
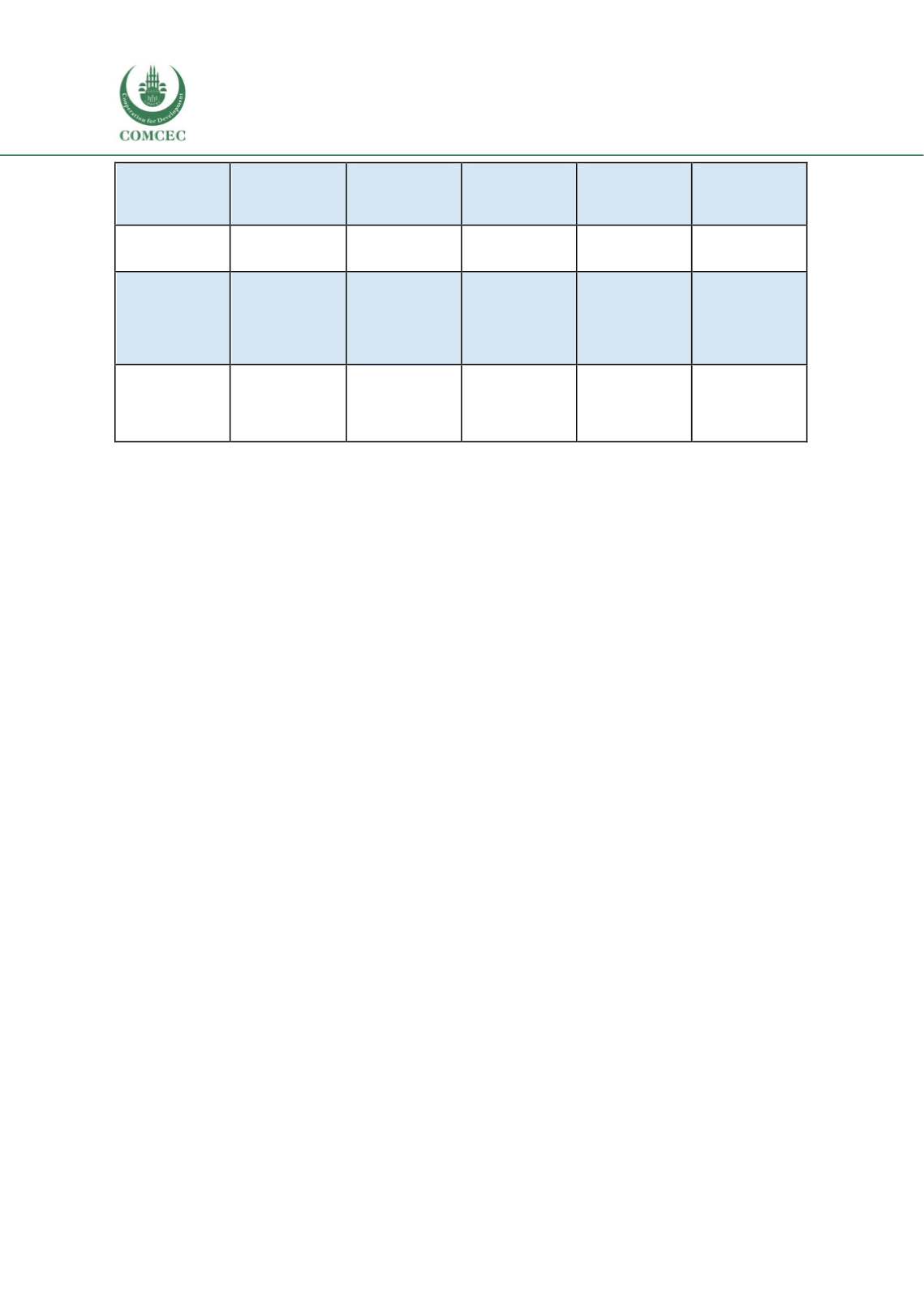
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
36
Planning &
organizing
Planning &
Organizing
Planning,
deciding,
realizing
Leadership &
decisionmaking
Build & apply
knowledge
Ability to
Understand
Organizational
structure
Self-
management
Self-management
& Competiveness
Controlling&
evaluation
Motivation &
discipline
Self
empowerment
and development
Self-
Development
Capability
Learning
Learning
Tasked based,
project based,
work-based,
action oriented,
content related
learning.
Student centered
learning
Learning
theories
Numeracy
Technology
Applying design,
numeracy and
technology
Master many
skills &
specialize in one.
Training
programs
It depend on
industries for a
particular
country
Information
technology,
logics, norms &
culture.
Technical
&interpersonal
Skills
1.9. Reasons of failing to improve skills development through VET
Due to defective formulation and implementation of VET strategies, the whole world has been
suffering from lack of skilled manpower. New technology, new forms of work places, rising
demand of quality products and curtailment of product life cycle lead us to a skill development
through vocational education and made a flexible workforce for the world (Attwell, 1999;
Gandhi & Zhou, 2010). There is a lack of vocational skills supply in the current labour market. If
we take TVET as a key tool for developing skilledworkforce then VET need to reform its policy,
curriculum, updatedwith new technology, increase the rate of enrolment in TVET and forming
job opportunities. There might be different reasons for which a country’s skill development
initiatives could be hampered. These could vary due to country’s economic and social aspects.
Developed countries like Australia, Canada, Japan and USA avowed “development of vocational
skills” and “promotion of lifelong learning” as core national strategy (Agbola & Lambert, 2010;
Coles & Leney, 2009; Drage, 2009; McGrath, 2012). A study (Newaz, Faruquee, & Farha, 2013;
Okolie & Yasin, 2017)) identifies six reasons of shortcomings for skill development:
1.
Awareness of TVET
2.
Opportunities of employment by TVET
3.
Social acceptance of TVET
4.
TVET policy and curriculum
5.
Program expenses
6.
Lack of funds
Other studies such as Beilmann and Espenberg (2016) and Leberman andShaw (2015) reported
reasons of identifying further on failing of skill development:
7.
Dropout rate
8.
Gender inequality
No specific study has been found in the literature that particularly focuses on current enrolment
rate of vocational education in all OICmember states. However, few reports have been published
that stated the enrolment rate of vocational education in the globe. From these reports, data
from few OIC countries are accumulated and presented at Table 1.9.
















