Reviewing Agricultural Trade Policies
To Promote Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
51
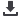
Table 3. 7 Measures Affecting Production and Trade (according to FAPDA Classification)
Consumer oriented
policies
Producer oriented
policies
Trade oriented
policies
Egypt
10
7
9
Lebanon
3
4
1
Morocco
1
-
2
Saudi Arabia
-
1
-
Tunisia
-
6
-
Arab group total
14
18
12
Arab group average
4.6
4.5
4.0
Afghanistan
10
20
6
Azerbaijan
3
3
1
Bangladesh
6
8
5
Guyana
1
2
-
Indonesia
4
18
9
Iran
1
6
-
Kazakhstan
15
17
6
Pakistan
5
4
8
Suriname
1
1
-
Tajikistan
1
-
-
Malaysia
-
1
-
Asian group total
47
80
35
Asian group average
4.7
8.0
5.8
Burkina Faso
20
14
1
Mali
3
4
-
Mozambique
3
3
1
Nigeria
11
37
7
Senegal
1
7
3
Uganda
5
3
1
Sierra Leone
-
1
-
African group total
43
69
13
African group average
7.1
9.8
2.6
OIC total
104
167
60
OIC average
5.4
7.9
4.2
Source: FAO FAPDA
The decision to strengthen the multilateral trading system was explained for “inclusive
prosperity and welfare” for the WTO Member countries and especially for the least-developed
ones. In this regard, they also attracted the attention to the potential benefit which could be
expected from the Agreement on Trade Facilitation (TFA)
10
as the first multilateral agreement
since the establishment of the WTO. However, they also noted that much less progress has been
made in agriculture. In this regard, it should be noted that the lack of success in the Doha Round
did result in a multitude of bilateral agreements and FTAs, comprising the risk to prevent
possible multilateral agreements by groupings such as the OIC.
1
0 Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA):Entered into force on 22 February 2017, it encloses provisions for accelerating the
mobility, release and clearance of goods. Effective cooperation between customs and related authorities are also covered, as
well as technical assistance and capacity building.