Islamic Fund Management
27
Malaysia, for instance, continues to map out strategies to strengthen the country’s
competitive edge in the industry. It provides tax incentives and has eased licensing
requirements for dealing with fund management and giving investment advice.
Malaysia’s move into private pension funds is particularly seen as a positive
development to lift up the industry to a higher level (MIFC, 2017). Further developments
in Malaysia as a case study for Islamic fund management is discussed Chapter 4 of the
report.
On the other hand, OIC-member countries also constitute examples like Morocco where
the Islamic fund management industry is yet to emerge. Another OIC country, which
would situate itself within the infancy category of Islamic finance /Islamic fund
management development, would be Ivory Coast. These countries are still establishing
the base infrastructure for Islamic finance development and slowly expanding to
develop the other sectors of the industry such as Islamic capital markets (ICM). This
report will provide further explanation of the state of the Islamic fund management
industry in the case of Morocco in later chapters.
Other OIC-member countries which can be classified as having a developing Islamic fund
management industry would include examples like Indonesia (with 2.96% of global
Islamic fund assets), Kuwait (with 2.49% of global Islamic fund assets), and Pakistan
(with 2.32% of global Islamic fund assets) (se
e Chart 2.3above). This report also covers
the case of Pakistan as an OIC-country emanating significant progress in Islamic fund
management.
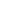
The IFSB (2018) notes that in terms of asset class, global Islamic funds were dominated by
equity-based funds (42%) as at end-2017, followed by money market funds (26%) and
commodity-based funds (14%). The other significant asset classes include fixed-income or
sukuk funds (10%) and mixed-allocation funds (7%), as depicted i
n Chart 2.4 .Chart 2.4: Islamic Funds by Asset Class (2017)
Sources: Bloomberg, IFSB (2018)
Note: There may be some overlap between the asset classes. For example, if a fund focuses on commodities by
investing in the equities of companies operating in that sector, it could in principle be treated as a commodity
fund or an equity fund. For the purposes of this report, the funds are categorised by asset class based on
classifications provided by Bloomberg.
To further develop the Islamic fund management industry, there are lessons to be learnt from
the development of the global fund management industry. In particular, the key pillars of the
industry in Europe and the US are pension funds and insurance companies (Quorum Centre,
2018). They provide trillions of dollars of new money coming into investment funds each year.