
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
118
interested. Therefore, one of the way is to train these people at our institute X” (P1Ug)
5.
Vocational education is not unpopular, that is, it doesn’t have less social value.
Clarification of this finding could be obtained from the analysiswe had on the qualitative
data.
6.
There is a shortage of specialized teachers in the vocational institutes in Uganda .
7.
As Uganda is gender sensitive, female skilled workers have equal chances to get
employment as male skilled workers.
8.
It is undecided whether Uganda cannot send many of their skilled people to foreign
countries due to English or other language barriers. In case of English, Uganda does not
have any problem, since English is its official language, but in case of other languages,
such as German, Spanish, Uganda may still have difficulties.
9.
Uganda does not have adequate TVET institutions for skills training.
10.
Youths’ opinions have been taken into consideration while formulating policies for the
development of vocational education in Uganda.
11.
The graduates are not competent to meet industrial requirement .
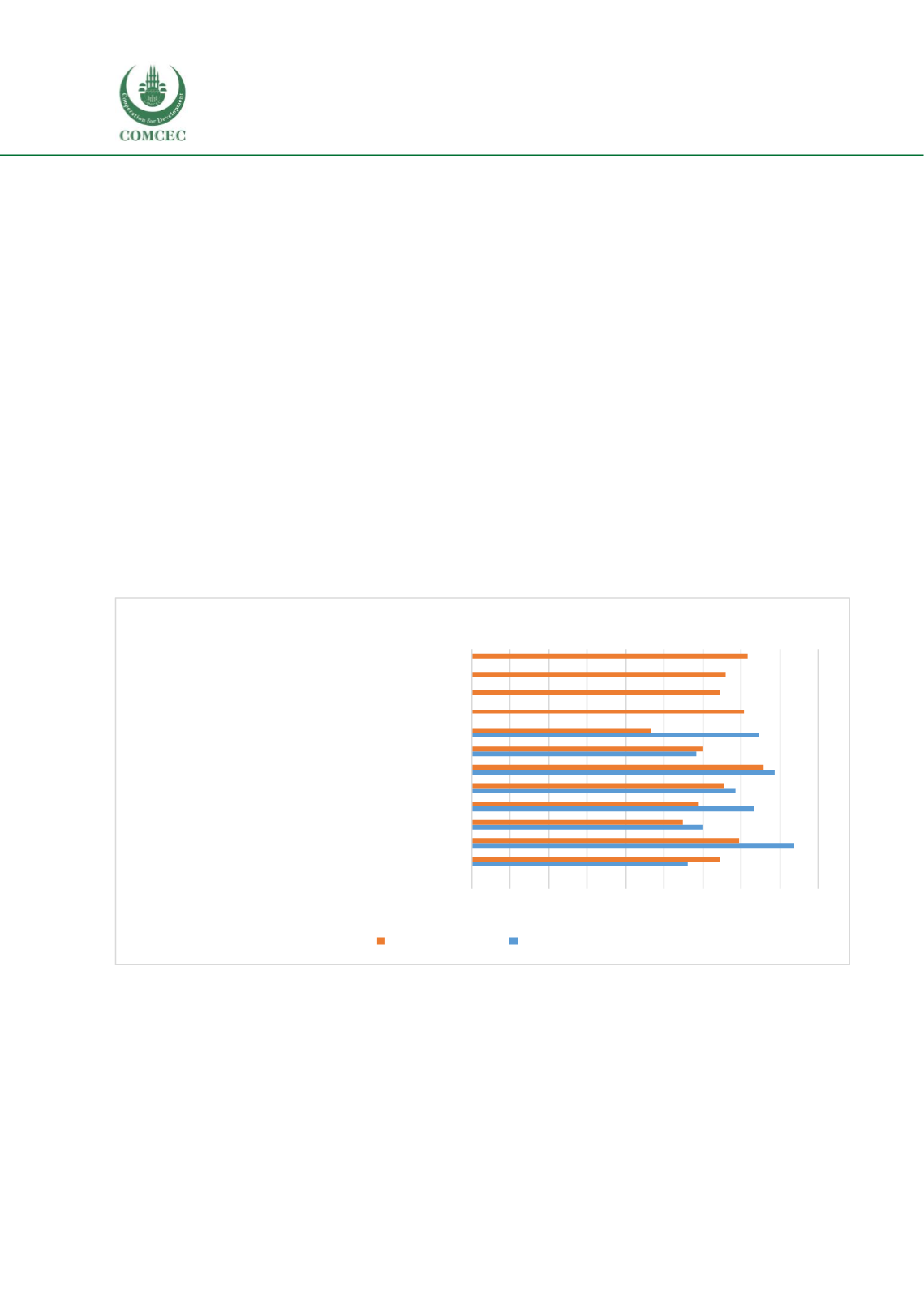
Figure 5.3: Challenges in Uganda’s TVET sectors
0,00 0,50 1,00 1,50 2,00 2,50 3,00 3,50 4,00 4,50
Uganda has necessary fund for TVET sectors
Have negative attitudes towards enrolling TVET sectors
Lesser women trained
Lack of long term plans for improving TVET sectors
Vocational education is less popular
Shortage of specialized teachers
High Female Skilled workers Unemployment
Language Barrier
It does not have adequate TVET institutions
Lack of competent instructors in TVET sectors
Youth opinions have not been taken
Graduates are not competent
Challenges in Uganda’s TVET sectors
X (Administrator)
X (Teachers)
















