Reviewing Agricultural Trade Policies
To Promote Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
161
A general overview of the case study countries
The analysis of the country-level data and especially the data on disaggregated agricultural trade
flows indicate that the OIC countries generally differ in geography, climate conditions and
product spectrum for which they have comparative advantage in global markets. Besides, the
OIC countries also exhibit some variation in export and import shares of OIC versus non-OIC
destinations and origins and in their agricultural export and import shares in three OIC groups.
The situation is reflected in the selected country case studies as well, as described below.
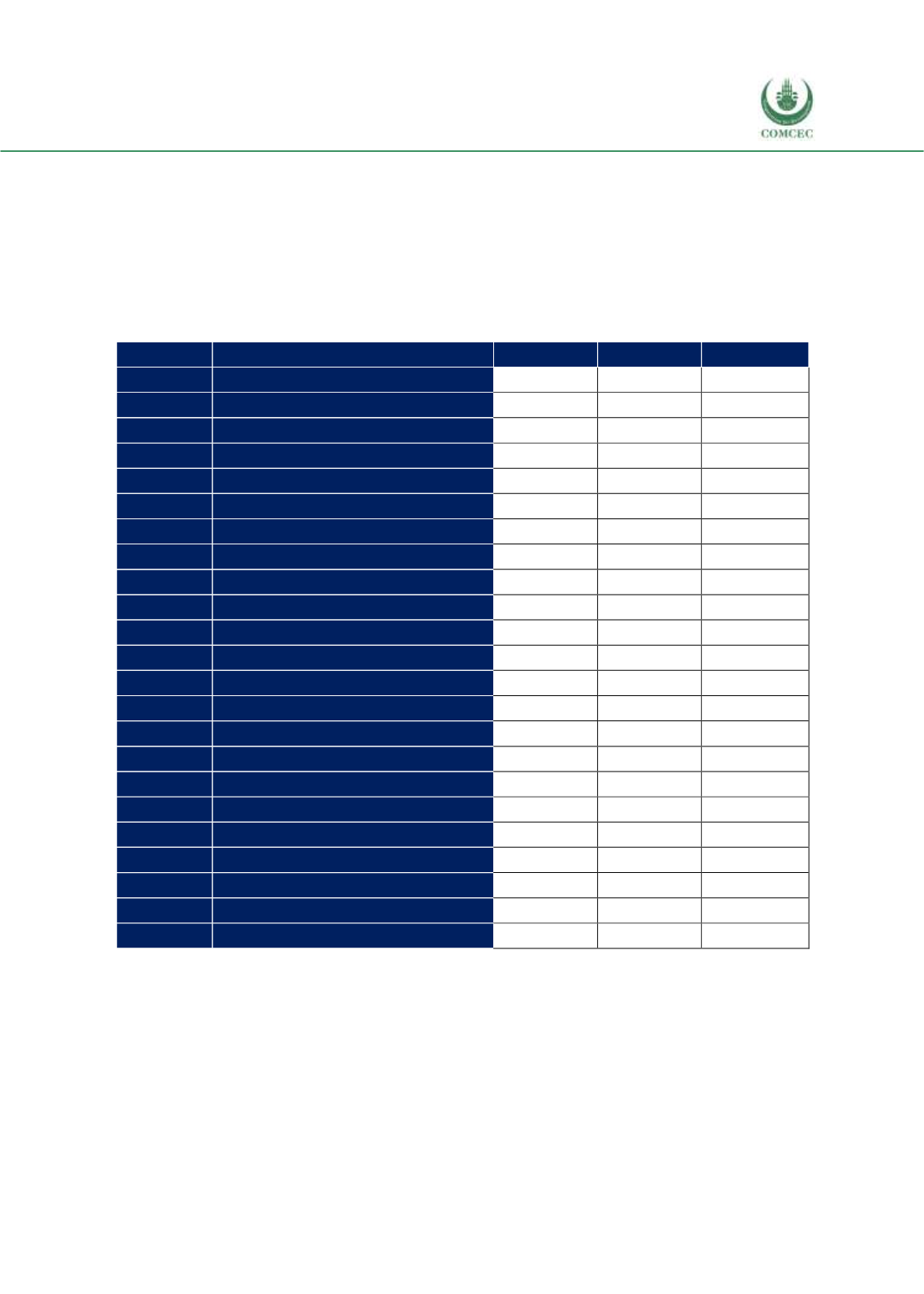
Table 4. 65 NTM Coverage and Frequency Ratios in Agricultural Products, Brazil
Code
Sector
CR
FR
Count
A
Animal
100.0
100.0
181
B
Animal
100.0
99.5
180
C
Animal
0.4
1.7
3
D
Animal
0.4
1.7
3
E
Animal
0.4
1.7
3
P
Animal
100.0
100.0
175
A
Vegetable
100.0
100.0
307
B
Vegetable
100.0
100.0
307
C
Vegetable
68.8
68.4
210
E
Vegetable
29.2
0.7
2
P
Vegetable
100.0
100.0
301
A
Food Products
99.6
98.4
185
B
Food Products
100.0
100.0
188
C
Food Products
13.7
14.4
27
E
Food Products
8.7
2.1
4
O
Food Products
10.6
5.3
10
P
Food Products
90.8
96.1
171
A
Hides and Skins
5.4
45.9
28
B
Hides and Skins
97.9
83.6
51
P
Hides and Skins
0.3
9.8
6
A
Wood
16.2
44.8
99
B
Wood
11.3
35.3
78
E
Wood
0.3
0.5
1
Source: WITS
Note: A: Sanitary and phytosanitary measures, B: Technical barriers to trade, C: Pre-shipment inspection
and other formalities, F: Charges, taxes and other para-tariff measures, G: Finance Measures, P: Export
related measures
For the two African countries, the role of agricultural sector in the economy is different from
each other with regards to shares in GDP, employment and exports. In Chad, agricultural sector
is important in providing livelihoods, yet with share in exports being very small. The country’s
main aim is to feed its population and, obviously, its agricultural sector has such a priority. This
is clearly the main reason of export duties. Yet, considering fast population growth, stagnating
exports during the last five years and increasing imports should be providing sufficient reasons