
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
71
4
Country Case Studies
4.1. Indonesia
4.1.1.
Indonesian Financial Sector and Islamic Finance: An Overview
The government of Indonesia has taken initiatives to strengthen the financial sector to
enhance its role in the development in the economy. A separate regulatory body, Otoritas Jasa
Keuangan (OJK), was established in 2011 to oversee all financial service sectors. OJK
developed a Financial Sector Masterplan 2015-2019 and is in the process of implementing it.
The aim of the Masterplan is to promote a financial sector that is contributive, stable, inclusive
and enabling. Some of the specific goals in the contributive role of the financial sector include
the funding of infrastructure and other priority economic sectors and the strengthening of the
role of the Shariah financial services sector (OJK 2016).
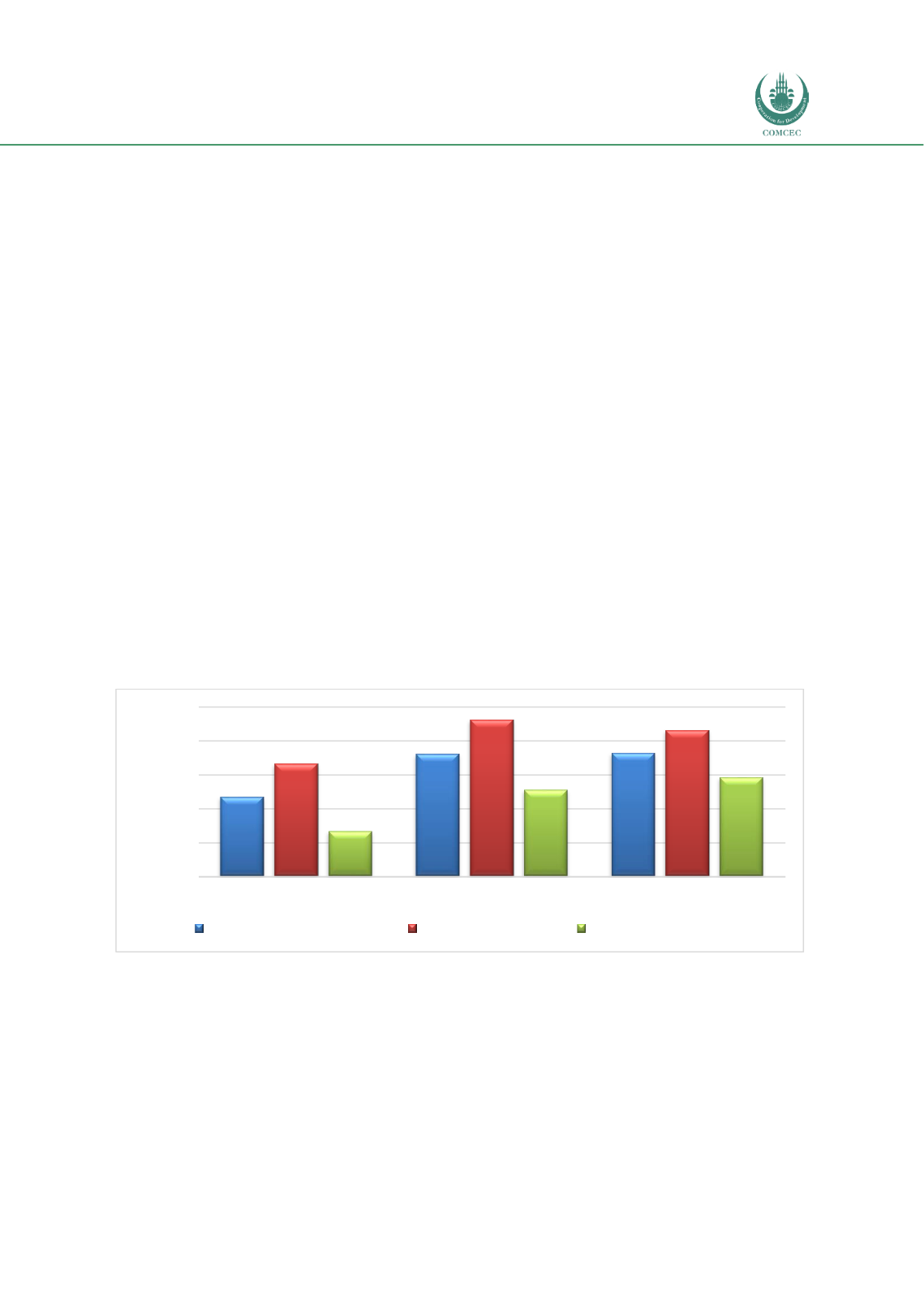
Chart 4.1.1 shows the overall status of the development of the financial sector, the financial
institutions and financial markets in Indonesia relative to the averages of the OIC countries
and the Asia and Pacific (A&P) Region. The overall development index of the financial sector in
Indonesia (0.36) is similar to that of the A&P region and higher than the OIC average of 0.23.
Both the financial institutions and financial market indices of Indonesia (0.43 and 0.29
respectively) are higher than the corresponding indices for OIC countries (0.33 and 0.13
respectively). While the financial institutions index for Indonesia (0.43) is slightly lower than
that of the A&P region (0.46), the financial markets index for the country (0.29) is better than
that of the A&P region (0.26).
Chart 4.1. 1: Relative Financial Sector Development in Indonesia (2016) (0-1 Highest)
Source: IMF Financial Sector Development Database,
http://data.imf.org/?sk=F8032E80-B36C-43B1-AC26-493C5B1CD33B&sId=1481126573525
The structure of the Indonesian financial system is shown in Chart 4.1.2. Among the financial
institutions, the deposit-taking financial institutions dominate the financial sector with assets
worth 55.4% of the GDP followed by the insurance sector with assets valued at 7.2% of the
GDP. The pension funds and mutual funds are relatively small with shares of 1.8% and 2.4% of
the GDP. In the financial markets, the stock market capitalization is 40.8% of the GDP and the
market value of the outstanding debt securities is 15.7% of the GDP.
0.23
0.36
0.36
0.33
0.46
0.43
0.13
0.26
0.29
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
OIC Average
Asia and Pacific Average
Indonesia
Index Value (0-1 Highest)
Financial Development Index
Fin. Institutions Index
Financial Markets Index
















