COMCEC Poverty Outlook 2018
16
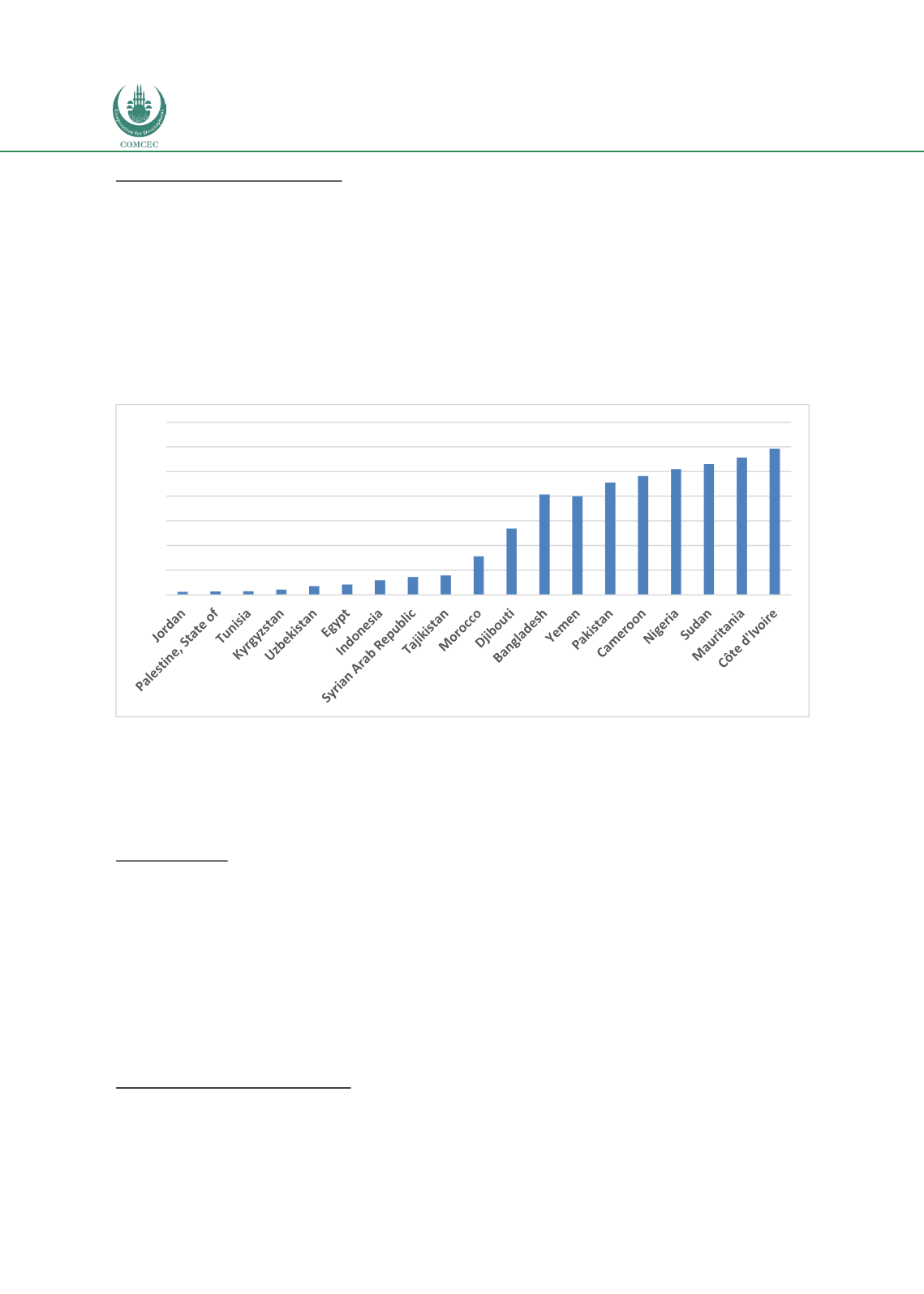
Multidimensional Poverty Index
MPI values for the lower-middle income OIC Member Countries are in the range of 0.004 (Jordan)
– 0.307 (Cote d’Ivore).
20
In the lower-middle income group, half of these countries have an MPI
value that is two-times or more higher than the highest MPI value in the upper-middle income
group. Indeed, the MPI values of more than half of the lower-middle income countries are above
0.073 which is the highest MPI value of the upper-middle income group
(Figure 17). In this group,
the share of population live inmultidimensional poverty ranges between 1.2 percent (Jordan) and
59,3 percent (Cote d’Ivore). In almost half of the lower-middle income countries, more than 40
percent of the population is multi-dimensionally poor.
Figure 17: Multidimensional Poverty in Lower-Middle Income OIC Member Countries (%)
Source: The UNDP (2016).
The contribution of deprivation in education to overall multidimensional poverty ranges between
3.7 (Uzbekistan) and 54.7 (Syria) and the contribution of deprivation in living conditions ranges
between 3.5 (Jordan) and 48.9 (Sudan), while the contribution of deprivation in health is the
highest which ranges between 20.3 (Mauritania) and 83.4 (Uzbekistan).
State of Hunger
In lower-middle income group, more than half of the countries, namely Bangladesh, Cameroon,
Djibouti, Cote d’Ivoire, Kyrgyzstan, Mauritania, Nigeria, Pakistan, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Yemen,
and Uzbekistan are in the position of “low income food-deficit country”.
21
Looking at the GHI
values of the countries in this group, a similar picture is observed (Table 3).
20
See Annex 8.
21
See Annex 5.
1,2 1,4 1,5 2,2 3,5 4,2 5,9 7,2 7,9
15,6
26,9
40,7 40,0
45,6 48,2 50,9 53,1 55,6
59,3
0,0
10,0
20,0
30,0
40,0
50,0
60,0
70,0