Child and Maternal Mortality
in Islamic Countries
82
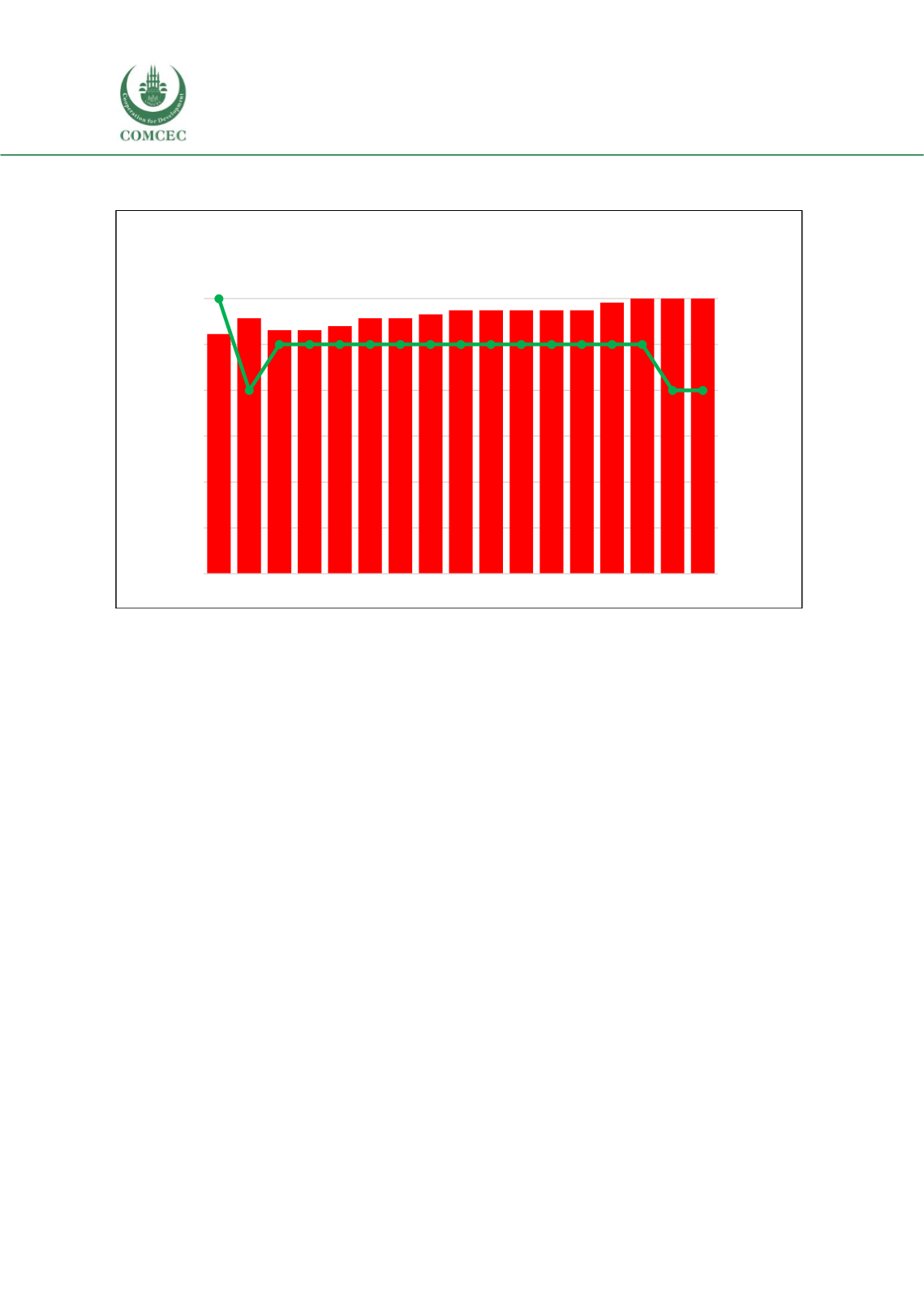
Figure 3. 27 Domestic Government Expenditure and Out of Pocket Spending (GGHE-D%GDP
and OOPS%CHE)
Source: WHO Global Health Expenditure Database.
3.1.5. Lessons learned from Bangladesh
Several key lessons were learned through desk reviews, extensive analysis of available data and
key informant interviews using semi-structured questionnaires in the four countries including
Bangladesh, Indonesia, Iraq, and Côte d'Ivoire. The triangulation of the data helped advance
linkages between various data sources related to MNCH services in the selected case study
countries.
Although the country achieved remarkable success in terms of reducing maternal and child
mortality, there remain major issues in terms of quality of care related to MNCH services.
According to the latest (2016) BMMS survey, maternal mortality rates stagnated Bangladesh,
which suggests the need for innovative approaches/interventions to reduce theMMR. According
to IHME/GBD estimates that Bangladesh will reduce U5MR to 18.6 by 2030 and achieve the SDG-
3.2.1 goal of reducing U5MR to less than 25 deaths per 1,000 live births.
It was agreed upon by all participants that Leadership and Governance is a challenge in the
Bangladesh Health System. While leadership may be strong and policies have been enacted to
improve MNCH, governance to monitor and enforce the policies seems to be lacking and the lack
of effective governance overlapped with other barriers to accessing healthcare services as well.
Adequate governance and monitoring of health centers and hospitals are needed to keep
providers accountable. Many experts mentioned "moonlighting" or having a private practice
after hours or, in some cases, even during office hours, as a pervasive issue among doctors.
Quality of Care was the most prominent barrier to accessing healthcare services that was
discussed by the Key Informants. Many Key Informants mentioned that while utilization of ANC
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
0,0%
0,1%
0,2%
0,3%
0,4%
0,5%
0,6%
2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
OOPS%CHE (Red Bars)
GGHED%GDP (Green Line)
Bangladesh: Domestic Government Expenditure and Out
of Pocket Spending (GGHE-D%GDP and OOPS%CHE)