
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
59
NZCS is targeting passengers for risk on a pre-arrival basis. The Automated Targeting System –
Global assesses passenger’s information against established risk profiles. The system is
automatically sending the information to the passengers that match a risk profile, and an analyst
reviews the information. The analyst is deciding whether an alert should be inserted into
CusMod system.
Up until 1981, the risk management was based on random selectivity,
“
collective memory
”
and
intuition of the customs officers. The CASPER system managed alerts on high-risk concealment
based on HS Code
.
Almost 95% of shipments were physically examined with the non-intrusive
inspection; the remaining 5% of shipments that were not examined was for the industrial
purpose (machinery, components, etc.). The feedback from the customs control was paper-
based, and analysis of the feedback was difficult. The CusMod CDPS is supporting the risk
selectivity. The risk identification/analysis is conducted outside of the CusMod system. The
CusMod is still operational until the new integrated system JBMS is made fully operational.
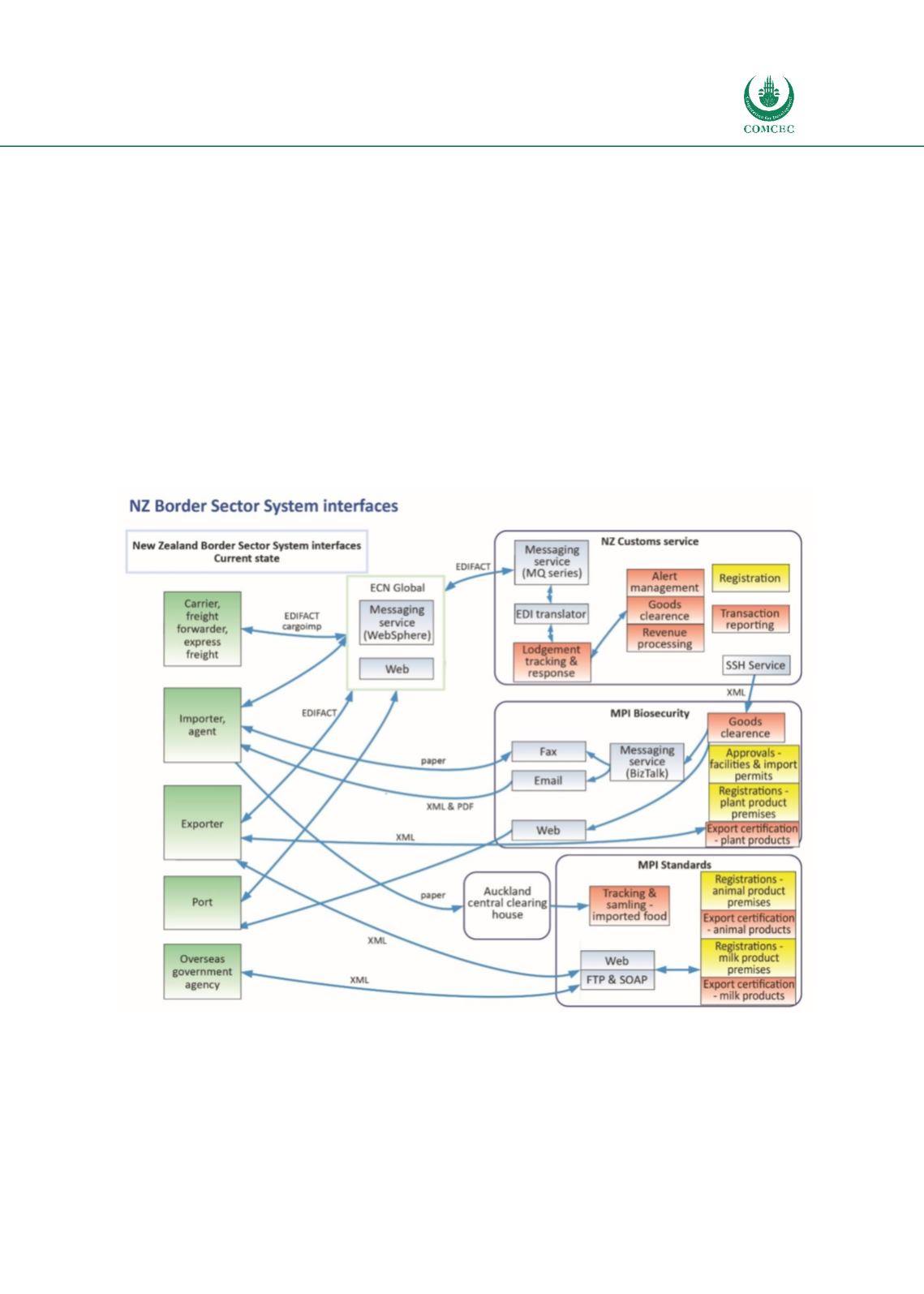
Figure 18presents the New Zealand Customs System Interfaces.
Figure 18: New Zealand Customs System Interfaces
Source: New Zealand Customs website
3.2.2.7
NZCS Post Clearance Audit
The NZCS is one of the most advanced CA worldwide in the application of PCA. The PCA process
contains following steps:
















