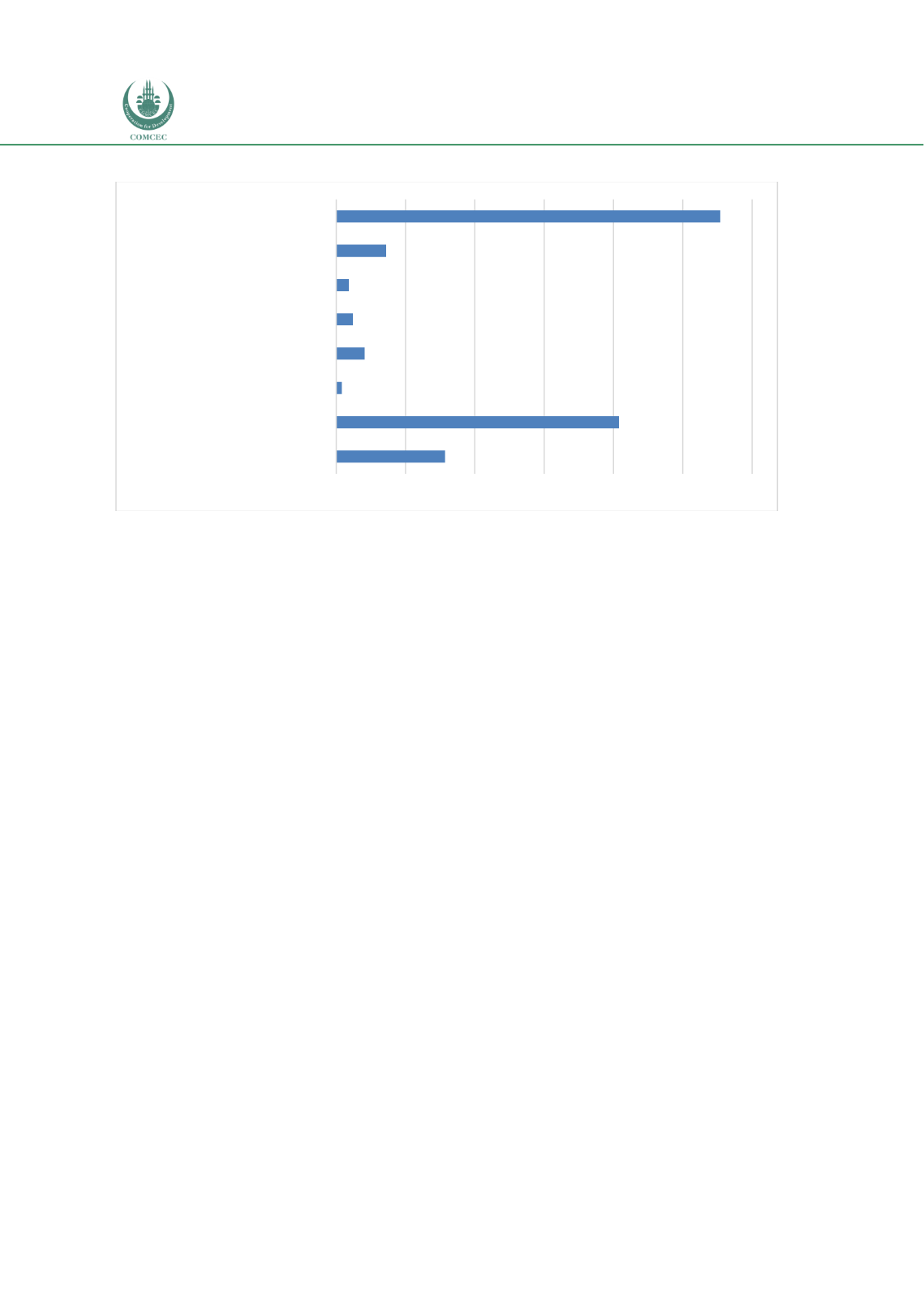
Chart 4.1. 2: Financial System Structure in Indonesia 2015 (% of GDP)
Source: IMF and World Bank (2017: 32)
4.1.1.1. Islamic Financial Industry
Islamic finance started relatively late in Indonesia with the establishment of the first Islamic
bank in the country in 1992. The industry has been growing since then and has diversified into
various sectors. The country has 4 fully-fledged Islamic banks, 22 Islamic banking units
(windows) and 160 Islamic rural banks (BPRS). Indonesia has taken a significant strategic
move in 2016 to enhance the role of Islamic finance with the enactment of Presidential Decree
Number 91 year 2016 that led to the formation of a national committee, namely the National
Committee on Islamic Finance (simply called KNKS). KNKS is chaired by the President of
Indonesia and comprises ten authorities which are Bank Indonesia, Ministry of Finance,
Ministry of Religion, Financial Services Authority (OJK), Ministry of National Development
Planning (Bappenas), Ministry of State Owned Enterprises (BUMN), National Ulama Council
(MUI), Coordinating Ministry for Economic Affairs, Ministry of Cooperative and Small and
Medium Enterprises (SME), and Deposit Insurance Corporation (LPS).
KNKS is a strategic committee to coordinate, harmonize and synchronize all policies and
actions pursued by those authorities to accelerate Indonesian Islamic finance. KNKS launched
its Blueprint for the period 2018-2024 to develop the Indonesian Islamic economy and finance.
The vision of the Blueprint is to make Indonesia as the World Islamic Economic and Finance
Hub with the 5 missions of increasing Islamic businesses, expanding Islamic financing,
deepening the Islamic financial markets, increasing Islamic economics and finance literacy, and
strengthening the international positioning. The strategic move goes beyond just focusing on
the Islamic banking industry, something which has been done in the past two decades.
Indonesia has realized the huge potential of its Islamic economic and halal industries that have
not been prioritized so far.
Under the Blueprint, Indonesia also plans to enhance the potential of the Islamic social sectors,
particularly zakat (alms giving) and waqf (endowment). However, the intention is not only to
increase the collections of such funds but to integrate the Islamic commercial and social
15.7
40.8
0.8
4.1
2.4
1.8
7.2
55.4
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Outstanding debt securities
Stock market capitalization
Other non-bank financial institutions
Financial intermediaries
Mutual funds
Pension funds
Insurance companies
Deposit-taking financial institutions
















