
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
37
Table1.6: Number in thousand (approximate) and percentage rate of enrolment to secondary
vocational education
Country Pakistan
Bangladesh
Brunei
Darussalam
Burkina
Faso
Djibouti
Kazakhstan Sudan
Year
Num
%
Num
%
Num
%
Num
% Num
%
Num
%
Num
%
2015
329
2.72
110
7.5
5.5
11.6
29
3.
1
4.3
7.
4
190 11.3
-
-
2014
366
3.25
102
7.2
5.6
11.4
28
3.
3
2.7
4.
6
185 11.1
-
-
2013
374
3.47
88
7.6
6.8
13.2
29
3.
9
2.3
4.
0
164
9.9
26
1.
4
2012
376
3.62
91
6.4
5.9
11.3
27
4.
0
2.2
4.
1
185 10.7
25
1.
5
2011
389
3.75
82
6.3
4.2
8.6
25
4.
3
1.8
3.
6
197 11.1
22
1.
4
Source: Adapted from (WorldBank, 2018)
The above mentioned seven OIC member states’ enrolment rate of vocational education is
increasing for the time being, with two exceptions of Pakistan and Burkina Faso where the
enrolment rate has decreased overtime. It is surprising that still the number of students
enrolling at VET sectors is not satisfactory. The reasons of this low enrolment rate in OIC VET
sector might be the combination of lack of awareness, minimum opportunities of employment
and low level of social acceptance. The rate of enrolment is not also very high due to having less
attractiveness of VET programs among many OIC countries. For instance, in many developing
countries in the globe generally and in OIC particularly, VET is considered as a second -class
education, and designed for the students who cannot complete formal education due to some
circumstances (Okolie & Yasin, 2017).
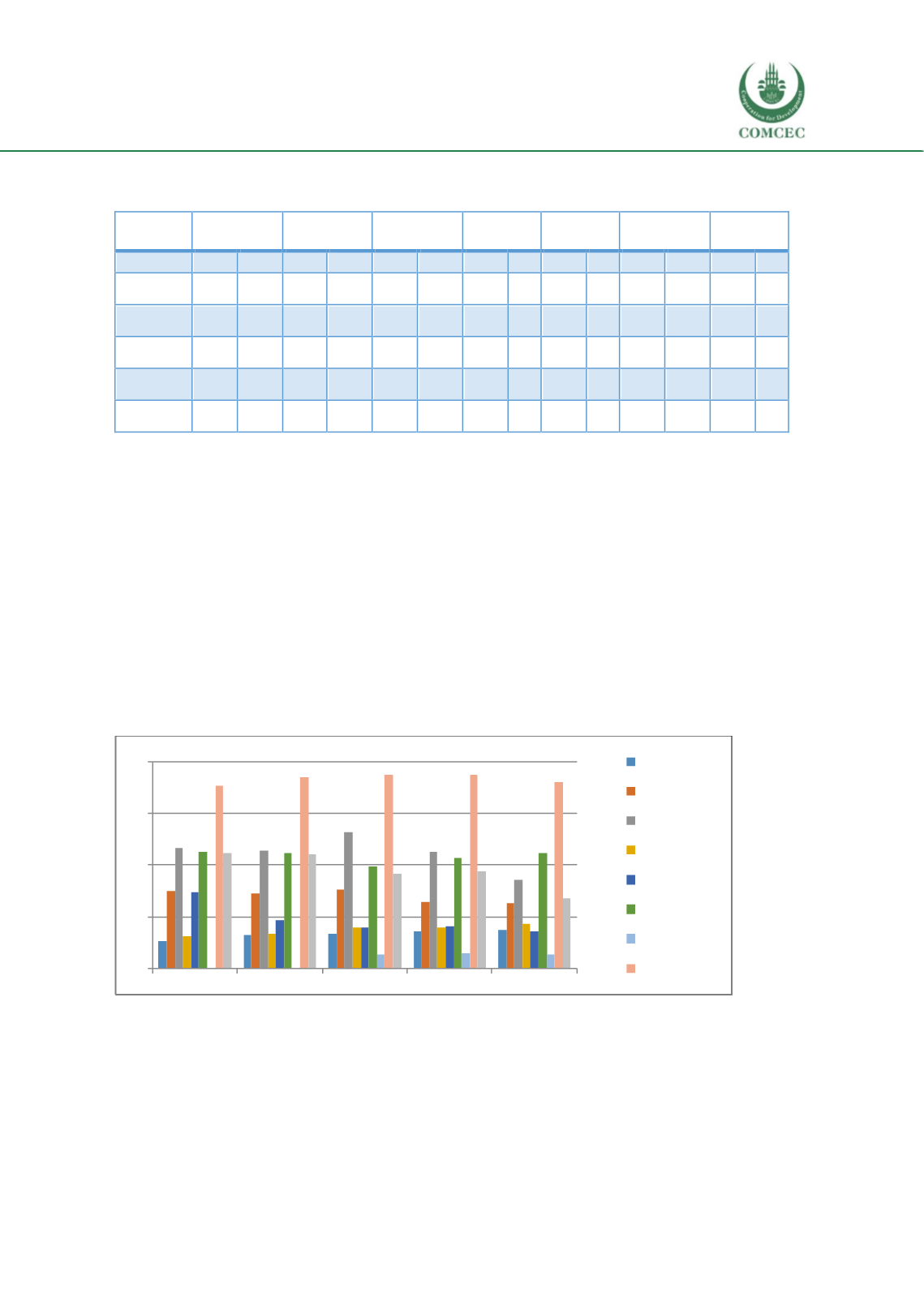
Figure 1.8: Comparison chart between the percentage rate of enrolment in vocational
education at high, low and medium income OIC countries
Source: Adapted fromWorldBank, 2018
From the bar chart (Figure 1.8) it can be easily displayed that most of the high income countries’
percentage rate of enrolment in secondary vocational education is much higher than themiddle
or low income countries.
Pecuniary issues related toskill development through VET linkwith some major factors like lack
of funds, expenses of VET program and employment of VET graduates. A huge financial support
0
5
10
15
20
2015
2014
2013
2012
2011
Pakistan
Bangladesh
Brunei
Burkina
Djibouti
Kazakhstan
Sudan
Indonesia
















