Child and Maternal Mortality
in Islamic Countries
86
The WHO/UNICEF/UNFPA/World Bank and UNPD estimates are model-based PMDF
(proportion of maternal deaths among deaths of females in reproductive age) predictions from
the covariates that are considered major determinants of maternal mortality. PMDF is
considered more stable and robust to misspecification than the MMR. The six covariates used in
the estimation model until 2005 were skilled birth attendance at birth, general fertility level,
GDP per capita (PPP), HIV prevalence level, two regional dummy indicators, and VR coverage
indicator. Since 2008, only the first three covariates are used directly in the model and the
estimated rates are adjusted for HIV prevalence and data quality factor. The regions are
considered as a discrete random variable. The estimated PMDFs are then converted to MMR.
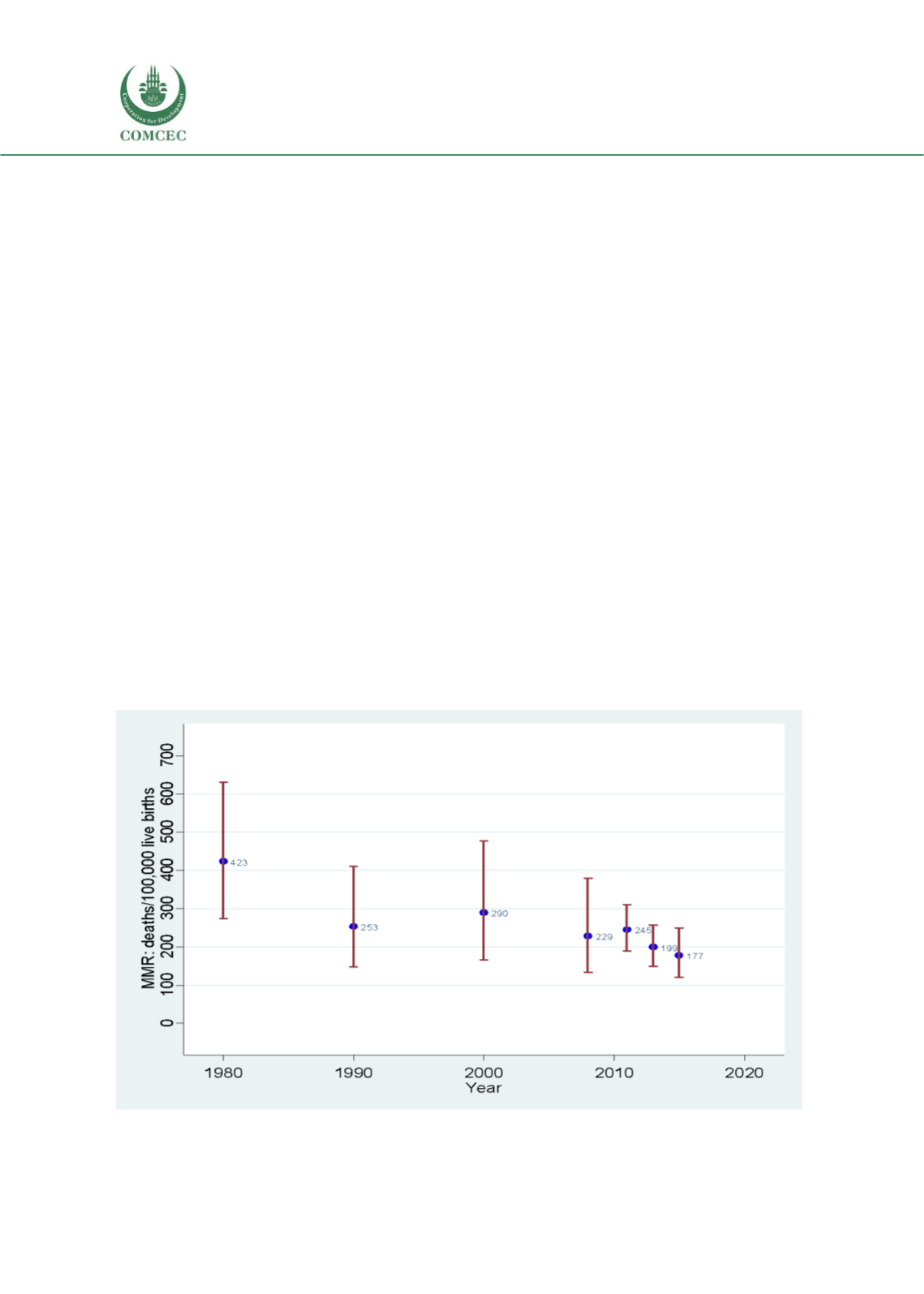
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) concurrently started to estimate MMR
globally since 2010. IHME's model-based MMR estimates in Indonesia were 423 (95% CI: 274-
631) per 100,000 live births for 1980, 253 (148-411) for 1990, 290 (166-477) for 2000, and 229
(133-379) for 2008.
73
Subsequently, the MMR estimates were updated in 2011 to 245 (189-
311)
74
, in 2013 to 199.3 (140..0-257.4)
75
and as a part of the Global Burden of Diseases (GBD)
in 2015 to 177 (121-248.6).
76
The IHME estimates are shown graphically in Figure 3.26.
The IHME estimates are also model-based which directly model MMR with a larger number of
covariates. The covariates include age-specific fertility rate, total fertility rate, age-standardized
HIV death rate for female individuals aged 15–49 years, neonatal death rate, lag-distributed
gross domestic product (GDP) per person, the proportion of deliveries occurring in facilities, the
proportion of deliveries overseen by skilled birth attendants, coverage of four visits of antenatal
care, and malnutrition in children younger than 5 years.
Figure 3.29. MMR estimates in Indonesia by the Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation and
Global Burden of Diseases Collaborators
Note: 1980-2000 estimates are based on Hogan et al. 2010. The estimates were revised in subsequent study
rounds, but not shown here.