
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
31
Table 2.4: Risk Appetite and Considerations of Different Financial Institutions
Institution
Investment
Horizon
Risk
Appetite
Investment
Objectives
Risks and Constraints
Commercial
Banks
Short term
Low
to
medium
Make net interest
margins
Asset-liability management (ALM)
mismatch risk
Intensifying
regulatory
environment (BASEL III)
Nonlife
insurance
Short term
Medium
Meet liability funding
costs calculated by
actuaries
ALM mismatch risk
Intensifying
regulatory
environment (IFRS II, Solvency II)
Investment
Company
Short
to
medium
term
Depends
on
funds
mandates
Maximize company
returns
Liquidity issue due to beneficiary
redemption
Life
insurance
and private
pension
Long term
Medium
Meet liability funding
costs calculated by
actuaries
ALM mismatch risk
Intensifying
regulatory
environment (IFRS II, Solvency II)
Public
pension
Long term
Medium
Meet liability funding
costs calculated by
actuaries
ALM mismatch risk
Rising longevity risk
Sovereign
wealth funds
Long term
Medium to
high
Maximize sovereign’s
wealth
Government mandate approval
issue
Endowments
and
foundations
Long term
High
Maximize
beneficiary’s wealth
Can have mandates that restrict
investment
in
developing
economies
Source: ADB (2018), African Economic Outlook 2018, African Development Bank, p. 109.
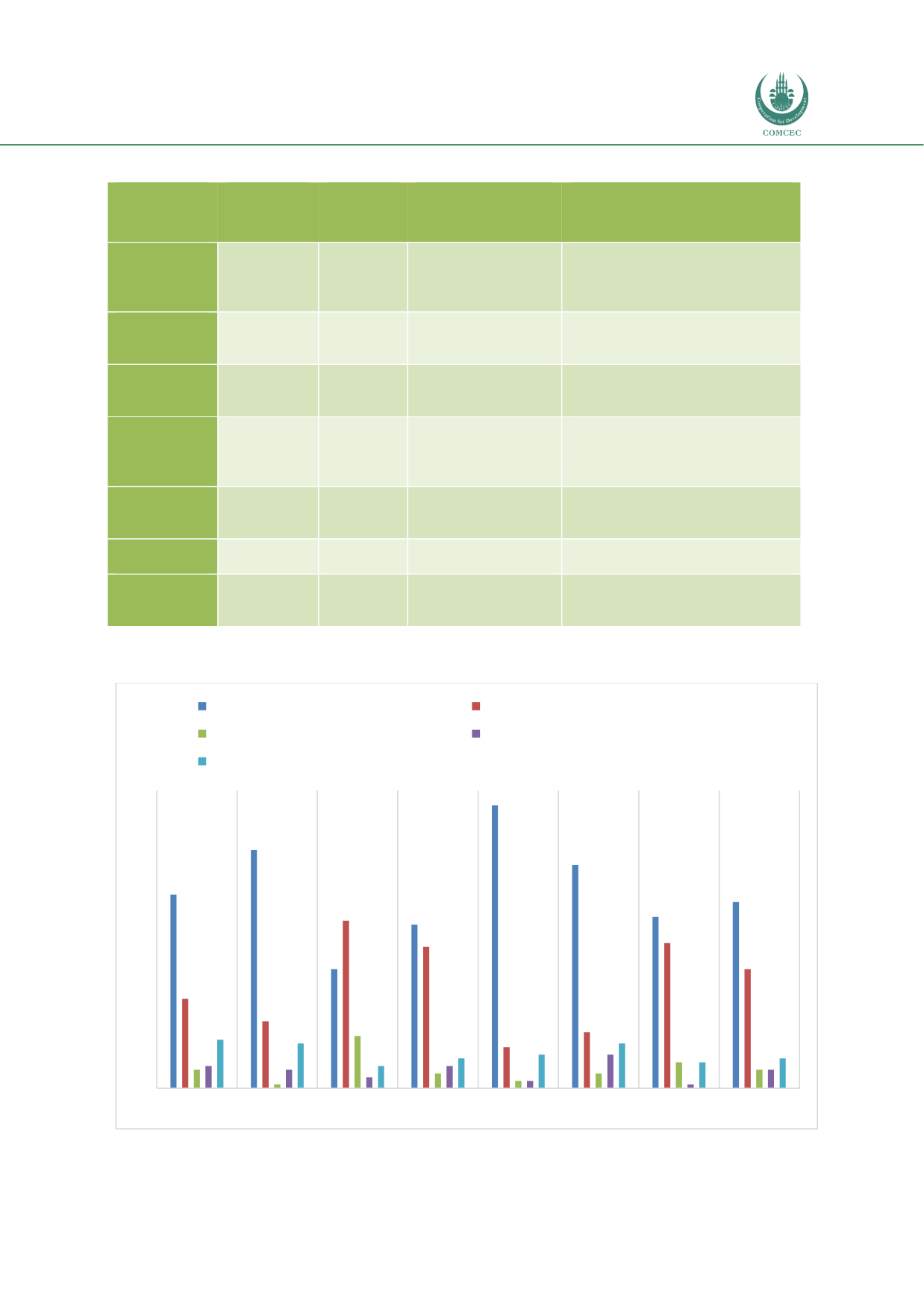
Chart 2.3: Global Infrastructure Investment-Equity and PPP by Type of Owner (%)
Source: PWC & GIIA (2017)
52%
64%
32%
44%
76%
60%
46%
50%
24%
18%
45%
38%
11%
15%
39%
32%
5%
1%
14%
4%
2%
4%
7%
5%
6%
5%
3%
6%
2%
9%
1%
5%
13%
12%
6%
8%
9%
12%
7%
8%
A F R I C A
A S I A
A U S T R A L A S I A E U R O P E
L A T I N
A M E R I C A
M I D D L E E A S T
N O R T H
A M E R I C A
G L O B A L
% OF TOTAL
Corporate
Infrastructure fund/investment firm
Pension fund
Sovereign wealth fund/government agency
Other
















