Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
111
Lessons Learned
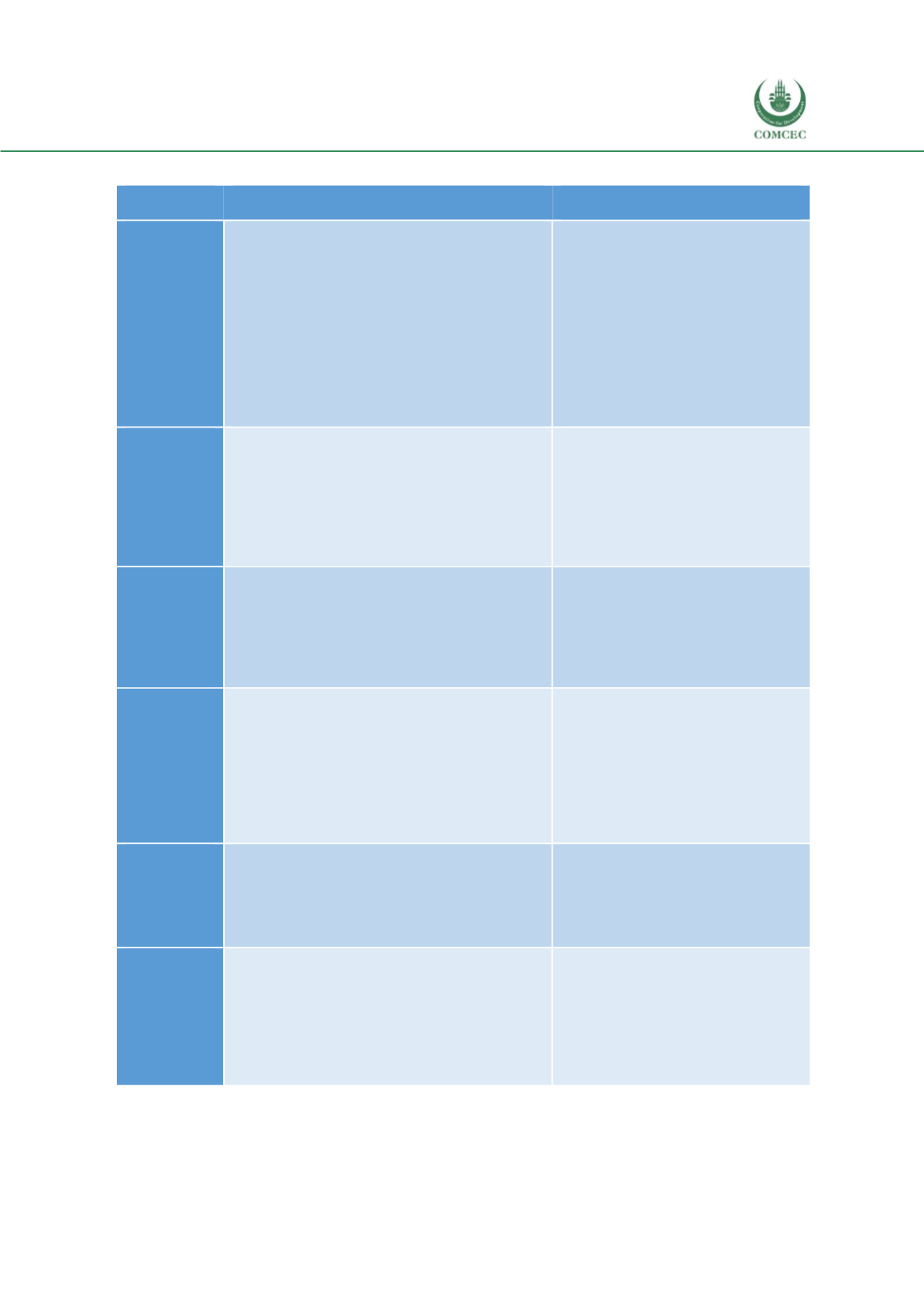
Area
Lessons and examples for the OIC to draw upon
Where experience differs from the
OIC
Government
Policy and
Structure
The Indonesian government has several
stakeholders that play a key role in a
comprehensive food security system. The Food
Security Agency (BKP) is specifically established
to ensure food security and works together with
other agencies. The cooperation creates a well-
organized food security system.
Financial support from the government for food
security from the government budget (APBN) for
each food stakeholder indicates the government's
commitment in realizing food security.
Not all governments are able to
extensively support food security in
the OIC as Indonesia has done. There
needs to be a coordinating OIC body
that provides additional financial
support in areas such as humanitarian
assistance and making important
investments, supplementing the work
of multinationals.
Monitoring
Indonesia uses hierarchical monitoring of food
security, from the central level to the district
level—especially the stock and price of rice and
other basic food staples in each district/city. The
data obtained is relatively adequate and
comprehensive to monitor the adequacy of food
staples and to ensure the people's purchasing
power on food staples.
All OIC countries do not yet have a
comprehensive database on food
security. Its members also might need
a more structured, coordinated and
systematic food-safety monitoring
scheme.
Mitigation
The food safetymitigation plan by the Indonesian
government is divided into two parts: contingency
mitigation to address agricultural risks such as
crop failure; and mitigation of the risk of natural
disasters and other uncertainties that threaten
food security, including distributing emergency
relief.
Food safetymitigation plans may need
to be conducted as a coordinated effort
across OIC countries.
Adaptation
Forms of government policies that improve the
adaptation of low-income communities with some
direct assistance to increase people's purchasing
power towards basic food needs. In addition, the
government has a program for farmers, especially
in the field of capital for farmers who lack capital,
so that the productivity of agricultural products
can be maintained for the benefit of food security
in Indonesia.
Individual OIC countries may not be
able to sufficiently provide for social
safety nets,
hence, coordinated
distribution of Zakat and other
charitable donations may be required.
Building
Resilience
There have been several programs that increase
farmers’ productivity, including procurement of
superior seeds and other agricultural production
facilities to increase productivity of agricultural
products as well as important initiatives to boost
rice production and education.
A pan-OIC level initiative to fund
research and technology adoption is
needed. In addition, a program to
diversify people's food is also needed
to prevent dependence on only one
staple food.
Cooperation
Cooperation between Indonesia and other
countries is needed for knowledge and technology
transfer,
which
will
indirectly
increase
agricultural production and the security of
agricultural products. Regional Cooperation
carried out by Indonesia in the scope of ASEAN
has a well-structured program and clear
objectives for food security in the ASEAN region.
A more structured program for food
security in an OIC collaboration
program in food security needs to
develop. A more collaboration is also
needed to fill gaps among OIC
members that have different strengths
weaknesses in food security aspects.