Child and Maternal Mortality
in Islamic Countries
79
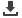
Figure 3.25. Overall health information systems and other surveillance systems, Bangladesh
3.1.4. Maternal, newborn and child health strategy policy in Bangladesh
Policies
It is evident that the Government of Bangladesh is dedicated to improving MNCH. Political
commitment has been articulated in several policies and strategic documents that have driven
and continue to drive progress. ‘Promise Renewed: Bangladesh Call for Action to End
Preventable Child Deaths by 2030', launched in July 2013 has prioritized 11 interventions
focusing on maternal, newborn and child health. The Bangladesh Every Newborn Action Plan
(BENAP) was developed based on the bottleneck analyses of priority maternal and newborn
interventions. A wide consensus now exists for a newborn care package including several high
impact interventions. Visible progress has been observed in addressing newborn complication
and deaths due to birth asphyxia, prematurity and infection through establishing SCANU in six
medical college and 20 district hospitals covering 26 districts and rolling out ETAT, sick
newborn care and Helping Babies Breathe (HBB) initiative training and equipping over 28,000
SBAs. Application of 7.1% chlorhexidine (CHX) for newborn umbilical cord care has been rolled
out across all 64 districts of the country, training over 85,000 health workers, supervisors, and
managers. Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC) has been established in several tertiary hospitals in
Dhaka as well as at selected district and upazila level facilities. The BENAP, however, requires
further scale-up through effective planning.
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has created a 5-year Program Implementation Plan
(PIP) for its 4
th
Health, Population, and Nutrition Sector Program (4
th
HPNSP) for 2017-2022.
52
The PIP is a document created to reflect the health nutrition population (HNP) sector
development activities of MOHFW and describes
what
needs to be done and
how
to achieve its
objectives through the implementation of the 4
th
HPNSP. The PIP (2017-2022) is guided by
Bangladesh’s Vision 2021 (transforming the country from a developing into a middle-income