Increasing Agricultural Productivity:
Encouraging Foreign Direct Investments in the COMCEC Region
54
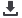
Table 21: Determinant groups and site selection considerations concerning FDI
FDI
determinant
Site selection
consideration
Cost factors
Quality factors
Economic
conditions
Labour
Labour
Potential to recruit local staff
Flexibility of labour environment
Infrastructure
Electricity
Power supply
Water
Water supply
Telecommunications and
broadband
Telecommunications and Internet
Internet
Availability and reliability of
shipping transportation
Natural gas
Freight shipment
Real estate
Real estate
Availability of land, office space,
building and sites
Construction
Office space
Living conditions
None
Schools, safety, healthcare, etc.
Access to markets
None
Size of local market
Proximity to raw materials,
components and equipment
Host country
policies
Macro policies
None
Access to foreign exchange
Legal and regulatory framework
Private sector
Cost of finance
Clear, stable and predictable
policies
Efficient financial markets
Trade and industry
Import duties
Openness of economy to trade
Export duties
Regional integration and access
to markets
FDI policies
None
Ease of entry
Restrictions on ownership
Investment protection and
incentives
Transparent and stable policies
Investor
strategies
General business
environment
None
Political, financial and economic
stability
Source: Compilation of MIGA 2007, FAO 2008 and OIC 2009 and Investment Consulting Associates (ICA) own research
Lessons from such corporate perspectives for governments and policy-makers revolve around
ensuring that key-policies with regard to the economy, private sector, FDI, trade and industry
are required to be investor-friendly and appropriate in order to attract FDI. The rationale for
FDI is not homogeneous and varies from industry to industry and according to investor and