
Education of Disadvantaged Children in OIC:
The Key to Escape from Poverty
242
C.
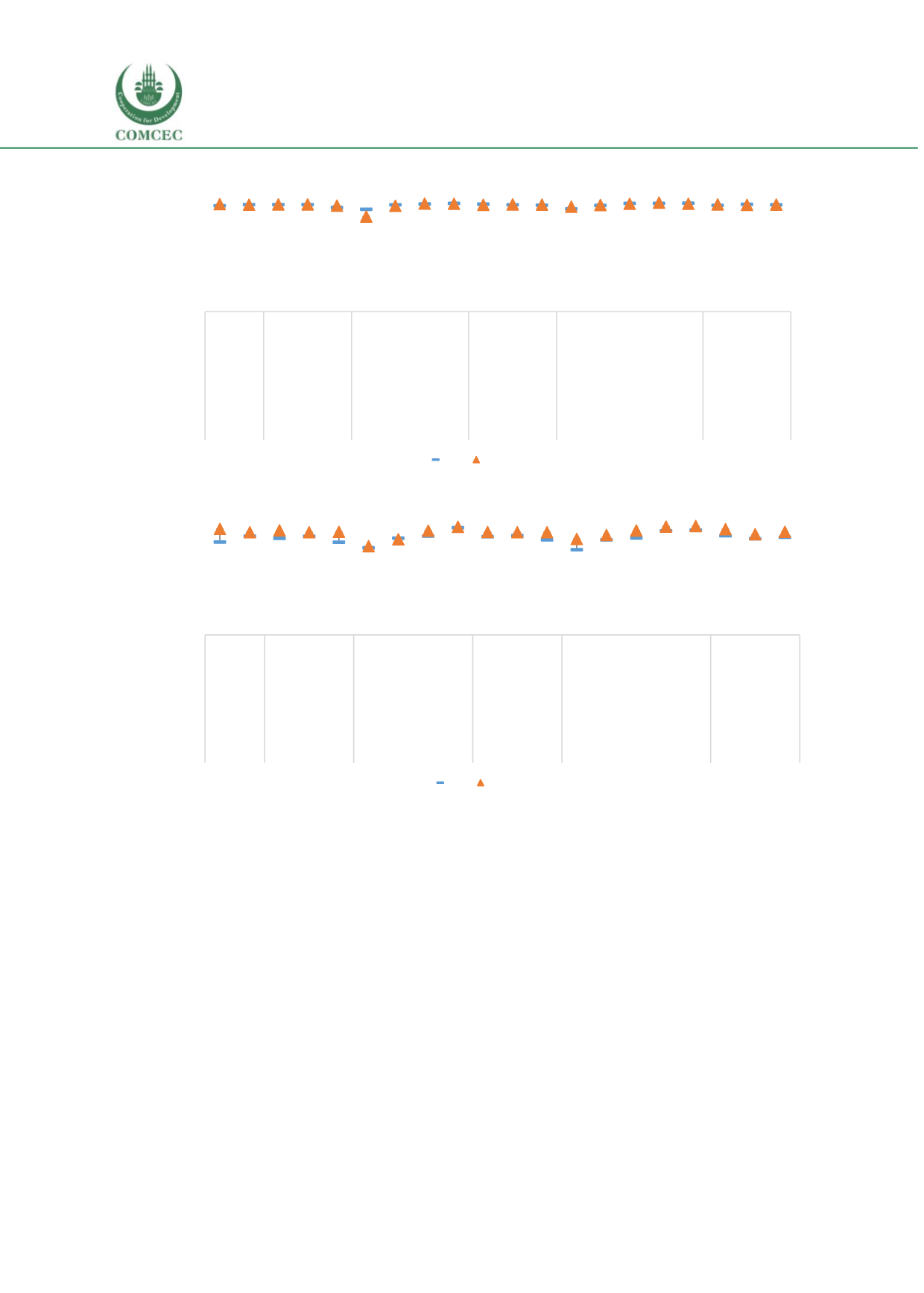
Finishing 5 years of education (12-15 year olds)
D.
Finishing 8 years of education (16-18 year olds)
Note: Authors’ calculations using DHS 1997 and 2012
Probit regressions
The second analysis used in the report is the probit regression method. The effect of
circumstances on school attendance and finishing school for children is measured using probit
regression making use of the most recent DHS dataset and another DHS dataset from 10 years
ago or more for each country. These regressions show the degree of the effect of circumstances
and which circumstances continue to matter. The probit equation that was used is as follows:
( ) = (
′
)
The circumstance variables X that are used in the probit regression is the same as the variables
that are used in HOI. These are location of the household, region of the household,
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Rural
Urban
North
Central
South
No education
Primary education
Secondary Education
Higher Education
1-2 children
3-4 children
5 or more children
Quint 1 (Poorest)
Quint 2
Quint 3
Quint 4
Quint 5 (Richest)
Female
Male
TOTAL
finishing 5 years of education (% of 12-15 year
olds)
1997 2012
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Rural
Urban
North
Central
South
No education
Primary education
Secondary Education
Higher Education
1-2 children
3-4 children
5 or more children
Quint 1 (Poorest)
Quint 2
Quint 3
Quint 4
Quint 5 (Richest)
Female
Male
TOTAL
finishing 8 years of education (% of 16-18 year
olds)
1997 2012
















