61
procedure much easier and smoother in terms of the applicant and the Customs Authority and
thus must be improved upon.
Country-Level Convergence
Country-level convergence indicates what percentage of all sub-variables is present in a
particular AEO program. If a country possesses all the sub-variables, than its score would be
100 percent. This can be considered as a vertical reading of the comparator matrix.
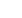
Table 3.6 shows the results of country-level convergence analysis for 8 OIC survey
respondents along with two of the international best practices (Japan and Canada) present in
APEC (2016). Accordingly, Morocco and Jordan exhibit 83 and 81 percent total convergence,
respectively. These countries are followed by Egypt and Turkey (76 percent), Uganda (74
percent), Indonesia (72 percent) and Tunisia (70 percent). The lowest amount of convergence
is observed in Oman (66 percent).
This result can be explained by two factors: (i) The age of the program-The correlation
coefficient between the launch year of the AEO program and the country-convergence
percentage is -0.778 indicating that as the AEO program matures, it embodies a more diverse
set of characteristics. (ii) The number of AEO companies-The correlation coefficient between
the number of AEO status holders and the country-convergence percentage is 0.710 signifying
the fact that a higher number of AEO companies is translated into higher convergence
probably through demands of these companies to be more involved in international supply
chains coupled with an increasing need for further advancements in the program for security
purposes.
Table 3.6. Country Level Convergence
AEO Launch
#AEOs
as of 2018
Convergence
Best Practice Countries
Canada
2008
1838
83%
Japan
2006
664
83%
OIC Countries
Egypt
2014
119
76%
Indonesia
2015
80
72%
Jordan
2005
88
81%
Morocco
2006
439
83%
Oman
2017
17
67%
Tunisia
2010
35
70%
Turkey
2013
332
76%
Uganda
2013
51
74%
OIC
75%
Source: Authors’ compilation using survey data and APEC (2016)
OIC AEO programs on average show a 75 percent convergence which is comparable to APEC
average (73 percent) but lower than the international best practice countries chosen for this