31
large margin. The group wise MMRs also suggest an interesting story of catching up: the Asian group,
which had worse MMR statistics than the Arab group two decades ago had consistently narrowed this
gap and finally surpassed the Arab group in the 2011-2015 period.
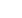
The trends in skilled birth attendance i
n Table 4 sheds more light on the challenge faced by the African
OIC countries: two decades of work/investment had seen only marginal if not insignificant increase of
4pp in skilled attendance (from 42 per cent in 1996-2000 to 46 per cent in 2011-2015). In contrast
during the same period Arab OIC countries have improved their skilled attendance levels by 17pp and
Asians by 21pp.
The table also include information on under-5 mortality, which provides a snapshot of how well a
country is performing in terms of addressing health related challenges at the early life. With access to
appropriate child health services, survival rate increases which in turns improves life expectancy at
birth. The trend analysis of under-5 mortality rate and maternal mortality rate are in
Table 4 .These
results corroborate the findings so far.
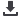
Table 4: Trends in maternal care in OIC countries
Maternal mortality
rate
(modelled
estimate,
per
100,000 live births)
Low
OIC
average
High
African
group
Arab
group
Asian
group
2011-2015
4.0
256.5
1360
653.2
134.7
126.2
(Kuwait)
(Sierra
Leone)
2006-2010
291.4
726.5
148.9
162.8
2001-2005
335.7
810.9
171.8
208.8
1996-2000
397.5
964.5
197.9
258.1
Births attended
by skilled health
staff (% of total)
Low
OIC
average
High
African
group
Arab
group
Asian
group
2011-2015
20.2
69.3
100.0
46.3
84.0
73.9
Chad
Brunei
Darussalam
2006-2010
64.2
42.4
79.3
66.7
2001-2005
57.5
41.1
75.8
57.7
1996-2000
52.9
41.7
66.8
52.7
Mortality
rate,
under-5 (per 1,000
live births)
Low
OIC
average
High
African
group
Arab
group
Asian
group
2011-2015
7.6
50.9
135.6
95.2
32.7
38.3
(Bahrain;
Malaysia)
(Somalia)
2006-2010
60.9
117.1
37.5
46.4
2001-2005
73.8
145.0
45.0
56.5
1996-2000
88.5
175.1
53.8
68.9
The above analysis of demand for health care by OIC countries provides the background for a detailed
discussion on universal health coverage, including financial risk protection and access to quality
essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines