FACILITATING INTRA-OIC TRADE:
Improving the Efficiency of the Customs Procedures in the OIC Member States
71
The use of ITC and automation has many benefits such as reducing the cost and time for
customs clearance, preventing corruption and increasing revenue. For example
according to the World Bank (2011), as a result of the reform program and installation
of ASYCUDA World, the revenue of Afghan Customs increased 1392 percent during
2003-2010 period, where increase in trade was 313 percent during the same period.
Most of the remaining Member States, which do not install the ASYCUDA have
developed ICT and automation in their customs services. However, ICT use in
submission and processing of the declarations is only available in some Member States.
According to Doing Business Report 2014, approximately 82 percent of the non-OIC
developing countries allow electronic submission and processing of customs
declarations. However, within the OIC, 35 countries, representing 61 percent of the total
Member States, are providing this opportunity. Table 14 shows the status of the
Member States in allowing electronic submission and processing of the declarations.
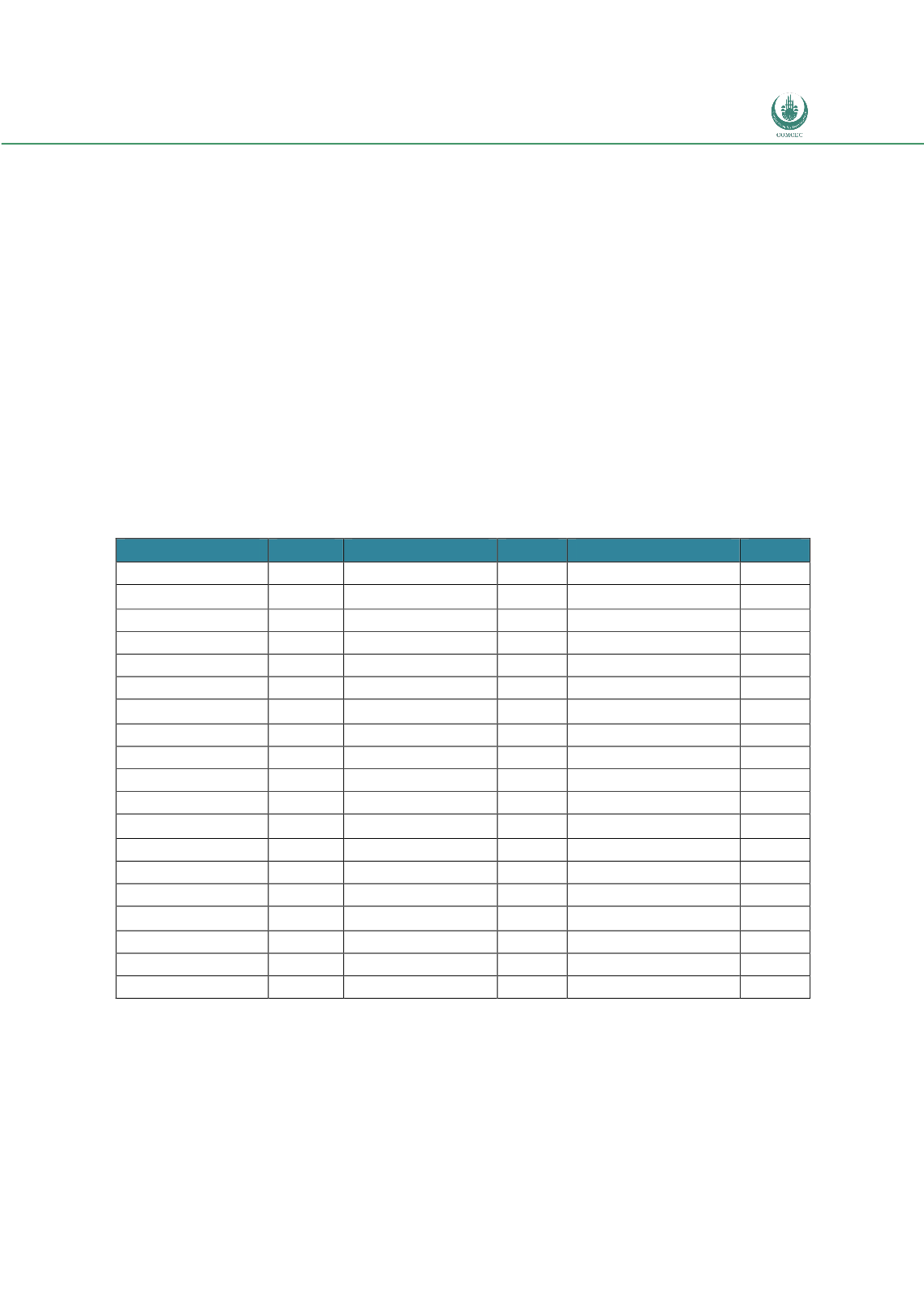
Table 14: Status of OIC Member States in Allowing Electronic Submission and Processing
of the Declarations
Country
Status Country
Status Country
Status
Afghanistan
Guyana
Pakistan
Albania
Indonesia
Palestine
Algeria
Iran, Islamic Rep.
Qatar
Azerbaijan
Iraq
Saudi Arabia
Bahrain
Jordan
Senegal
Bangladesh
Kazakhstan
Sierra Leone
Benin
Kuwait
Somalia
n.a.
Brunei Darussalam
Kyrgyz Republic
Sudan
Burkina Faso
Lebanon
Suriname
Cameroon
Libya
Syrian Arab Republic
Chad
Malaysia
Tajikistan
Comoros
Maldives
Togo
Cote d'Ivoire
Mali
Tunisia
Djibouti
Mauritania
Turkey
Egypt, Arab Rep.
Morocco
Turkmenistan
n.a.
Gabon
Mozambique
Uganda
Gambia, The
Niger
United Arab Emirates
Guinea
Nigeria
Uzbekistan
Guinea-Bissau
Oman
Yemen, Rep.
Note: (
): Allowing (
): Not Allowing (n.a.): Information not available
Source: Doing Business Report 2014
The ICT systems used by the Member States have various features to improve customs
clearing process. The table below illustrates the features of the systems used by some
of the Member States.