FACILITATING INTRA-OIC TRADE:
Improving the Efficiency of the Customs Procedures in the OIC Member States
57
indicate that the cost of implementing such measures vary across countries. The
coverage of such measures and the existing situation before implementing the measures
may be an important factor leading to such differences.
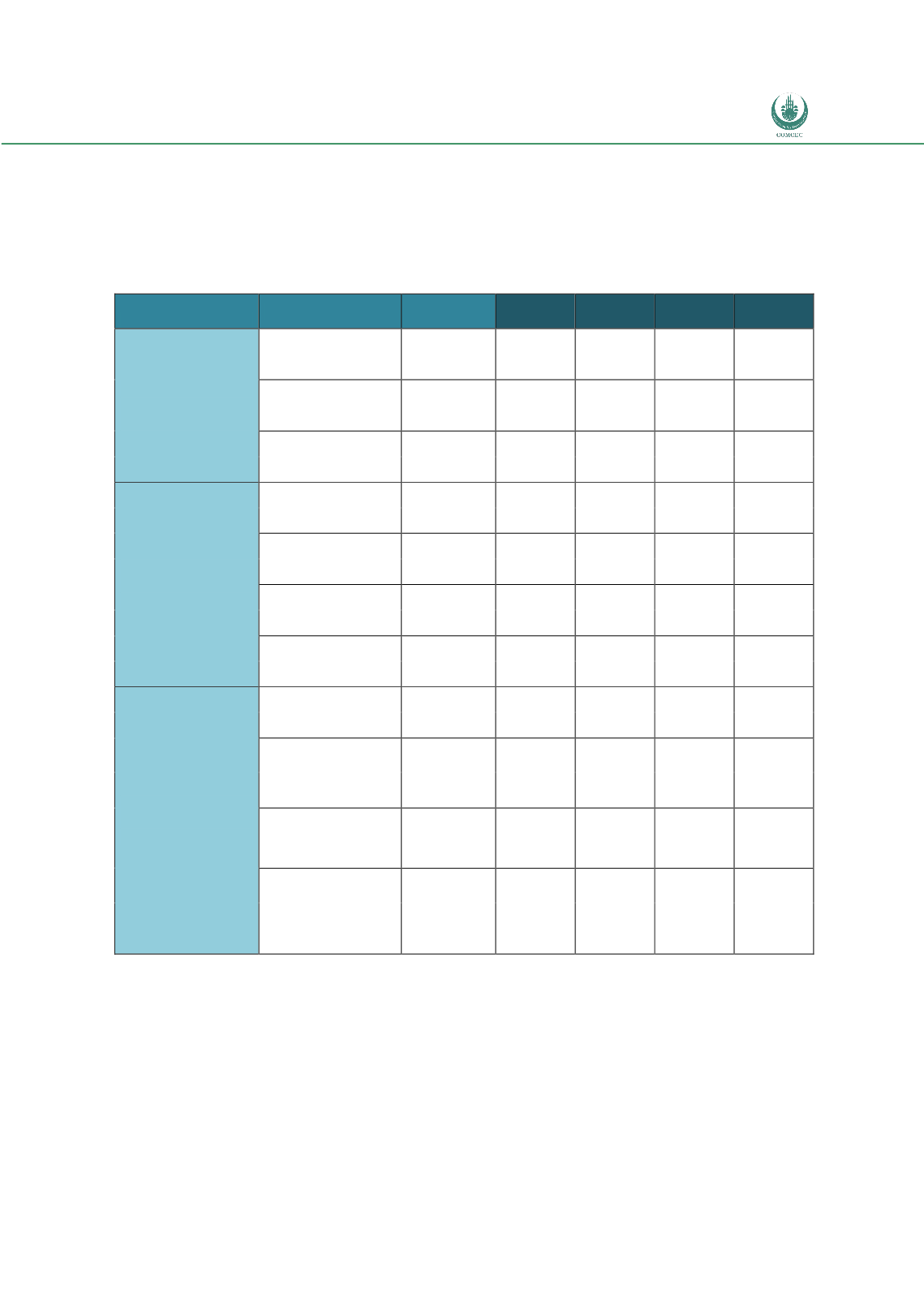
Table 9: Financial Cost of Selected Trade Facilitation Measures in Some Countries (in
Euros)
Measure
Action
Burkina
Faso
Colombia
Kenya
Mongolia
Transparency and
Predictability
Measure
Internet publication
inception 18800
50000
238870
operation
24345
Enquiry points
inception 48500
120000
43980
operation
41680
Advance rulings
inception 30000
76973
25000
20915
operation
657632
Procedural
Simplification and
Streamlining
Risk Management
inception 60000
771300
operation
250000
231745
Pre-arrival processing
inception 45000
1000000
290785
Post Clearance audits
inception 14000
400000
327785
operation
170880
Authorized Economic
Operators
inception 5500
1848145
120000
693920
operation
481099
32170
Cooperation and
Coordination between
Border Agencies
Single Window
inception 3049000
4100000
350000
17016345
operation
32615
Co-ordinated
documentary and
physical controls
inception
1025000
Development of
shared facilities with
neighbors
inception
59645
Allignment of
working
hours/procedures with
neighbors
inception
4390
Note: Operational costs are expressed on a yearly basis
Source: Data and information from Moise (2013)
There are several types of sources for financing the customs reform programs. The
government budget is the first option. The governments shall determine the customs
reform as one of its priorities. Because modernization of the customs will not only
facilitate trade but also increase the customs revenues.