Islamic Fund Management
158
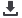
Pillar 4 – Tax Framework
Thrusts
Issues and Challenges
Key Recommendations
Implement measures to secure
commitments
from
targeted
segments (supply and demand
sides) to sustain the long-term
growth of Islamic funds.
Despite tax incentives, there are
still
more
opportunities
for
investments to grow.
Apart from providing tax rebates,
the government should also
consider
matching
individual
investments in Islamic funds (e.g.
the government to match every
USD1 saved in Islamic funds and to
introduce tax incentives for SRI
funds).
Pillar 5 – Market Infrastructure
Thrusts
Issues and Challenges
Key Recommendations
Facilitate new digital business
models to promote seamless reach
for Islamic funds.
Connectivity
to
the
masses
remains a challenge for regulators
and fund managers.
Leverage the use of mobile phones
to interface with applications such
as robo-advisors, to improve ease
of fund investment and market
education.
Promote merit-based fees and
transparency of costing structure.
High up-front transaction costs
deter
penetration
of
retail
investors.
Regulators
to
engage
with
developed
countries
and
implement
transparent
cost
structures, with the aim of making
transaction costs more effective.
Sources: RAM, ISRA
Developing Markets
The level of financial inclusion was a key concern during the review of Pakistan and South
Africa. The creation of a broader base of captive investors is important for the development of
the Islamic fund management industry, especially in developing markets. The sustainability of
ICM performance is the backbone to facilitating organic growth.
Table 5.3lists the common
issues and proposed solutions.
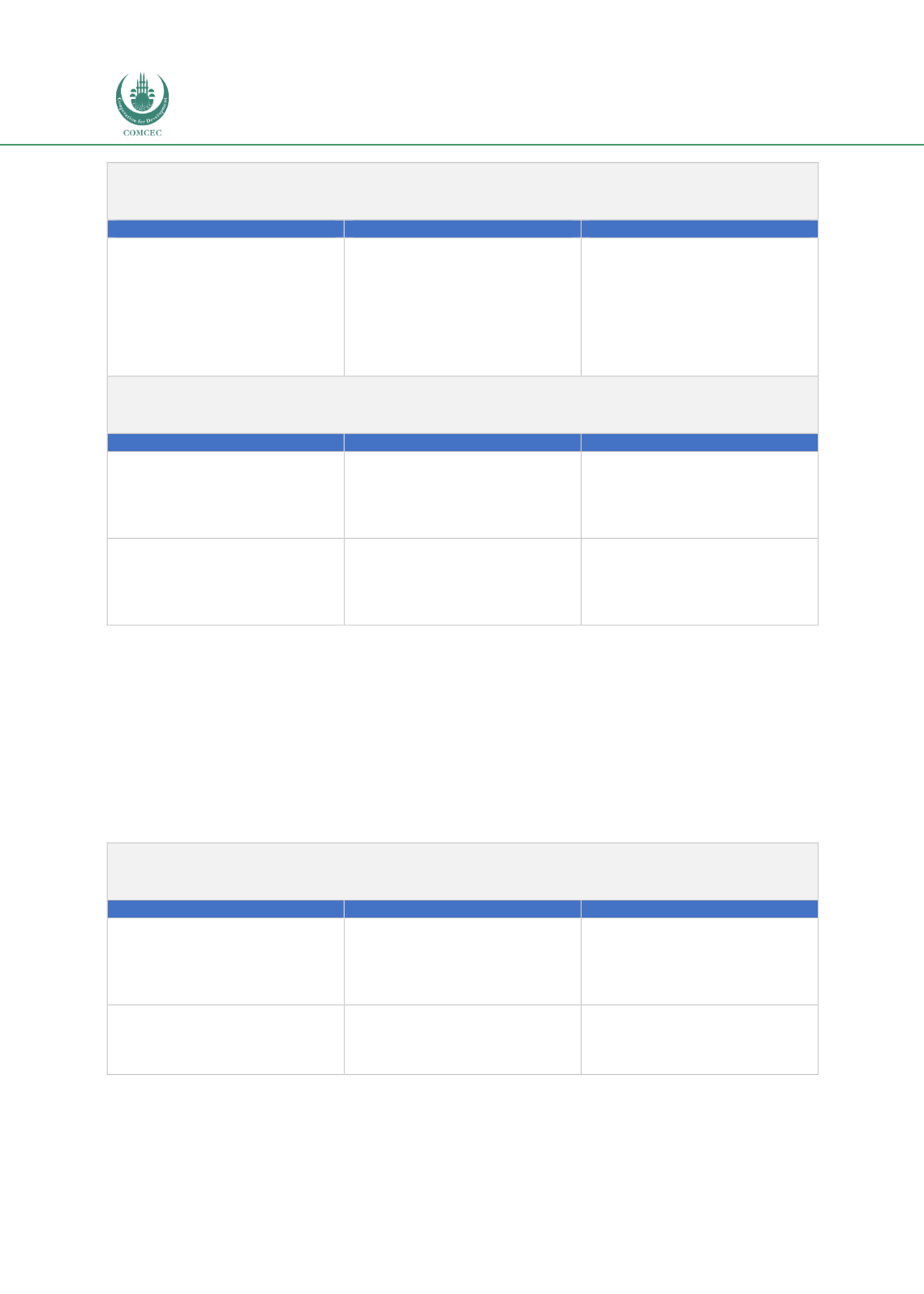
Table 5.3: General Recommendations for a Developing Market
Pillar 1 – Legal, Regulatory and Shariah Framework
Thrusts
Issues and Challenges
Key Recommendations
Develop investors’ trust and
confidence
in
products
and
services.
Lack of trust in the feasibility of
investments in Shariah funds.
Regulators and market players
work together to improve the level
of awareness and highlight the
governing rules for investor
protection.
Establish comprehensive legal,
regulatory
and
Shariah
frameworks.
Lack of effective implementation
and enforcement of laws and
regulations, giving rise to gaps in
the system.
Review existing policies and
guidelines and address the gaps.