Child and Maternal Mortality
in Islamic Countries
96
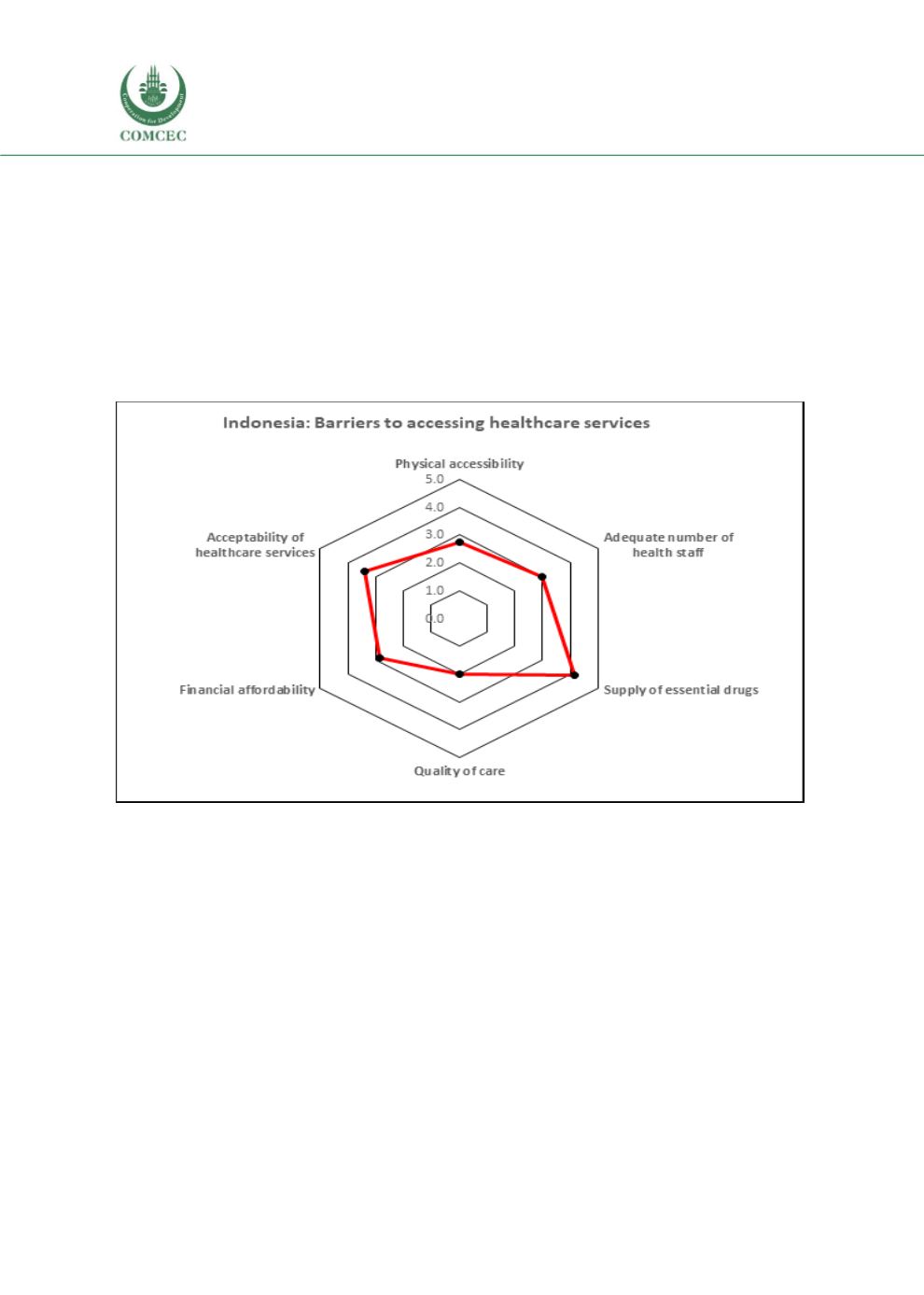
Perceived barriers to accessing healthcare services
Similar to Bangladesh, quality of care (mean value of 2.0) was considered a major barrier for
accessing health care services (Figure 3.40). The supply of essential drugs (mean value of 4.1)
was considered the least important barrier. Adequate number of health staff (3.0), financial
affordability (2.9), physical accessibility (2.8) and acceptability of health care services (3.4) were
perceived as moderate barriers.
Figure 3.40. Barriers to accessing healthcare services, Indonesia
(1= Most significant barrier; 2= Second most significant barrier; 3= Moderate barrier; 4=
Somewhat of a barrier; 5= Not a barrier)
We provide here some selected quotes from the key informant interviews: "Quality of care is the
number one problem in the Indonesian health system. Most mothers receive ANC from the midwives
and the quality of the midwife services needs to improve. "
"Financial affordability is a barrier for poor people. Financial affordability is also related to the
geographical area because in some areas the care might not be expensive but transport is the main
expenditure."
Perceived barriers to MNCH services
After the supply of essential drugs, the acceptability of MNCH services was considered a lesser
barrier for accessing care (Figure 3.41). Physical acceptability was slightly more important
barrier for accessing MNCH services compared to general health care services. The quality of
care was perceived as the most important barrier (average score was 1.4 for MNCH, compared
to 2.0 for the general health care services).