
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
115
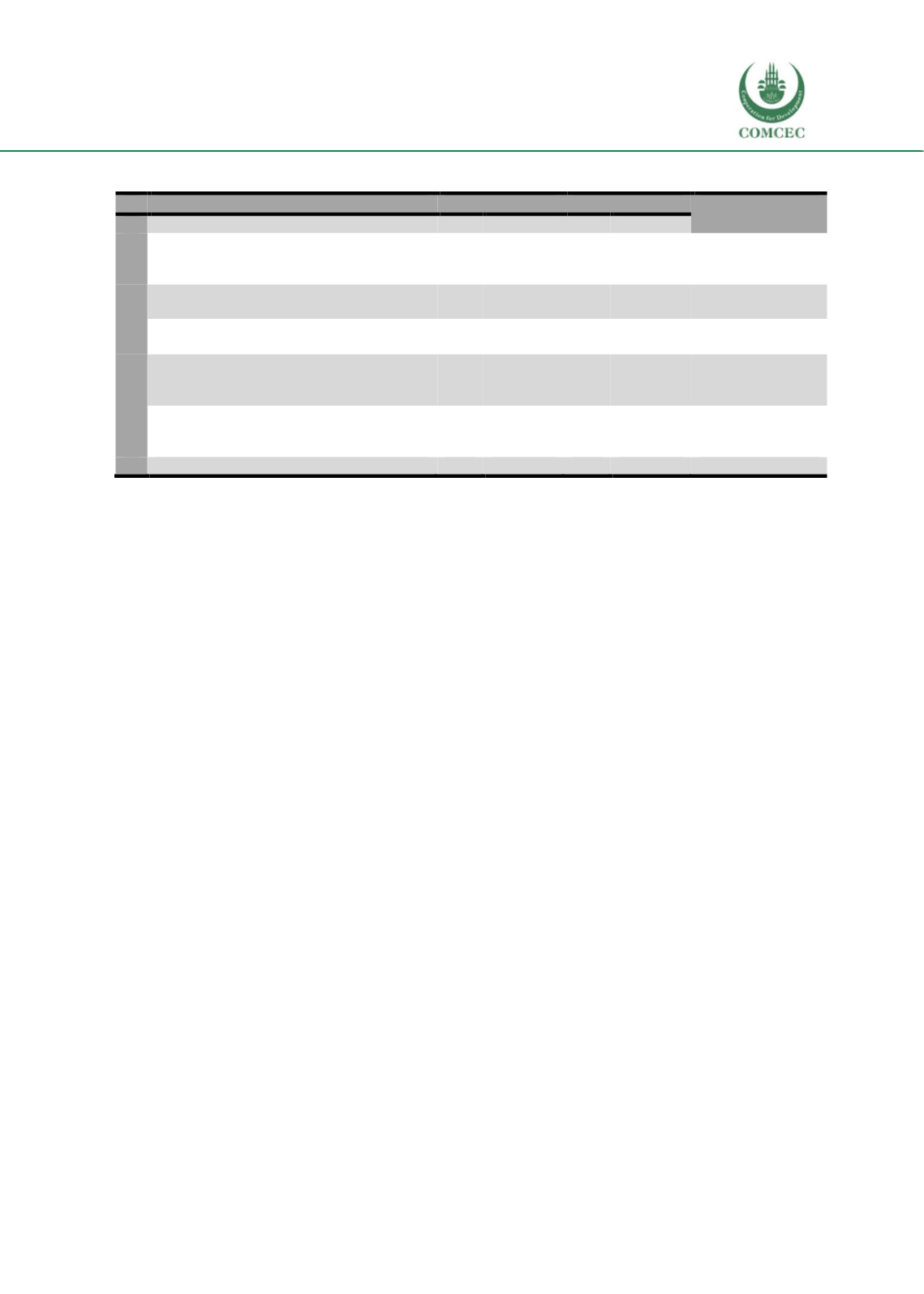
Table 5.6: Analysis (Success) in TVET sector of Uganda
S
Teacher
Administrator
Comments
Item
Xt
Result
Xa
Result
1
Integration of some basic skills training at
school level will provide the young
generation with necessary skills
4.40 4.40>3.5
3.56 3.56>3.5
Accepted
2
The TVET institutions focus more on skill
training than theoretical knowledge
3.99 3.99>3.5
3.16 3.16<3.5
Undecided
3
Training in vocational institutions is less
costly
2.09 2.09<3.5
2.11 2.11<3.5
Not Accepted
4
The instructors are competent to conduct
subjects which needed newknowledge and
skills
4.22 4.22>3.5
Accepted
5
The current skill trainings are updated
training
programs
which
produce
competent skilled workforce
4.19 4.19>3.5
Accepted
6
Skilled workers are not getting jobs
3.33 3.33<3.5
Not Accepted
From Table 5.6 and Figure 5.2, we conclude that Uganda has already achieved the following
successes:
1.
Integration of basic skills in school level provides young people with necessary skills to
get an occupation for a sustainable future.
2.
TVET institutions in Uganda focus more on skill training than theoretical knowledge. On
the basis of qualitative analysis, some interviewees explained that a bigger percentage
(those that are fully vocational) is focusing on practical aspect as compared to theory,
which is in support of teachers’ view:
“
In Uganda we have technical institutions and vocational institutions. In
vocational institutions seventy five(75%) percent of the training are hands on
and only while twenty five (25%) percent is theory.
” (P5Ug)
3.
Vocational training is not free in Uganda to attract all kinds of people.
4.
The instructors in TVET sectors are competent to conduct sessions that require new
knowledge and skills
5.
Current skill trainings in Uganda TVET sectors offer updated training programs which
produce competent skilled workforce
6.
Skilled workers in Uganda are easily securing jobs due to the skilled acquired.
















