Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
13
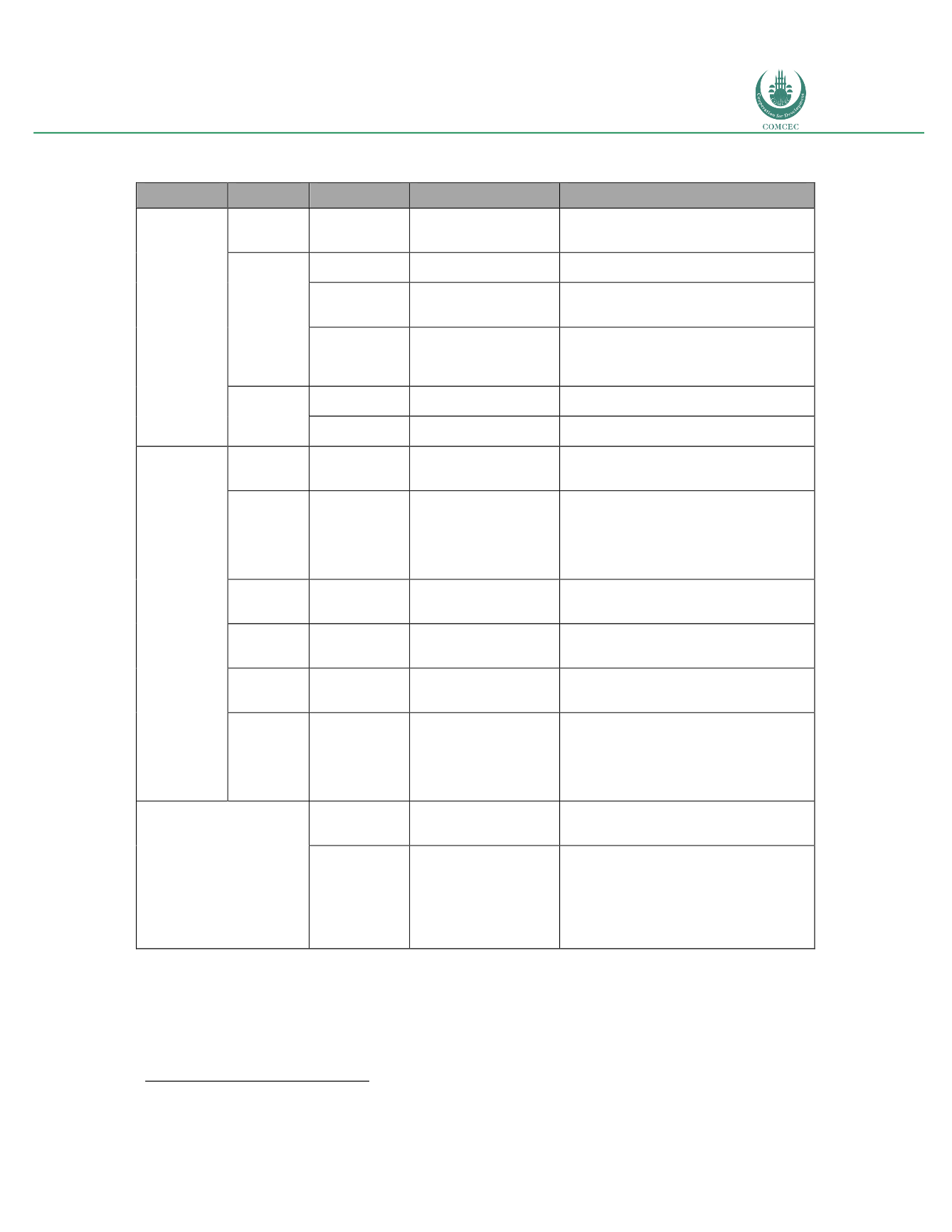
Table 2: Research results of fixed broadband Impact on GDP growth
Country
Study
Data
Effect
High Income
Economies
All
countries
Qiang & Rosotto (2009) 1980-2002 for 66 high
income countries
10 % broadband penetration yielded an
additional 1.21 percentage points of GDP
growth
OECD
Czernich et al.
(2009)
25 OECD countries
between 1996 and 2007 The adoption of broadband raises per-capita
GDP growth by 1.9-2.5 percentage points
Koutroumpis
(2009)
2002-2007 for 22 OECD
countries
An increase in broadband penetration of
10% yields 0.25% increase in economic
growth
Bojnec & Ferto
(2012)
Dynamic Panel modeling
of 34 OECD countries
broadband data between
1998 and 2009
Positive relationship of broadband on GDP
growth
United
States
Crandall, Lehr
& Litan (2007) 48 States of US for the
period 2003-2005
Not statistically significant results
Thompson &
Garbacz (2009) 46 US States during the
period 2001-2005
A 10% increase in broadband penetration is
associated with 3.6% increase in efficiency
Low and
Middle
income
economies
All
countries
Qiang & Rosotto (2009) 1980-2002 for 120
countries (low and
middle income)
10 % broadband penetration yielded an
additional 1.38 in economic growth
China
Kumar et al.
(2016)
Autoregressive
Distributive Lag for
Chinese Internet,
broadband, mobile and
export data between
1977-2013
All the indicators of ICT have a positive and
statistically significant elasticity coefficient
ranging from 0.010 to 0.080
Jordan
Katz & Callorda
(2016)
Simultaneous equations
of Jordan data between
2006 and 2014
0.73% of GDP growth for every 10 %
increase of mobile penetration
Morocco
Katz & Callorda
(2016)
Simultaneous equations
of Morocco data
between 2006 and 2014 0.84% of GDP growth for every 10 %
increase of mobile penetration
Panama
Katz & Koutroumpis
(2012)
Simultaneous equations
of Tunisia data between
2000 and 2010
0.45% of GDP growth for every 10 %
increase of mobile penetration
Africa
Chavula (2013) Cross-sectional
endogenous model of
fixed lines, internet and
mobile lines for 49
African countries
between 1990 and 2007
1% increase leads to 0.21% increase in GDP
per capita
World
Choi & Yi
(2009)
200 countries between
1991-2000 for Internet
penetration
Internet has a positive effect on GDP growth
Vu (2011)
102 countries internet
data up to 1995
For the average country, the marginal effect
of the penetration of internet users was
larger than that of mobile phones, which in
turn is larger than that of personal
computers. The marginal effect of ICT
penetration, however, lessens as the
penetration increases.
Source: compiled by Telecom Advisory Services
As table 2 indicates, most studies concluded that broadband penetration has an impact on GDP
growth. However, the magnitude of the contribution appeared to vary widely, from 0.25 to
1.38 percent for every increase in 10 % of fixed broadband penetration
3
.
3
Or .36% if the standard assumption that 1% increase in productivity or efficiency results in 1% increase in GDP is made.