Sustainable Destination Management
Strategies in the OIC Member Countries
118
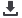
Figure 20: Funding Sources
Source: DinarStandard Analysis
Both public and private domestic sources are used to fund sustainable tourism initiatives in OIC
and leading non-OIC countries. However, it is worth noting that the ability of the private sector
to finance sustainability initiatives is hindered in many OIC countries by the shortage of
resources of tourismbusinesses and their inability to get loans due to either absence of collateral
or scarcity of financial instruments to support sustainability initiatives. In terms of foreign
funding, both OIC and Non-OIC countries have received international funding, however, while
many OIC countries have received bilateral funding, leading non-OIC countries mainly received
funding from regional organizations.
Table 15: Access to Funding – Select Leading Non-OIC Countries
386
Domestic
sources
Foreign
sources
Project Funding Example
Denmark
Public
Private
Regional
International
The European Regional Development Fund provided
funding for the “Baltic Sea Tourism Center - Sustainable
development structures for active tourism” setting up an
organization in the Baltic Region (covering Denmark,
Sweden, Poland, Germany, and Lithuania) taskedwith the
protection of coastline, parks and other natural and
cultural resources.
Sweden
Public
Private
Regional
International
New
Zealand
Public
Private
Regional
International
The UNWTO New Zealand's first Tourism Monitoring
Observatory as part of its International Network of
Sustainable Tourism Observatories to monitor the
Economic, Environmental and Social impact of
Tourism.
387
386
All information provided is based on case study findings unless otherwise mentioned.
387
UNWTO Website.