
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
92
and people. Most of the OIC MS CAs also lack advanced analytical capabilities needed to identify
and target suspect transactions and patterns of noncompliance.
Some of the OIC MS with analytical tools already in place, technology, and design parameters
often limit the accuracy and usability of data for effective CRM. The CRM system should be
designed to support the continuity between the different phases of the CRM process.
Due to the low rate of responses on the Survey received from the MS CA, we conducted the
analysis based on previous assessments, the coverage of the CRM in the CDPS and information
available on the Internet. The coverage of the CRM cycle stages varies across the OIC MS. The
average coverage of CRM cycle stages is 4.10.
According to the findings, most OIC MS, rely mainly on their CDPS to support CRM with a focus
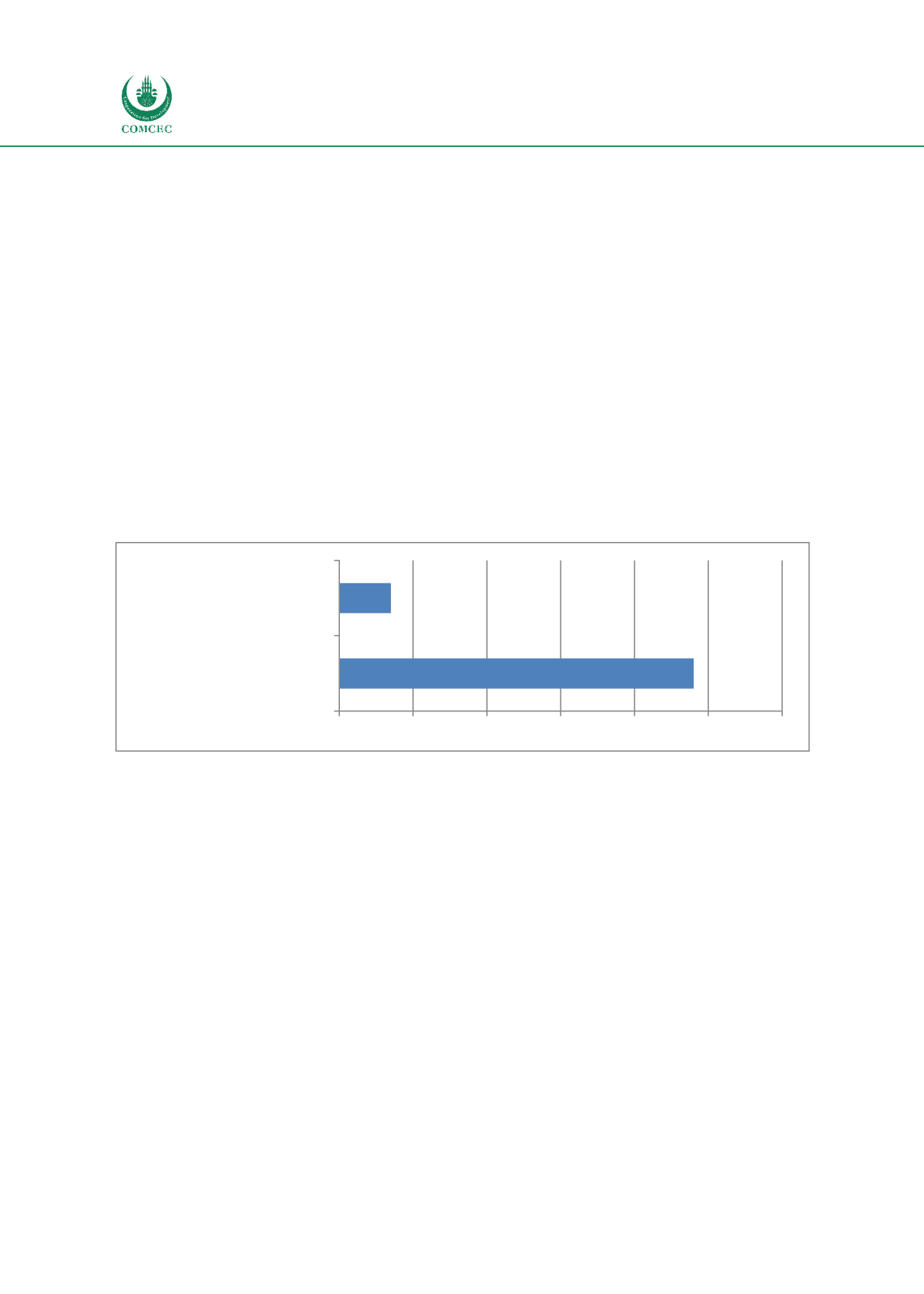
of the selectivity functionality. In total, 48 OIC MS CAs have embedded RM module in the CDPS
and seven OIC MS (Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cameroon, Indonesia, Malaysia, Turkey and the United
Arab Emirates) have an Integrated CRM (ICRM) systems that cover the entire CRM cycle
(Figure 30)and cross-agency collaboration. It was not possible to obtain the information for the current
status on CDPS for Somalia and Iraq. Of the 48 OIC MS using an embedded RM module, 34 OIC
MS use ASYCUDA (ASY++ and AW) as CDPS.
Figure 30: OIC MS Integrated and embedded CRM
Source: Author’s compilation
Apart of the 7 OIC MS
(Figure 30), that is using integrated CRM system (ICRM) and LE IT
Systems; the other CAs still handle all customs offenses, irregularities, and contentious cases
manually (paper-based). Some of the CAs developed in-house or implemented a COTS system in
IT systems, which are external to the CDPS. AW “offers a contentious" module that is a simple
formwith one dropdown list (7 types of irregularities) fromwhich the customs officer can select
only one type of irregularities, and one text box (free text) to enter the modus operandi.
Thus, there is a missing link in CA data architecture to build a comprehensive, structured
database layer on the informationmentioned before. This is initially a significant barrier to build
a CRM supportive IT system, and advanced analysis systems (DW, BI and data mining).
Most of the information related to the modernization of CA of the OIC MS is focusing on
modernization/replacement of the CDPS or the development of Integrated CRM IT systems. The
ultimate objective of the OIC CAs is to establish a dynamic integrated risk analysis and
management system. The appropriation of the methods required to develop such a system can
only be done progressively in an environment that has customs has the culture or the
information collection or data mining.
48
7
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
CRM module embed in CDPS
Integrated CRM System
















