Analysis of Agri-Food Trade Structures
To Promote Agri-Food Trade Networks
In the Islamic Countries
117
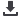
Figure 65:
In Degree Centrality, Ten Leading Tunisian Agricultural Imports, 2005-2016, Number
Source: UN Comtrade.
Agricultural Quality Framework
Agricultural Quality Related Policies and Infrastructure
Tunisian agricultural policy is quite comprehensive. It is based on five pillars:
Development of infrastructure;
Human resources;
Incentives and support to farmers;
Support to agricultural products exports; and
Research and Development.
Since independence in 1956, the Tunisian government has mobilized resources for water
infrastructure, which is currently well established. Indeed, the hydric infrastructure is very
important and a whole system of mobilization-transfer-allocation of surface water resources
could maintain the production of agricultural production, in addition to potable water. The
infrastructure is also well developed for soil conservation, fight against desertification and
management of forests.
Various education institutions (11 high education institutions in addition to vocational training
centers) and familiarization programs insure a relatively good level of the competencies of local
farmers.
The new investment code offered farmers different incentives, including mechanization and the
use of new technologies. These incentives can be classified into 3 categories:
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
Wheat
Other
cereals
Maize Sugar
Animal
feed
Tobacco Oil seeds Cork and
wood
Soya bean
oil
Sugar
products
2005 2016