
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
35
The table above (Table 1.7) clearly identifies the main skill gaps that are needed for
employability in the current era and to bridge the skills gap in the south Asia. These skills differ
from one region to another, for example skills like values and ethics might not serve in Europe
or Africa, while it is crucial in south Asia. In many cases, the skills might be the same or
similarities exist among these skills depending on the workplaces, industries and the overall
economy of the particular country.
1.8.4. Skill gap in Arab Region
There are mainly two types of countries in Arab peninsula namely: developed countries (Saudi
Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar) and less developed countries (Palestine, Somalia, Yemen,
Syria) (GROUP, 2018). The Arab region, more particularly the Middle East and North Africa
(MENA) region is facing a challenge of having huge unemployment which is affecting most of its
countries’ youth population. Dimova, Elder, and Stephan (2016) reported that unemployment
rates among the young people, in this region, are twice as high as the global average. The main
reason of this huge unemployment rate is related to their attitude, such as many young people
leave their jobs from the labour market due to family issues or discouragement with their labour
market prospects, reluctant of youth to gain skills from VET institutions, low levels of
entrepreneurship (Dimova et al., 2016).
Additional, the participation ofwoman in the labour market is another reason to create skill gap
in most of these countries. In almost all the countries among the Arab region, the rate of skilled
women is less thanmale which also increases unemployment rate. With this brief background,
it is clear that the rate of youth unemployment in Arab region is high. Skill gap and lack of skilled
manpower is one of the reasons of this increase in unemployment. The previous report
identified the existence of skill gap in VET sectors which are: basic skills (soft skill s, problem
solving skills, independent thinking ability, and creativity skills); specific and functional skills
(The
Bayt.com,May 2016).
Apart from the above stated efforts, this study further identifies skills that are essential for filling
the vacancies in the labour market. The following comparison table (Table 1.8) is constructed
focusing on both developed and developing countries toprovide a comparative study among the
employable skills in theworkplace (both formal and non-formal sectors). This comparison table
is constructed based on the few studies (e.g., Jayaram & Engmann, 2017; Jin, 2014; Kurnia,
Dittrich, & Murniat, 2014; Paryono, 2014).
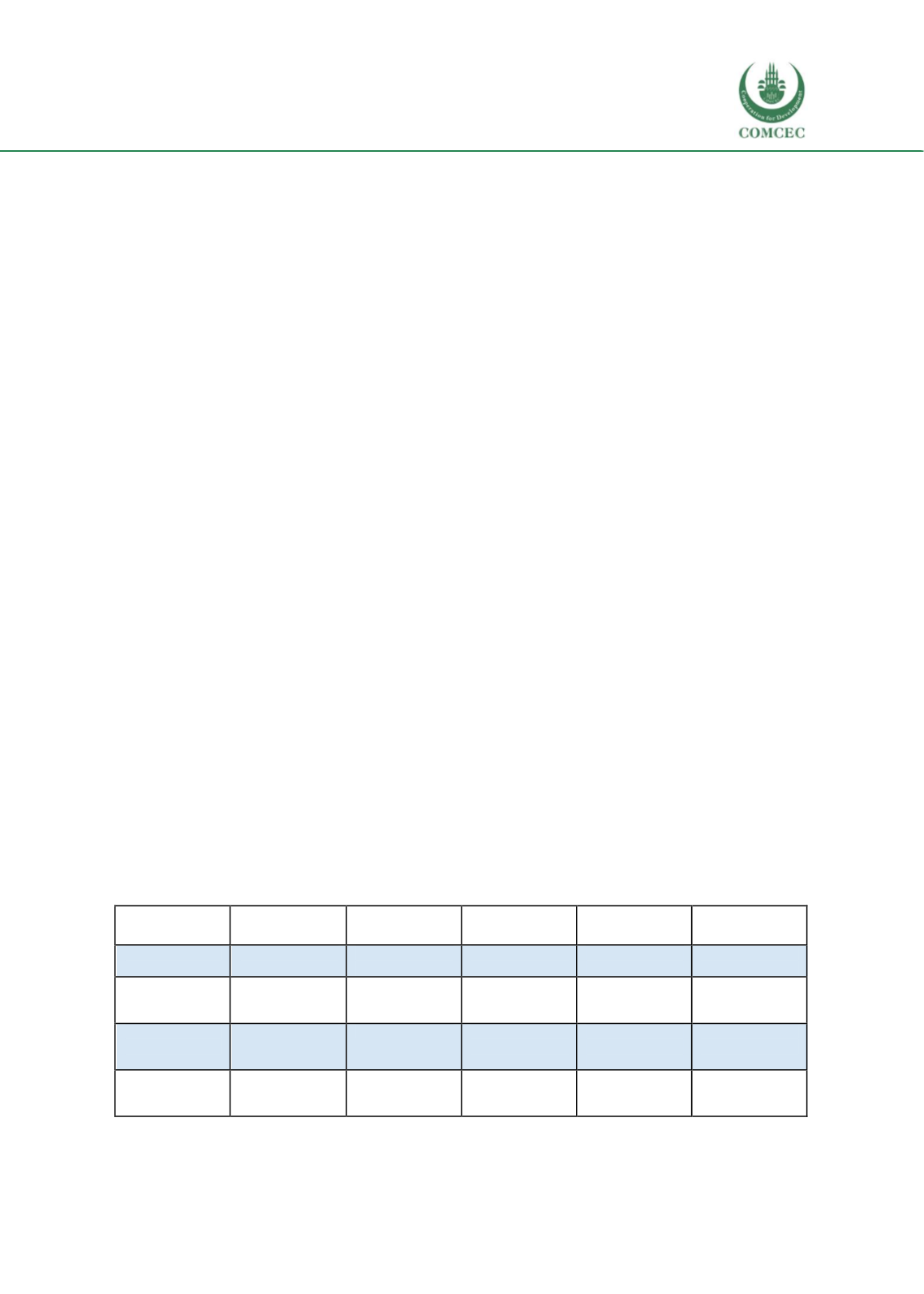
Table 1.8: Skills required in some developed and OIC countries
Australia
Brunei
(OIC)
China
Africa
Indonesia
(OIC)
Korea
Communication
Communication
Information &
communication
Communication
skills
Information &
communication
Communication
Skills
Teamwork
Workingwith
others
Group work
Working groups
& individual
tasks
Understanding
each other
Problem
solving
Problem solving
Problem solving
Numeracy &
critical thinking
Analyze & solve
complex
Problems
Problem-Solving
Skills
Initiative &
Enterprising
Initiative &
Enterprising
Internship &
enterprise
Enterprise
Crafts and
Entrepreneurship
Resource
Management
Capabilities
















