Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
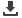
50
Country
Population Covered
(3G) (
%
)
Connections
Penetration (
%
)
Demand Gap (
%
)
Central America
87.96
43.09
44.87
Southern Asia
57.53
10.82
46.71
Eastern Africa
62.22
12.54
49.68
(*) A higher number of connections than coverage could indicate two lines per individual in some cases
Sources: International Telecommunications Union; Telecom Advisory Services analysis
As expected, in the case of mobile broadband, the prorated demand gap for developed regions
(OECD countries) is fairly small. This is explained by the reduced gap in Australasia, East Asia,
North America, and Northern Europe. On the other hand, most of the emerging world exhibits
a mobile broadband demand gap averaging 33%, meaning that a third of the population served
by mobile broadband networks does not acquire the service.
The reduction of the demand gap requires targeting the reasons for non-adoption, even after
broadband networks have been deployed. As mentioned in chapter II, the residential
broadband demand gap is the result of three obstacles:
•
Limited affordability: certain portions of the population either cannot acquire a
device or purchase the subscription needed to access the Internet
•
Lack of digital literacy
•
Lack of relevance or interest: the value proposition of applications, services, and
content does not fulfill a need of the adopting population
A compilation of research on adoption barriers indicates that affordability remains a
preeminent variable in explaining the non-adoption of broadband, particularly in emerging
countries. In the developed world, approximately 20% of non-adopters have responded in
surveys that affordability is one of the principal reasons for not acquiring broadband. In the
developing world, affordability has been cited by an average of 30% (see table 16).
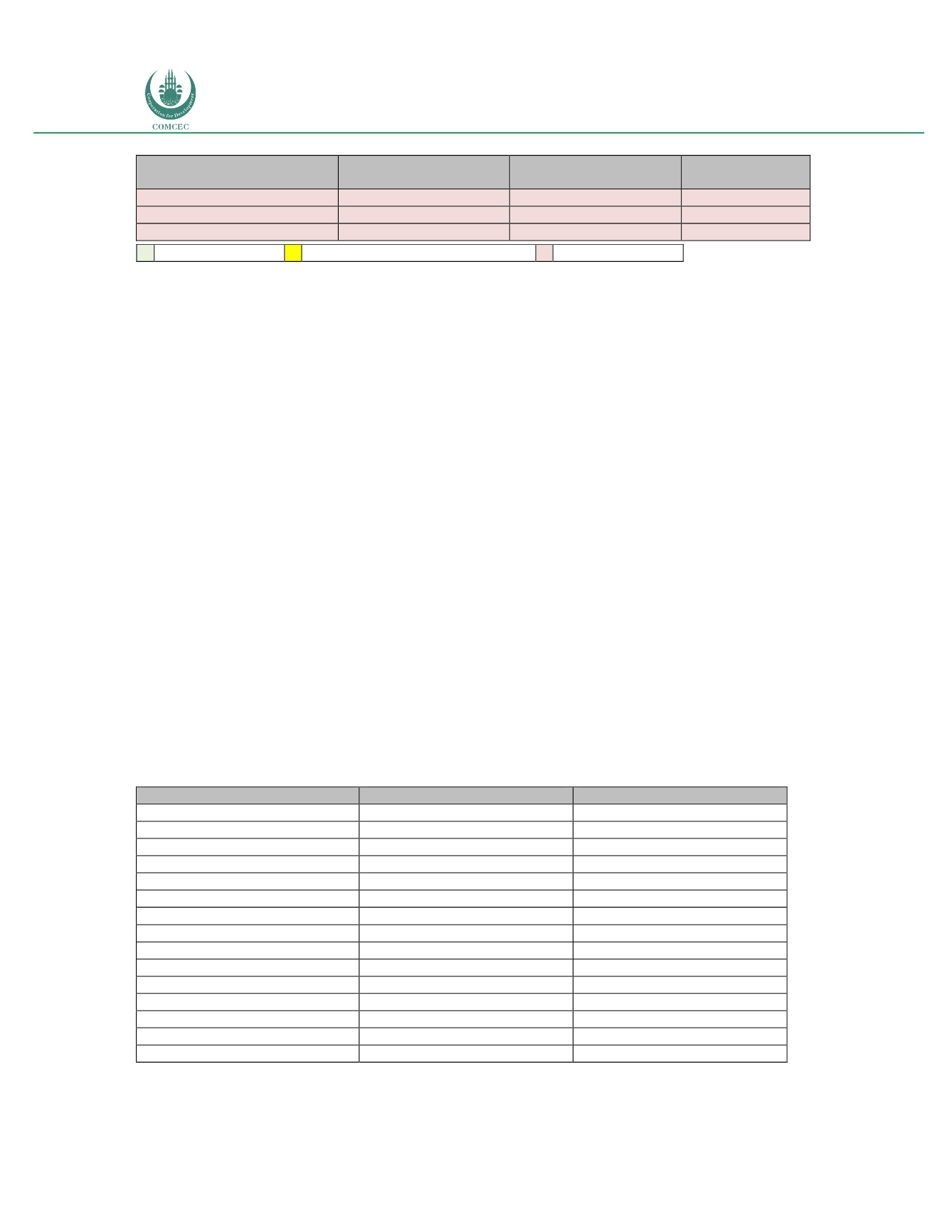
Table 16: Percentage of households mentioning afford bility as a reason for not purchasing
broadband
Country
Percentage
Source
Costa Rica
60
MINAET (2011)
Mexico
43
INEGI (2015)
Colombia
40
MITIC (2010)
Brazil
37
CGI (2015)
Australia
26
AGIMO (2009)
United States
24
NTIA (2011)
Portugal
20
ITU (2013)
Argentina
18
INDEC (2015)
United Kingdom
16
OFCOM (2011)
Puerto Rico
16
PRBT (2012)
Hungary
15
ITU (2013)
Chile
13
Subtel (2015)
Estonia
13
ITU (2013)
Spain
11
ITU (2013)
France
8
ITU (2013)
Source: Compiled by Telecom Advisory Services
Demand gap <10% Demand gap between 10% and 20% Demand gap >20%