
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
95
Malaysia ranks fifth among 41 countries in the Infrastructure Investment Index that measures
the attractiveness of infrastructure investments for investors as reported by ARCADIS (2016).
Given the high ranking, the private sector has played an important role in the development of
the infrastructure sector of the country. The total investment in the infrastructure provided by
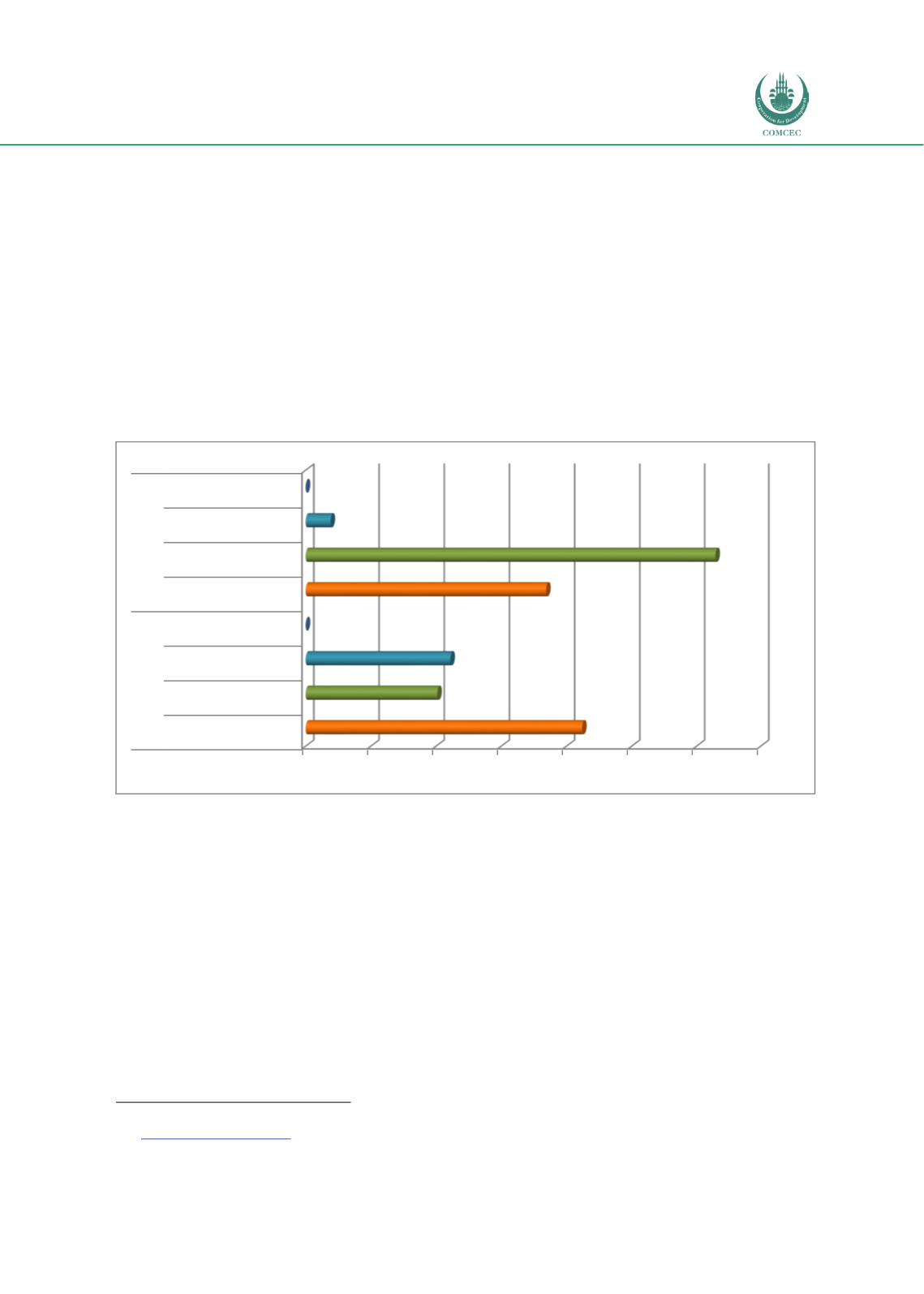
the private sector in Malaysia is shown in Chart 4.2.7. During the 2005-2010 period, the
infrastructure investments from the private sector amounted to a total of USD 8.477 billion (or
USD 1.412 billion per year on the average). Most of the investments were made in the
telecommunications sector (USD 4.239 billion), followed by the transport (USD 2.219 billion)
and energy sector (USD 2.018 billion). During 2011-2016 the private sector invested USD
10.362 billion in infrastructure (or USD 1.727 billion per year), with most of it going into the
energy sector (USD 6.293 billion) followed by the telecommunications sector (USD 3.687
billion) and transport sector (USD 381 million).
Chart 4.2. 7: Private Sector Investment in Infrastructure: Malaysia (USD million)
Source: World Bank, World Development Indicators Database.
Table 4.2.2 shows the current trends and the investment needs of infrastructure for 2016-
2040 for Malaysia.
35
The table shows that in the next 25 years Malaysia is expected to have a
short-fall of USD 77 billion in infrastructure financing (or USD 3.08 billion per year), the bulk
of which (USD 70 billion) will be needed to build roads and USD 6 billion for ports. The annual
gap represents 0.96% of the GNI of 2015.
36
It should be noted that the gaps identified in Table
4.2 represent additional funding needs that are beyond the current levels of investment. While
this gap can be partly filled by the government, the private sector also has an important role to
play to provide funding.
35
Global Infrastructure Outlook, A G20 Initiative, provides information on the infrastructure needs and gaps in 56 countries.
See
https://outlook.gihub.org/36
The gross national income of Malaysia was USD 320.5 billion in 2015 (World Bank 2017d:12)
0
1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 6,000 7,000
Telecommunications
Energy
Transport
Water & Sanitation
Telecommunications
Energy
Transport
Water & Sanitation
2005-10
2011-16
4,239.1
2,018.5
2,219.3
0.0
3,686.9
6,293.9
381.0
0.0
















