
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
118
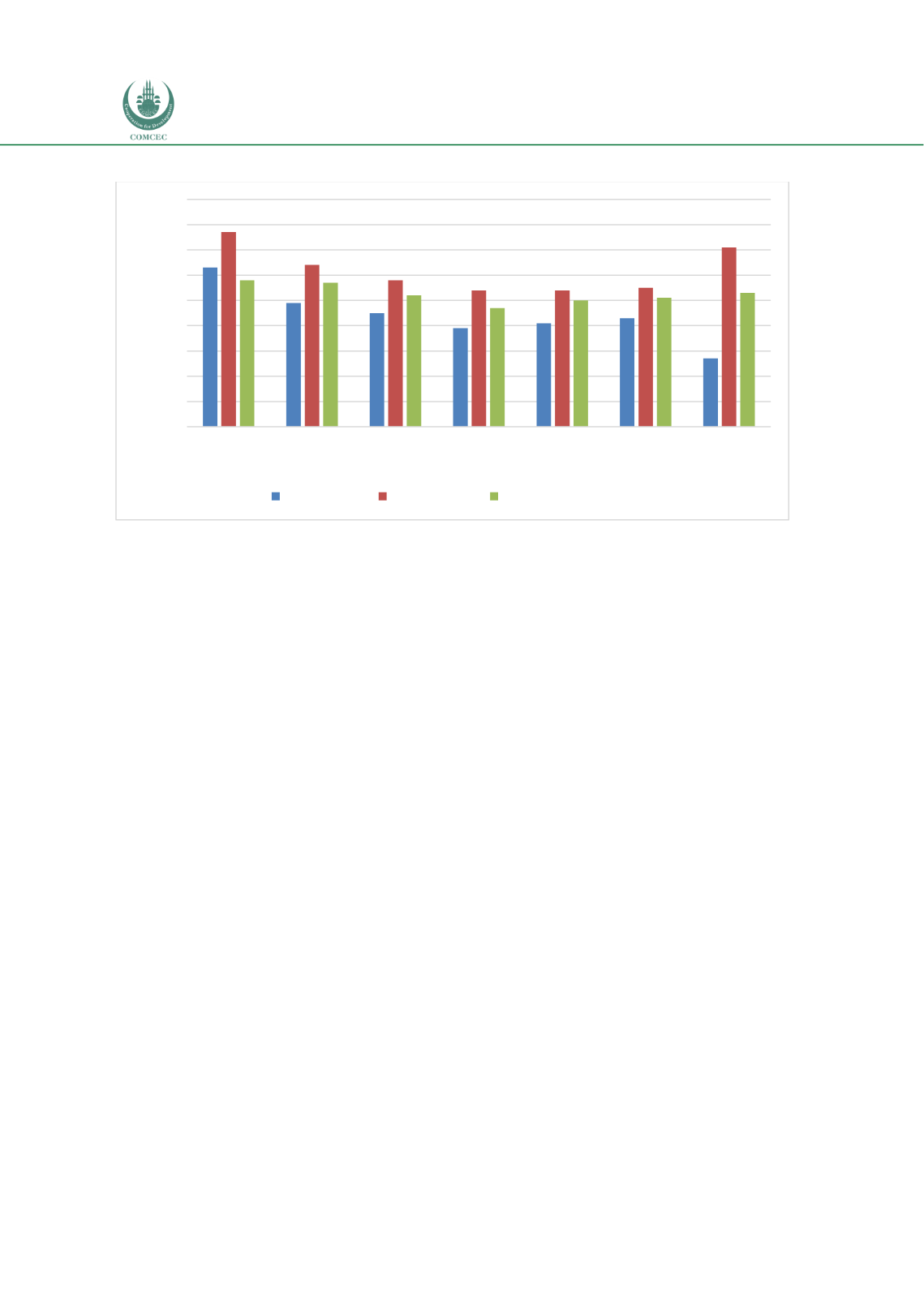
Chart 4.3. 4: Procurement Regime of PPPs: Nigeria (0-100 Highest)
Source: World Bank (2018f)
4.3.5.
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Islamic Finance
Nigeria has no dedicated laws for Islamic Finance. However, the legal framework for Islamic
finance was derived from the existing conventional finance laws by leveraging on some
provisions to establish Islamic financial institutions. The main laws leveraged upon were:
Company and Allied Matters Act (CAMA) 1990, Banks and Other Financial Institutions Act
(BOFIA) 1991, Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) Act 2007, Investment and Securities Act (ISA)
2007, National Insurance Commission (NAICOM) Act 1997, Insurance Act 2003, and Nigerian
Deposit Insurance Act 2006. These Acts empowered the regulatory bodies to make four key
regulations that facilitated the emergence and development of the Islamic finance industry in
Nigeria. On infrastructure financing, there are no separate general or specific laws or
regulations put in place for Islamic finance.
There are some developments in the regulatory environment which have enhanced the
prospect for sukuk issuance. These include the Rules on Sukuk issued by SEC in 2013, the
Guidelines on tax treatment for Sukuk issued by FIRS in 2013, the launching of Non Interest
Capital Market Products (NICMP) Master Plan in 2015 by SEC, the Guidelines on granting
liquidity status to State Government’s Sukuk issued by the CBN in 2016, and the Guidelines on
investment by Pension Fund Administrator issued by PENCOM (COMCEC 2018).
4.3.6.
Role of Islamic Finance in Infrastructure Finance
As indicated, the National Integrated Infrastructure Master Plan (NIIMP) shows huge gaps in
the funding needs expecting in the infrastructure development in Nigeria during 2018-2043.
While the figures indicate tremendous infrastructure financing opportunities, the role that
different sectors of Islamic finance can play to fill some of the gaps are discussed next.
63
49
45
39
41
43
27
77
64
58
54
54
55
71
58
57
52
47
50
51
53
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
High income Upper-middle
income
Lower-middle
income
Low income Sub-Saharan
Africa
OIC Members
(40)
Nigeria
Index (0-100 Highest)
Preparation Procurement
Contract management
















