Single Window Systems
In the OIC Member States
29
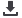
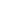
Figure 11: Single Window IT Data Architecture Model
Source: Authors’ own construction
A Single Window common data repository provides a more complete view of business
operations and deeper insight into critical business processes. It also enables additional
services, such as business intelligence and data mining, and therewith allows for integrated risk
management (IRM). It also makes integration of future change requests at the level of
application and services simpler as these changes are implemented in one location on the level
of the common data model.
2.1.8.
Single Window Interoperability
Interconnectivity and interoperability, meaning the ability to exchange of data and information
across systems, are now becoming important aspects of Single Windows. Recent Single Window
visions such as the WCO Single Window perspective clearly stress the fact that Single Windows
operate in an environment made up of multiple functional IT systems and only jointly have the
ability to deliver trade facilitation services
27
. To better respond to complex regulatory
challenges and to improve the delivery of services to traders, a Single Window has to embed
system-to-system connectivity or services. This enables Single Windows to provide to agencies
collaborative, networked and interconnected workflows and business processes.
27
Jonathan Koh Tat Tsen, Single Windows and Supply Chains in the Next Decade. Ten years of single window
implementation: Lessons learned for the future. Discussion paper (2011) under
https://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/trade/Trade_Facilitation_Forum/BkgrdDocs/TenYearsSingleWindow.pdf(Accessed January 2017)