FACILITATING INTRA-OIC TRADE:
Improving the Efficiency of the Customs Procedures in the OIC Member States
68
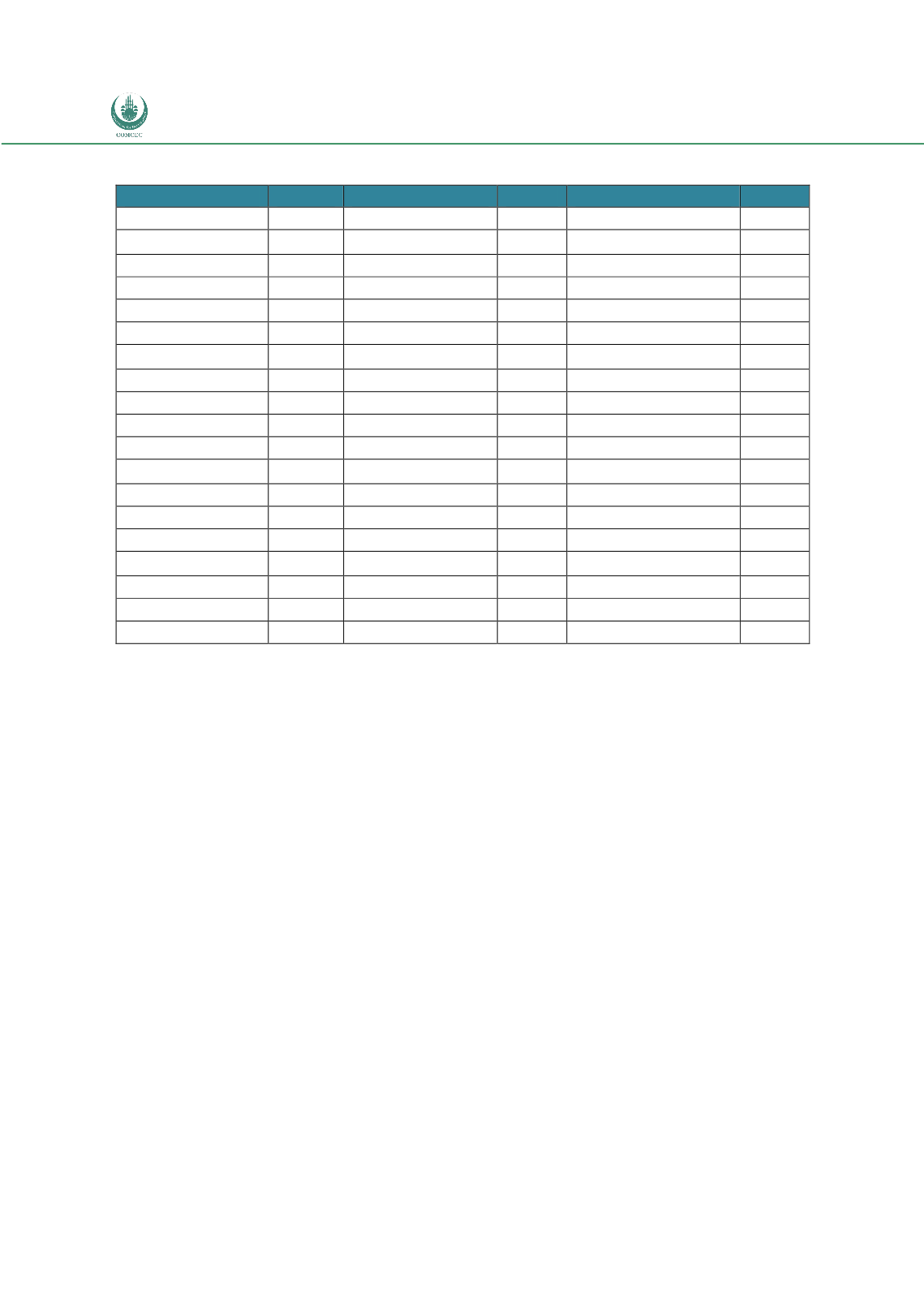
Table 13: Status of Member States in Using Risk-based Inspections
Country
Status Country
Status Country
Status
Afghanistan
Guyana
Pakistan
Albania
Indonesia
Palestine
Algeria
Iran, Islamic Rep.
Qatar
Azerbaijan
Iraq
Saudi Arabia
Bahrain
Jordan
Senegal
Bangladesh
Kazakhstan
Sierra Leone
Benin
Kuwait
Somalia
n.a.
Brunei Darussalam
Kyrgyz Republic
Sudan
Burkina Faso
Lebanon
Suriname
Cameroon
Libya
n.a.
Syrian Arab Republic
Chad
Malaysia
Tajikistan
Comoros
Maldives
Togo
Cote d'Ivoire
Mali
Tunisia
Djibouti
Mauritania
Turkey
Egypt, Arab Rep.
Morocco
Turkmenistan
n.a.
Gabon
Mozambique
Uganda
Gambia, The
Niger
United Arab Emirates
Guinea
n.a.
Nigeria
Uzbekistan
Guinea-Bissau
Oman
Yemen, Rep.
Note: (
): Using,, (
): Not Using (n.a.): Information not available
Source: Doing Business Report 2014
The criteria for the risk management are determined by the customs administrations.
Most of the Customs Administrations develop their risk management techniques
according to the importer, origin of the country, product category etc. However, it is
worth noting that, the Customs Administrations shall establish a dedicated risk
management department or directorate for implementing the risk management system
successfully. Also, the staff of the relevant department shall be trained on the risk
management system. Moreover, international and inter-agency cooperation is also
crucial for making the system stronger.
Determining the risk situation is also a major issue. The experiences show that, the red
channel, which requires physical examination, is still high in the Member States using
the system. For example, according to the WTO Country Policy Review, goods
channeled to red line were 34 percent in Uganda in 2012, which is relatively high
compared to other countries.
Some of the Member States including Bahrain, Brunei, Kyrgyz Republic, Malaysia,
Morocco, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Tunisia, Turkey and UAE are also using
IT based risk management systems. These countries are categorizing the goods
according to the risk, based on their assumptions.