Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
8
I.
INTRODUCTION
Broadband is defined as a high capacity data transmission technology that allows a large
number of messages and traffic types (video, data, and voice) to be communicated
simultaneously. The term broadband is also used to define high-speed access to the Internet
that is always on and faster than traditional dial-up connectivity. Along these lines, broadband
refers to a variety of technologies that can be broadly categorized in terms of fixed (including
copper-based Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL), cable modem, and fiber optics),
fixed wireless (such as WiMAX), and mobile (which includes 3G, 4G and the upcoming 5G
technologies).
Ever since its introduction in the early 1990s, broadband technology has undergone a
dramatic diffusion around the world, including within the countries of the Organization of
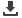
Islamic Cooperation (OIC). As of the end of 2015, 14.95% of households in the OIC Member
Countries are connected to broadband technology, while 29.41% of individuals have mobile
broadband connectivity. These statistics are even more impressive when considering that
broadband did not start its diffusion process 2001 in the case of fixed, and 2007 for mobile
(see figure1).
Figure 1: OIC Member Countries: Diffusion of fixed and mobile broadband
Source: International Telecommunications Union; Telecom Advisory Services analysis
It is in this context of massive adoption that policy-makers and researchers have been studying
the whole range of social and economic effects related to broadband, as well as developing
conceptual frameworks that help define policies aimed at maximizing its penetration and
measuring its contribution. This report focuses precisely on defining such a framework and
developing a set of recommendations to enhancing broadband penetration within the OIC
Member Countries. It is organized into six chapters. Chapter II develops a conceptual
framework to help the development of policy recommendations aimed at enhancing
broadband penetration. It explores five key issues:
0.02$ 0.08$ 0.2$ 0.46$ 1.06$ 1.84$
3.33$
4.52$
5.96$
7.37$
8.87$
10.5$
12.02$
13.77$
14.95$
0$ 0.01$ 0.05$
1.17$ 5.93$
8.76$
11.06$
15.42$
22.66$
29.41$
0$
5$
10$
15$
20$
25$
30$
35$
2000$
2002$
2004$
2006$
2008$
2010$
2012$
2014$
Fixed Broadband (% households)
Mobile Broadband (% population)