Increasing Agricultural Productivity:
Encouraging Foreign Direct Investments in the COMCEC Region
52
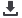
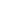
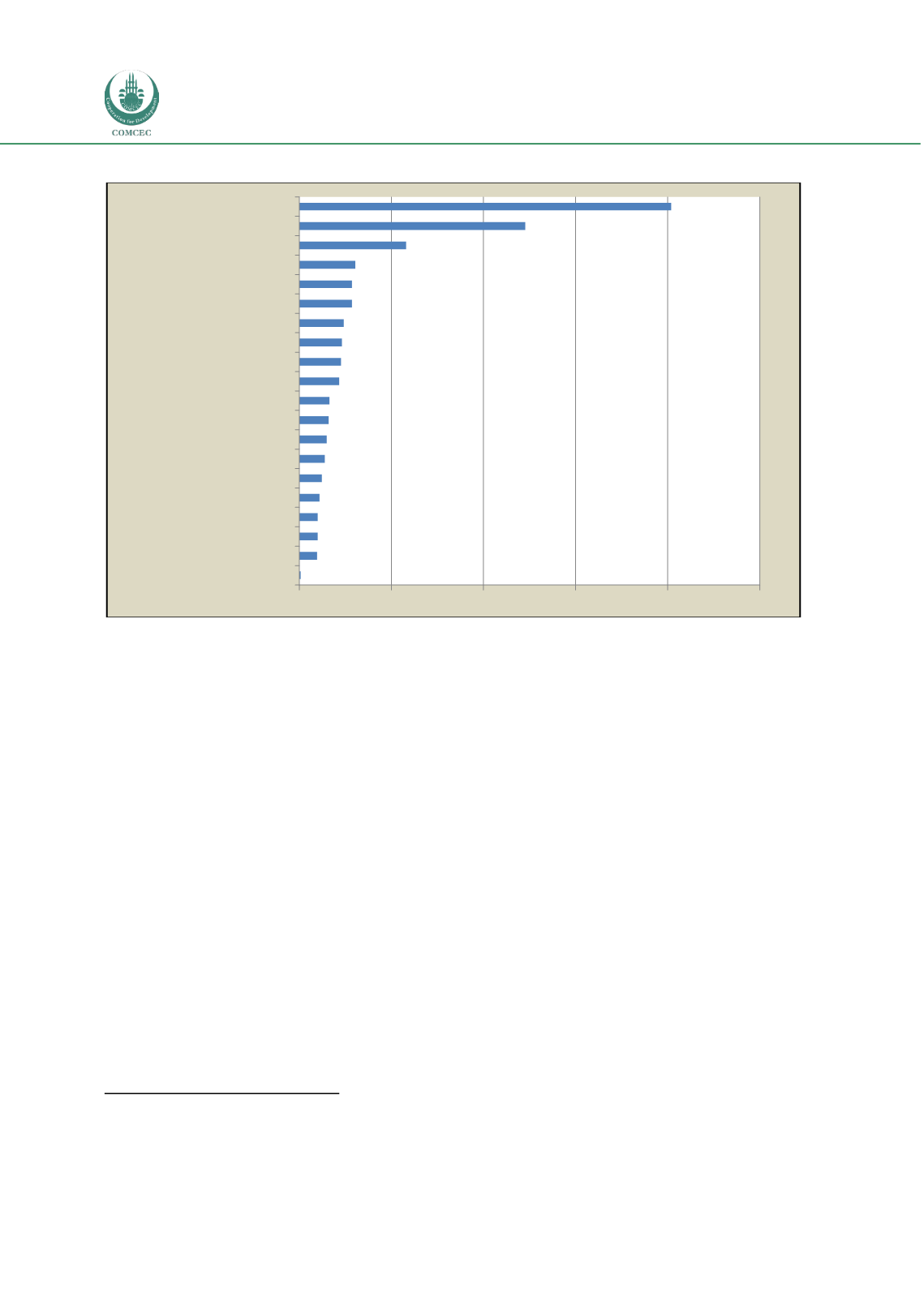
Figure 23:
Total Renewable Water
Resources (km3/year, 2012)
Source: FAO (2013)
Figures 21 to 23 show that 37 COMCEC Member Countries (20 of them are LDCs) enjoy a high
potential in at least in terms one of the critical agricultural resources (agricultural labour force,
arable land and water resources).
3.3
Location Benchmarking for FDI in Agriculture in the COMCEC Region
Location benchmarking is an approach commonly used by foreign investors to assess potential
investment sites for future FDI intensions by reducing the foreign investor’s site selection
options to a short-list of locations best suited to the requirements of the investment project.
73
As
an analytical tool, location benchmarking can be applied to identify FDI potentials from a
corporate perspective. Using location benchmarks as a means to systematically compare
locations by industry sector and measure their potential to attract FDI assists investment
promotion intermediaries to better understand local competitiveness for FDI and to develop
marketing strategies to attract inward investment.
74
Therefore, specifically benchmarking
agriculture among countries in the COMCEC Region proves to be valuable in terms of identifying
challenges and weaknesses of the agriculture industry in the COMCEC Region.
From an investor perspective, location benchmarks capture a snapshot of a particular industry
in one location at a static point in time. The investment location decision usually consists of two
aspects:
73
MIGA, 2007
74
FAO, 2008
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
Egypt
Iraq
Mali
Tajikistan
Kazakhstan
Suriname
Iran
Sudan
Sierra Leone
Gabon
Mozambique
Guinea
Turkey
Guyana
Nigeria
Cameroon
Pakistan
Malaysia
Bangladesh
Indonesia