Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
11
II.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK REGARDING BROADBAND
PENETRATION
The development of policies aimed at increasing broadband penetration require outlining a
conceptual framework that measures the payback in terms of social and economic returns and
identifies the barriers that prevent broadband from achieving universal adoption. The
following chapter begins by reviewing the research evidence regarding broadband social and
economic contribution, emphasizing the impact on economic growth and job creation (section
II.1). Its purpose is to highlight why increasing broadband adoption is critical to fostering
economic development. Having demonstrated broadband economic impact, evidence is
presented to show the difference in economic contribution for developed and emerging
countries (section II.2). The third component of broadband impact conceptual framework has
to do with its technological underpinnings, reviewed in section II.3. Finally, the main
challenges regarding broadband supply and demand are presented in section II.4. The purpose
of the final section is to provide an understanding of the key barriers that prevent countries
from achieving high broadband adoption and, therefore, harnessing its full economic potential.
II.1. Impact of broadband on economic and social development
Broadband contributes to economic growth initially through a series of effects similar to those
generated by the deployment of any type of infrastructure. Beyond deployment effects,
broadband, as a general purpose technology, generates externalities, ranging from GDP growth
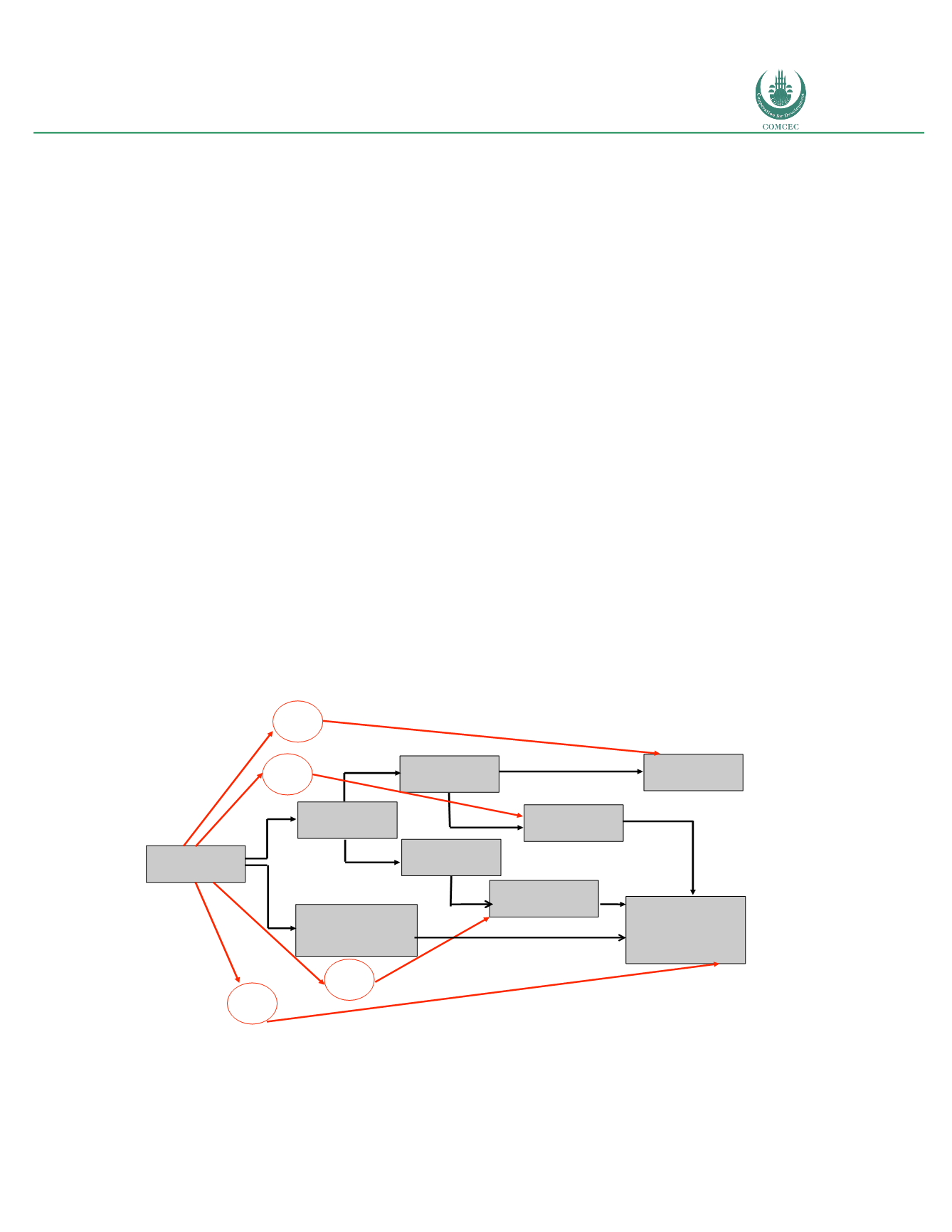
to job creation and enhancement of consumer surplus (see figure 2).
Figure 2: Social and economic contribution of broadband
Source: Katz (2012)
Figure 2 depicts four distinct social and economic contributions of broadband. Effect 1 refers
to the impact on GDP and job creation resulting from investing in the deployment of
Broadband
Deployment
Direct
benefits
Investment in
Infrastructure
deployment
Residential
penetration
Consumer
surplus
Household
income
Enterprise
penetration
Total Factor
Productivity
Contribution to
employment
and GDP
growth
I
III
II
IV