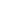
114
While qualification/training is also perceived by 30% stakeholders as important, it doesn’t rank
very favorably compared to other features. It is also notable that experience is also perceived by
a relatively small number of stakeholders as an important feature of an effective principal.
Participating stakeholders were also asked about their views on the main barriers to quality
education at the primary and secodnary level in Malaysia (
Figure 3.2.11
). Once again, the lack
of effective school leadership and lack of motivated teachers were identified by the majority as
one the three most important barriers, both in case of primary and secodnary education. This
was followed by a lack of good/well-qualified teachers. This similiarily aside, there was
considerable differences in perceived barriers to quality education across primary and
secondary education. Lack of facilities and funding were highlighted as greater obstacles to
quality education in primary school compared to secondary.
31
On the other hand, lack of
parental important was identified as the third most commonly perceived barrier in secondary
education (ranked sisth in primary). Surprisingly Malaysia has linguistic groups and has
experimented for decades regarding the use of English as a medium of instruction
.
Yet
only a
small proportion of stakeholders interviewed perceived language of instruction to be an
important barrier in primary and secondary education. Similarly, in spite of Malaysia’s highly
centralized educational system, the stakeholders interviewed didn’t consider the lack of school
autonomy to be a problem in primary and secondary education
.
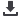
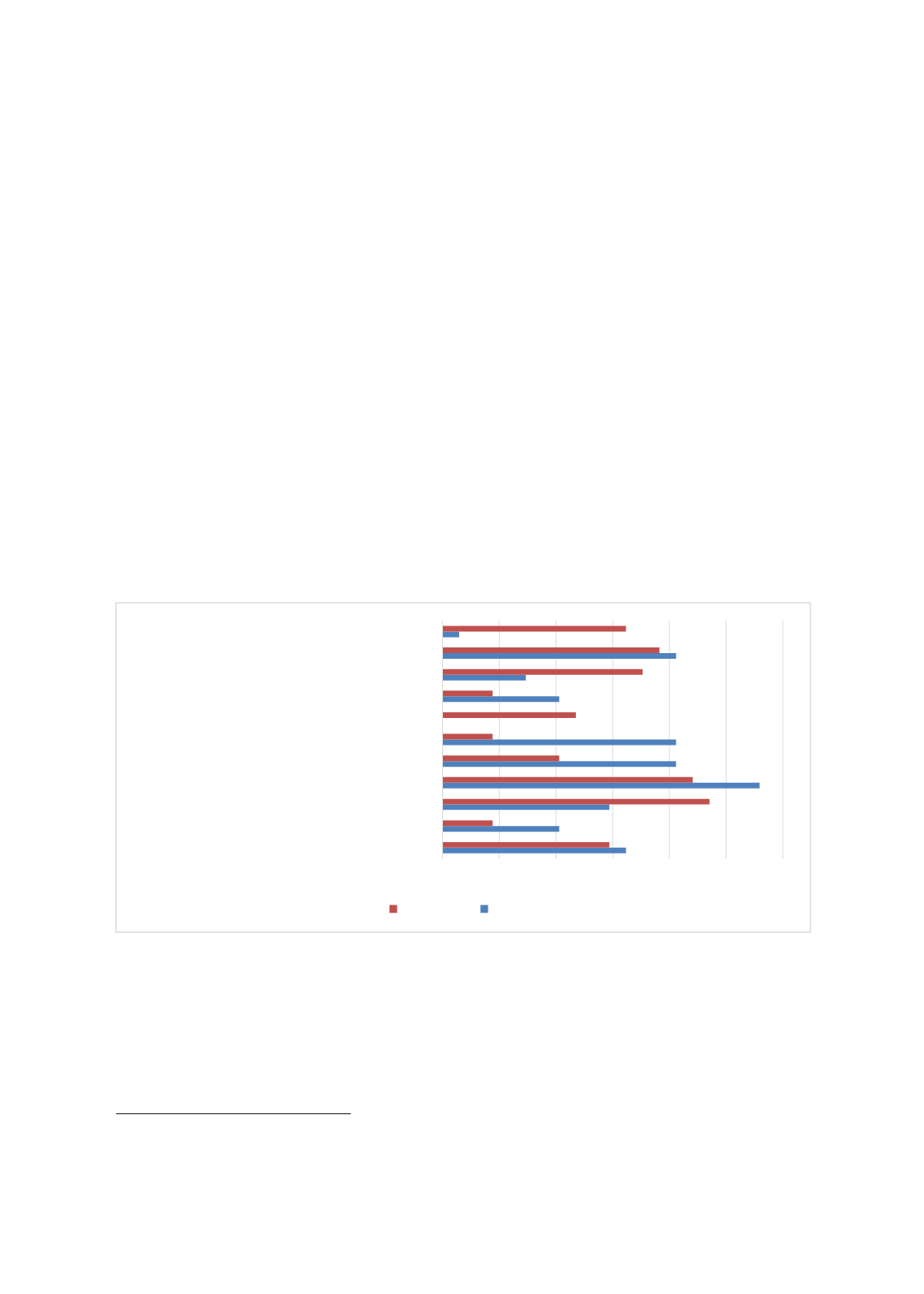
Figure 3.2.10: Important Features of an Effective School Principal and Teacher
Source:
Authors’ calculation based on stakeholders survey data.
Given these responses, stakeholders were asked to identify three factors that they considred as
most important for improving education quality in Malaysia. The most popular response was
the need to promote student-centered learning followed by school-learning culture organization
within the school compound, other thab ethos, the values and beliefs of school leaders, teachers,
and children are covert forces that shape the school culture (Hofstede & Hofstede, 2005; Schein,
31
There are many and different types of primary schools in Malaysia which along with the location of the
schools cause variation in funding received from the government.
0
0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6
Well qualified/trained
Focused on professional development
Focused on improving teaching & learning…
Motivated
Promotes learning opportunities within/outside…
Robust and rigorous in self-evaluation
Ensures progress and personal development of…
Assesses and tracks pupil progress
Supportive of weaker students & provides extra…
Good at communication
Good at engaging w students, making a session…
Secondary Primary