
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
32
technical skills, and
Transferable skills: Ability to apply present or academic skills to solve a new
situation. For examples, many studies reported that, employees are gaining skills via
VET sectors in the field of carpentry, masonry, electricity, plumbing, painting, and
roofing (Dougna, 2003).
Recently, many employees are looking for gaining skills in the area of technology and computer
literacy (computer-aided design, or CAD), and computer-aided management (CAM) due to
increase demand in this area (locally and nationally) (Sosale &Majgaard, 2016)
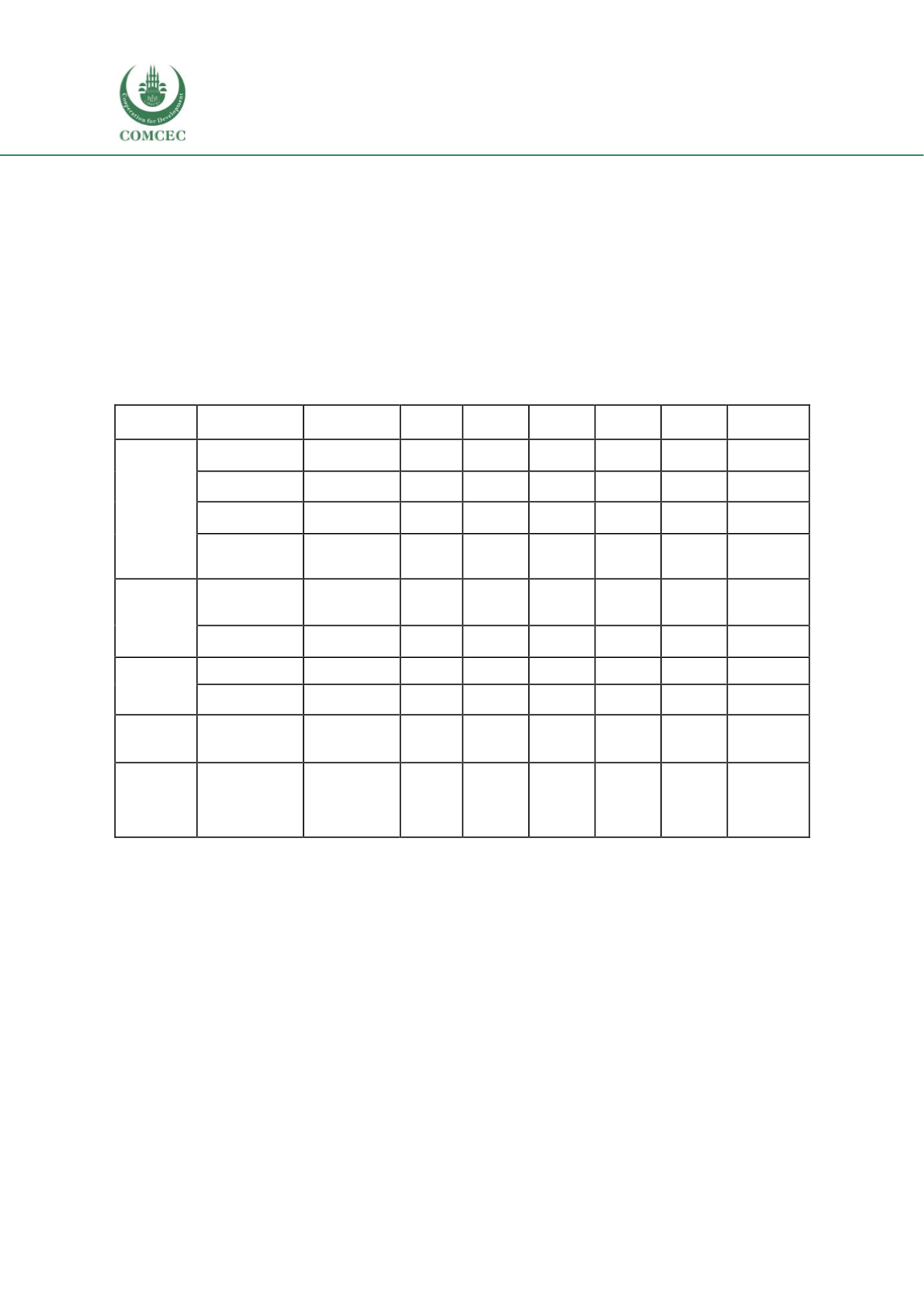
. The table below,
summaries the skills map in different trades of Cameroon.
Table 1.6: Skills in different areas in Cameroon
Constraints
Infrastructure
Wood
Ag/
Agribus
Cotton
Palmoil
Tourism Technology
Job-
relevant
skills
constraints
Insufficient
basic skills
X
X
Technical skills
mismatch
X
XXX
X
X
XXX
X
Behavioral
skills mismatch
Insufficient
entrepreneurial
skills
X
X
Lack of
labor
demand
Slow job-
growth
economy
X
X
X
X
Employer
discrimination
X
Job search
constraints
Job matching
X
X
Signaling
competencies
X
Firm start-
up
constraints
Lack of access
to financial or
social capital
XX
X
X
Social
constraints
on the
supply side
Excluded-
group
constraints
(ethnicity,
gendered)
X
X
(Source: Cunningham, Sanchez-Puerta, & Wuermli, 2010)
Table 1.8 above, illustrates clearly that, there is a significant gap between current skills and
labour markets in Cameroon. Similar as other African countries, TVET on Cameroon is
characterized by the poor linkage with the labour market.
1.8.3. Skill gap in Asia
Research was conducted in Asia, more particularly in South and Southeast Asia to identify
current skill gap in this region. The main skill gaps identified are listed in the Table 1. Jayaram
and Engmann (2017) identified two broad skill areas among the three South Asian countries
(India, and two OIC member states: Bangladesh and Pakistan) namely: (i) non-cognitive skills
such as communication, leadership, teamwork, honesty/ethics, and flexibility. (ii) skills linked
to the ability to learn. It may varies depending on contexts (location), for instance India (Delhi):
critical thinking and analytical skills; Pakistan (Lahore): conceptual understanding, India
(Bhopal): quest for knowledge.
















