
Risk Management in Transport PPP Projects
In the Islamic Countries
107
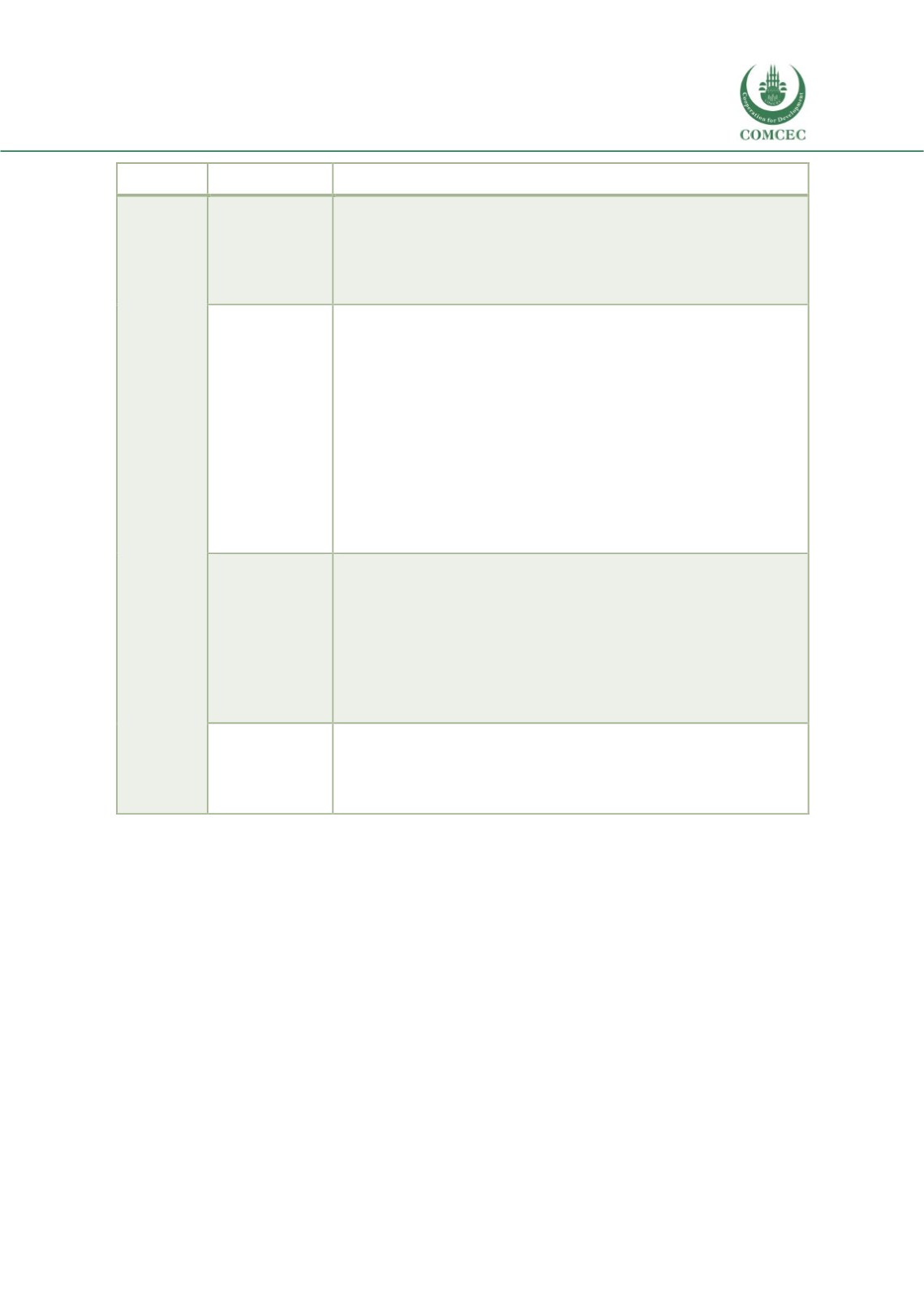
Risk type
Risk category
Usual allocation of risks (public/private/shared)
Project
risks
Financial credit
risks
Financial credit risks are retained by the
private sector
, who is also
responsible for defining the project financing structure of the PPP
initiative and for timely reaching the financial close. Delays in reaching
the financial close and commercial close may result in early termination
of the contract unless these are attributable to the public sector.
Design,
construction and
operation risks
Design, construction and operation risks are generally borne by the
private sector.
The public part may in some cases retain part of the
risks of the construction phase, when this may be needed to ensure the
bankability of the projects. This may be the case for instance in urban
mass transit, where given the high capital investment it is more
convenient that the infrastructure costs and related risks are borne by
the public sector, and then the infrastructure is transferred to the private
party for operation. Other exceptions are represented by the risk of
damage to the environment, which are generally shared by the private
and the public sectors. Second, land purchase and site risks are generally
borne by the public sector, which is best-placed to select and acquire
land.
Financial
sustainability
risks
Financial sustainability risks are generally borne by the
private sector
.
This is the general rule for most sectors (and in particular for brownfield
projects) where revenue are predictable with a sufficient degree of
reliability; in case of projects where revenue streams are not easily
predictable (i.e. road greenfield projects), in the past the state has
provided financial guarantees, sharing the risk with the private partner.
Service Delivery Requirements (SDR) are also generally included in BOT
with clearly defined penalties.
Other risks
(force majeure
and early
termination)
Force majeure and early termination risks are
shared
. The ability of the
private partner to bear force majeure risk is limited, and the public
sector typically bears the risk after a certain period of time or level of
cost.
Source: Authors.
According to the legal provisions, any
PPP contract
must contain, at a minimum, clauses
concerning:
The object, the perimeter of the activities contracted and their description;
The terms of the provision of services and, if necessary, the extent of the exclusivity of the
rights conferred by the contract;
The legal regime of property and the terms of state occupation, including on the actual
rights conferred, if any, to the operator, in accordance with applicable legislation;
The rights and obligations of the parties, including confidential information;
The duration of the contract, the terms of its extension, as well as the rights and obligations
of the parties when it expires;
















