Planning of National Transport Infrastructure
In the Islamic Countries
28
In the Netherlands, United Kingdom and France, procedural steps in NTI projects have legal
foundation and are concluded with official ministerial decisions. In Denmark and Austria the
national parliament provides legitimacy for NTI projects. This clearly communicates a strong
political commitment and backing.
Many other EU Member states, like Bulgaria, Germany, Italy Romania and Spain, closely follow
EU guidelines that provide a detailed methodology and procedure. This is directly related to the
TEN-T network, through which EU Member States mutually connect and extend their NTI
networks.
In most OECD countries the Ministry of Finance (MoF) plays a decisive role in NTI planning by
providing mandatory instructions regarding discount rate, and planning horizon, to be applied
in project appraisal. Examples of these legally based instructions are the Green Book (United
Kingdom, 2018, the formal version is the online version)
9
in the United Kingdom and CPB (2013)
and Commission on Discount Rate (Werkgroep Disconotvoet, Netherlands, 2015, the formal
version is the online version)
10
in The Netherlands, following MoF guidelines.
Many IFIs, like the ADB, World Bank and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank that provide
soft
finance
, have very detailed formal procedures for
project approval
. Equally most OECD countries
have formal description of project appraisal (guidelines) methods. NTI planning and project
appraisal are strongly interlinked, as NTI plans consist of projects, and projects form an NTI
plan. The guidelines not only include procedures and methodology, but often prescribe
parameters and ways to price project effects that are not market-price (see also sectio
n 2.6).
Apart from national and international public finance, there are
private sources of finance and
user-based finance
. These tend to play an increasing role in financing of NTI (OECD, 2014 and
OECD, 2015).
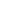
Private finance via public–private partnerships (PPP) is extensively used in Australia, Canada,
India, the Netherlands, and the UK. PPP is a way to relieve annual state budgets from sudden
financial shocks and to manage risk. PPP is a form of procurement and contracting and has
various formulas: Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT), Design-Build-Finance-Operate (DBFO), or
Build-Own-Operate (BOO) (European Commission, 2003). The figure below illustrates the
various PPP constellations.
9
Available from
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-green-book-appraisal-and-evaluation-in-central- governent10
Available fro
m https://www.rwseconomie.nl/discontovoet