Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
67
Second, the U.S. Government has played a critical role in supporting Human Capital
Development in Agriculture. There is an extensive pipeline of agricultural professionals, with
35,646 degrees awarded toAgriculture majors.
256
Youth involvement is critical for the future of
agriculture. The government’s direct support of Agriculture Research and Study at Land Grant
Universities is further supplemented by a number of initiatives, including FFA, a youth
organization that preparesmembers for careers in agriculture and is officially endorsed by the
Office of Education
257
and 4H, a youth development program supported by land-grant
universities and local county offices.
258
Third, the U.S. has experienced substantial innovations in agriculture, driven largely by the
private sector. However, the research infrastructure that has been set up and funded by the
USDA has also played a significant role in innovations. The USDA seeks to supports innovation
through its Alternative Farming Systems Information Center, which encourages new technology
development.
259
Notable innovations that have been developed through investments include
hydroponic farming techniques inwhich food is produced in controlled, soilless settings.
260
The
USDA also directly issues grants to fund new technologies that are available to a broad range of
stakeholders, including businesses, non-for-profit institutions, and local and state governments,
with grants including $15 million in funding Child Nutrition Technology Innovation .
261
Cooperation
The U.S. plays a major role as a global food exporter, benefitting from 20 free trade agreements
with FTA partner countries accounting for 47% of exported U.S. products across all
categories.
262
It is also involved in extensive global cooperation and support.
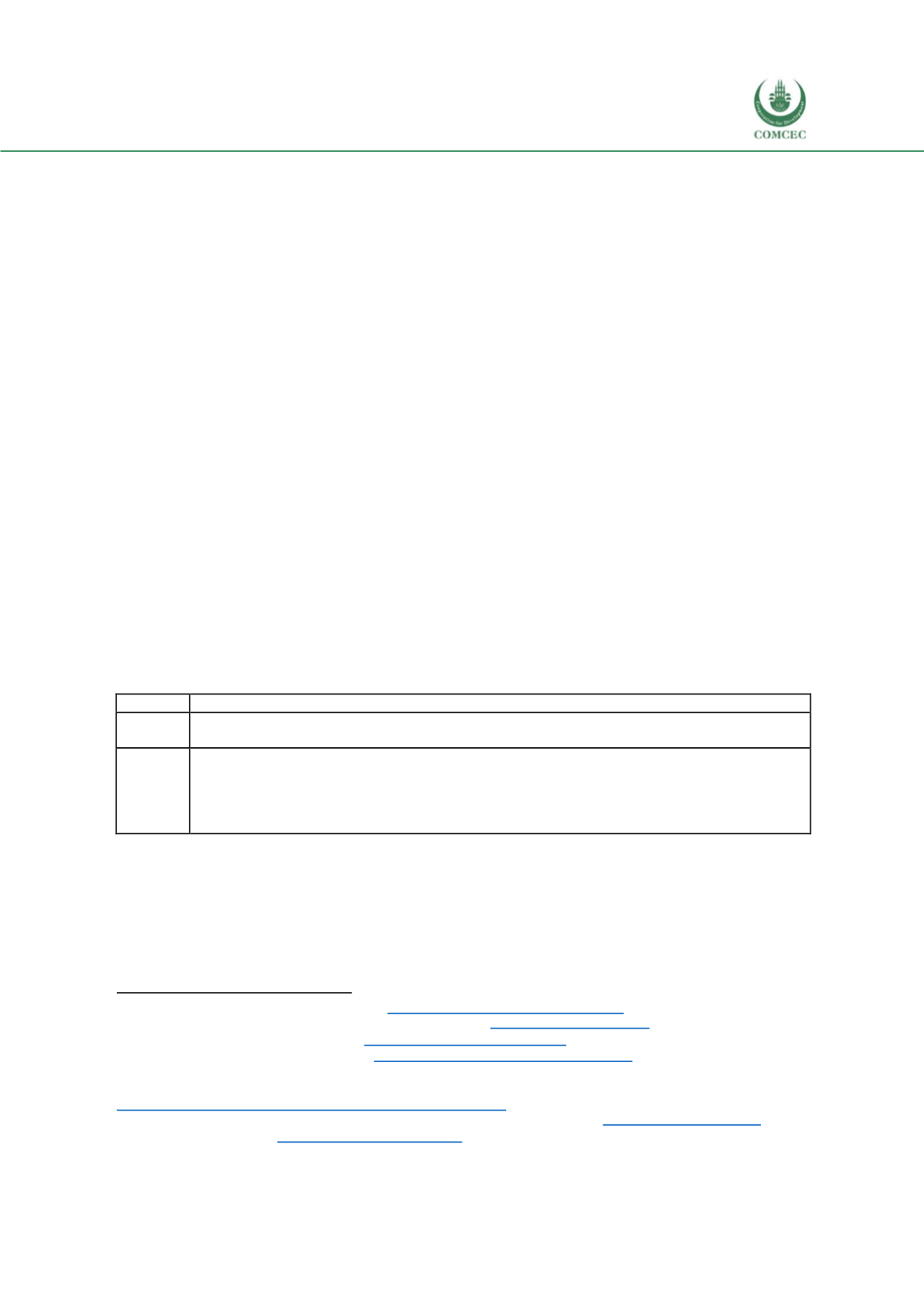
Table 37: U.S. Sample Initiatives and Cooperation
Entity
U.S. Involvement
UN FAO
The U.S. hosts a liaison office for the UNFAO and works closely with the organization to provide
information and share best practices around the world to support food security.
Feed the
Future
The U.S. governments global food hunger and food security initiative, working with partner
countries to develop their agriculture sectors, with notable impact, including, for example,
working with the Ugandan Government to improve agriculture and food security for over 2
million farmers. The U.S. also exports surplus production around the world to provide stability
to commodity prices.
263
256
Data USA. (n.d.). Agriculture. Retrieved fro
m https://datausa.io/profile/cip/agriculture257
Future Farmers of America. (2019). About FFA. Retrieved fro
m https://www.ffa.org/about/258
4H. (2019). What Is 4H?. Retrieved fro
m https://4-h.org/about/what-is-4-h/259
USDA. (n.d.). About AFSIC. Retrieved fro
m https://www.nal.usda.gov/afsic/about-afsic-1260
Ibid.
261
USDA Food and Nutrition Service. (2019). FY 2019 Technology Innovation Grants (TIG). Retrieved from
https://www.fns.usda.gov/fy-2019-technology-innovation-grants-tig262
International Trade Administration. (n.d.). Free Trade Agreements. Retrieved fro
m https://www.trade.gov/fta/263
Feed the Futurewebsit
e. https://www.feedthefuture.gov/