COMCEC Financial Outlook 2018
3
A financial system consists of institutional units and markets that interact for the purpose of
mobilizing funds for investment and providing facilities for the financing of commercial activity.
The role of financial institutions within the system is primarily to intermediate between those
that provide funds and those that need funds and typically involves transforming and managing
risk. In this regard, the financial system has significant effects for whole economic systems, and
a healthy financial system contributes to economic growth by easing access to finance,
increasing financial literacy and allocating resources efficiently.
In order to achieve a well-functioning system, financial markets require depth, access, efficiency,
and stability. Depth means that financial institutions and financial markets are a sufficient size.
Access reflects the degree to which economic agents use financial services. Efficiencymeans that
financial institutions are able to successfully intermediate financial resources and to facilitate
transactions. Finally, stability refers to low market volatility plus low institutional fragility.
These characteristics of the market have been measured by using particular indicators to
compare financial systems across countries and over time.
6
In this context, the purpose of this outlook is to shed light on recent financial developments by
using the above-mentioned characteristics of the financial markets and to analyze the financial
markets of the OIC countries over time.
In this Financial Outlook, OIC Member Countries have been categorized into four major groups
according to the World Bank Income Grouping Methodology (according to their GDP Per Capita
levels). According to this categorization, 17 countries are in OIC-Low Income Group (OIC-LIG);
17 are in OIC Lower Middle Income Group (OIC-LMIG); 16 are in OIC-Upper Middle Income
Group (OIC-UMIG), and 7 are in OIC-High Income Group (OIC-HIGH) as shown in the table below:
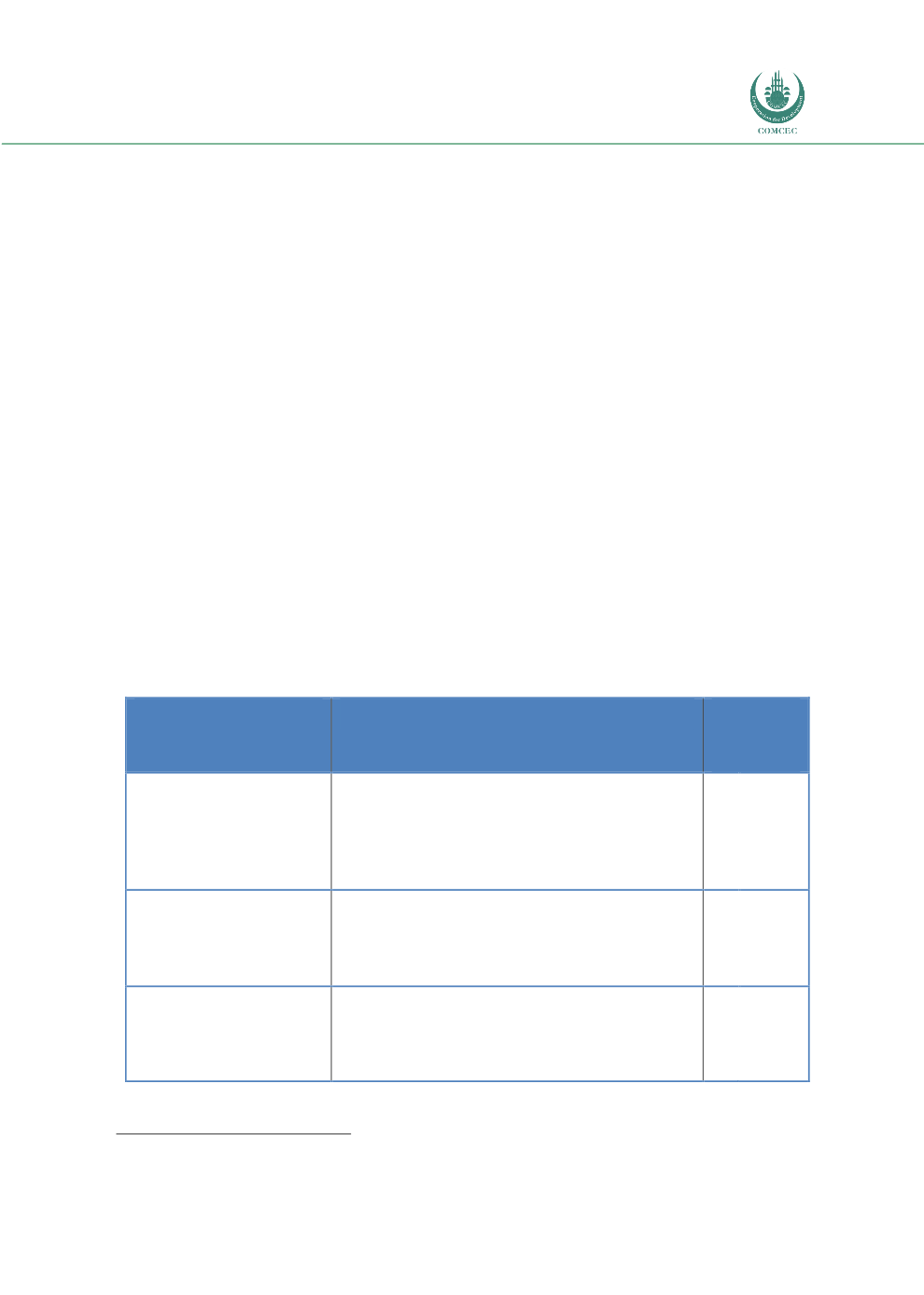
Table 1: Categorization of OIC Member States
CATEGORIES
COUNTRIES
NUMBER
OF
COUNTRIES
OIC-Low income group
(1,025 USD or less)
Afghanistan, Benin, Burkina Faso, Chad, Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Sierra
Leone, Somalia, Syrian Arab Republic, Gambia The,
Tajikistan, Togo, Uganda, Yemen
17
OIC-Lower middle-
income group
(1,026 USD to 3,995
USD)
Bangladesh, Cameroon, Comoros, Cote d'Ivoire,
Djibouti, Arab Rep. of Egypt, Indonesia, Kyrgyz
Republic, Mauritania, Morocco, Nigeria, Pakistan,
Palestine, Senegal, Sudan, Tunisia, Uzbekistan
17
OIC-Upper middle
income
(3,996 USD to 12,375
USD)
Albania, Algeria, Azerbaijan, Gabon, Guyana, Iran,
Iraq, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Lebanon, Libya, Malaysia,
Maldives, Suriname, Turkey, Turkmenistan
16
6
Cihak, M., Demirgüç-Kunt, A., Feyen E., Levine, R., 2012