48
Oil Importing MENA OICs
A high level of economic competitiveness is not a feature of these MENA countries. On average, oil
importing countries in this region score poorly on most indicators.
8
Low levels of growth affect their
ability to perform well in international export markets and relatively poor performance in exports deprives
these countries from earning valuable foreign exchange. While emerging economies have doubled their
share of global exports since 1990 (measured on a per capita basis) countries in the MENA region have
only been able to maintain their share. The corollary for high export performance is in general high
economic growth. Stagnant GDP growth in the region mirrors the low level of export share in the global
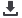
market. Figure 3.4 shows the gulf of difference that has opened up in trade competitiveness between
MENAP oil importing countries and their counterparts in the emerging and developing economies since
the early 1990s.
Figure 3.4.: Difference in Trade Competiveness between MENA Oil Importing Region countries
and Emerging and Developing Economies
Note: MENAP Oil importers include Djibouti, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Mauritania, Morocco, Syria and
Tunisia as well as Afghanistan and Pakistan.
Source: IMF, World Economic Outlook; national authorities and IMF staff calculations
A sustained reliance on Europe based on both proximity and historical linkages accounts for around 60%
of total exports since the 1970s. The Asia Pacific region attracted only 15% while Latin American
countries accounted for a very low 1%. This imbalance indicates that the MENA countries have not been
able to benefit from the high growth rates in Asian and Latin American countries. Part of this
concentration on Europe can be explained by the basket of primary and consumer goods which are the
mainstay of MENA country exports (64% of total exports which is close to 66% of most African
countries). A simple comparison with these goods and the high technology, high value added and
intermediate and capital goods, shows that is the latter category of goods (only 7% for MENA countries
which compares favourably with the 6% for LICs and adversely with Asian countries and their share of
37%) which have seen high levels of growth in recent years.
Unlike some sub-Saharan African countries the MENA oil importing economies do not suffer from the
disadvantages of proximity to markets, tariff rates, the existence of free trade agreements and cultural
8
Some parts of the material on oil importing countries have been sourced from the IMF Report ‘Trade
Competitiveness and Growth MENA, by Masood Ahmed. (accessed 27-5-2013) . Oil importing countries
include Egypt.