Islamic Fund Management
84
Islamic ETFs
As at April-2018, there were six Islamic ETFs listed on Bursa Malaysia. The main difference
between a conventional ETF and an Islamic ETF is the benchmark index that the latter tracks.
An Islamic ETF only tracks an Islamic benchmark index, the constituents of which comprise
Shariah-complaint companies. Islamic ETFs are considered a liquid and cost efficient financial
instrument that offers investors lower transaction costs than buying and selling unit trusts.
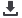
Figure 4.5depicts the basic structure of an Islamic ETF in Malaysia while
Table 4.7summarises the Islamic ETFs listed on Bursa Malaysia as at April-2018. Typically, ETFs are
structured as open-ended funds.
Figure 4.5: Basic Structure of an Islamic ETF in Malaysia
Buy ETF units
Advisory on
Shariah
matters
Sell ETF units
Manager
Trustee
Investors
ShariahAdvisor/
Committee
StockExchange
Islamic ETF
Sell ETF units
Buy ETF units
Liquidity Providers
Sell ETF units
Participating Dealers
Buy ETF units
Sell ETF units
Buy ETF units
Source: Investment in Unit Trust Funds that are Listed and Traded on the Stock Exchange, SC